Dark Reactions
... site of the Calvin cycle. The decarboxylation creates a 3 carbon compound such as pyruvate which can return to the mesophyll cell and become recarboxylated. The C-4 pathway functions as a CO2 delivery system, carrying carbon dioxide from the oxygen rich surface of the leaf to the bundle sheath where ...
... site of the Calvin cycle. The decarboxylation creates a 3 carbon compound such as pyruvate which can return to the mesophyll cell and become recarboxylated. The C-4 pathway functions as a CO2 delivery system, carrying carbon dioxide from the oxygen rich surface of the leaf to the bundle sheath where ...
Reaction of glycolysis
... •This reaction is catalyzed by phosphoglyceromutase •Mutase is an enzyme that catalyzes the intramolecular shift of a chemical group from one position to another within the same molecule such as phosphoryl group ...
... •This reaction is catalyzed by phosphoglyceromutase •Mutase is an enzyme that catalyzes the intramolecular shift of a chemical group from one position to another within the same molecule such as phosphoryl group ...
Glycolysis - Fairfield Public Schools
... often used to refer to aerobic respiration Although carbohydrates, fats, and proteins are all consumed as fuel, it is helpful to trace cellular respiration with the sugar glucose C6H12O6 + 6 O2 6 CO2 + 6 H2O + Energy (ATP + heat) ...
... often used to refer to aerobic respiration Although carbohydrates, fats, and proteins are all consumed as fuel, it is helpful to trace cellular respiration with the sugar glucose C6H12O6 + 6 O2 6 CO2 + 6 H2O + Energy (ATP + heat) ...
Slide 1
... – Normally, there are 3 separate fatty acyl CoA dehydrogenase enzymes for STEP 1 of b-oxidation • Specific for short, medium and long acyl chains, respectively ...
... – Normally, there are 3 separate fatty acyl CoA dehydrogenase enzymes for STEP 1 of b-oxidation • Specific for short, medium and long acyl chains, respectively ...
Methylocapsa palsarum sp. nov., a Methanotrophic Bacterium from a
... 0.2 µm). The filters were left floating on a surface of the liquid medium M2 in Petri dishes and ...
... 0.2 µm). The filters were left floating on a surface of the liquid medium M2 in Petri dishes and ...
Cellular Respiration
... Each NADH & H+ converts to 3 ATP. Each FADH2 converts to 2 ATP (enters the ETC at a lower level than NADH & H+). ...
... Each NADH & H+ converts to 3 ATP. Each FADH2 converts to 2 ATP (enters the ETC at a lower level than NADH & H+). ...
Urea cycle defects and other metabolic emergencies
... • Consult genetics if available – this is their field • Eliminate the insulting agent – in case of new patient, need to eliminate as much as possible – NPO – Promote anabolism - High parenteral caloric intake • Low lipids (fatty acid oxydation defects, ketone body metabolism, etc) • Low proteins (UC ...
... • Consult genetics if available – this is their field • Eliminate the insulting agent – in case of new patient, need to eliminate as much as possible – NPO – Promote anabolism - High parenteral caloric intake • Low lipids (fatty acid oxydation defects, ketone body metabolism, etc) • Low proteins (UC ...
Are Aggregates of Enzyme Molecules More Effective than Individual
... Citation: Pundir CS (2016) Are Aggregates of Enzyme Molecules More Effective than Individual Enzyme Molecules? Mol Enz Drug Tar 2:2 ...
... Citation: Pundir CS (2016) Are Aggregates of Enzyme Molecules More Effective than Individual Enzyme Molecules? Mol Enz Drug Tar 2:2 ...
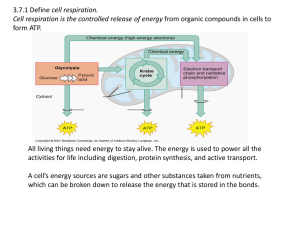
3.7:Cell Respiration Aerobic cell respiration: glucose
... Cell respiration is the controlled release of energy from organic compounds in cells to form ATP. ...
... Cell respiration is the controlled release of energy from organic compounds in cells to form ATP. ...
Complex Formation Between Iron(III) and
... Hydroxamic acids having one or moreCONHOH– groups have been extensively studied as a consequence of their biological importance which is related with their ability to form metal ion complexes (Fernandes et al., 1997). Hydroxamic acids and other compounds containing the hydroxamate group are ubiquito ...
... Hydroxamic acids having one or moreCONHOH– groups have been extensively studied as a consequence of their biological importance which is related with their ability to form metal ion complexes (Fernandes et al., 1997). Hydroxamic acids and other compounds containing the hydroxamate group are ubiquito ...
amino acids
... yields without the bitter β-form byproduct. • may hydrolyze into its constituent amino acids under conditions of elevated temperature or high pH. At room temperature, it is most stable at pH 4.3, where its half-life is nearly 300 days. At pH 7, however, its half-life is only a few days ...
... yields without the bitter β-form byproduct. • may hydrolyze into its constituent amino acids under conditions of elevated temperature or high pH. At room temperature, it is most stable at pH 4.3, where its half-life is nearly 300 days. At pH 7, however, its half-life is only a few days ...
Chapter 23 - Digestive
... • Anabolism: Uses raw materials to synthesize essential compounds • Catabolism: Decomposes substances to provide energy cells need to function – Require two essential ingredients: 1.oxygen 2.organic molecules broken down by intracellular enzymes (e.g., carbohydrates, fats, and proteins) ...
... • Anabolism: Uses raw materials to synthesize essential compounds • Catabolism: Decomposes substances to provide energy cells need to function – Require two essential ingredients: 1.oxygen 2.organic molecules broken down by intracellular enzymes (e.g., carbohydrates, fats, and proteins) ...
Chapter 35: The Digestive and Endocrine Systems
... simple carbohydrates found mainly in fruits, such as plums, strawberries, and oranges. During digestion, complex carbohydrates are broken down into simple sugars, such as glucose, fructose, and galactose. Absorbed into the bloodstream through the villi of the small intestine, these sugar molecules c ...
... simple carbohydrates found mainly in fruits, such as plums, strawberries, and oranges. During digestion, complex carbohydrates are broken down into simple sugars, such as glucose, fructose, and galactose. Absorbed into the bloodstream through the villi of the small intestine, these sugar molecules c ...
2010 Ruminant Carbohydrate Digestion
... • Rhamnose units are substituted in the chains – Chains twist ...
... • Rhamnose units are substituted in the chains – Chains twist ...
ATP - Luzzago
... and fatty acids (used in generating acetyl CoA) • Fatty acids are broken down by beta oxidation and yield acetyl CoA • An oxidized gram of fat produces more than twice as much ATP as an oxidized gram of carbohydrate ...
... and fatty acids (used in generating acetyl CoA) • Fatty acids are broken down by beta oxidation and yield acetyl CoA • An oxidized gram of fat produces more than twice as much ATP as an oxidized gram of carbohydrate ...
Nutrient uptake by protocells: a liposome model system
... to have access to ionic nutrients in the environment. It remains uncertain whether the observed permeation rates could sustain the activity of an enzyme with a relatively high turnover rate, and we are now testing this possibility. The ATP permeability coefficients (calculated here under the assumpt ...
... to have access to ionic nutrients in the environment. It remains uncertain whether the observed permeation rates could sustain the activity of an enzyme with a relatively high turnover rate, and we are now testing this possibility. The ATP permeability coefficients (calculated here under the assumpt ...
Introduction Milk is the exclusive nutrient source for the neonate. ... practices and availability of highly selected sows have allowed for...
... Valine and other BCAA are taken up by the mammary gland in quantities higher than their output in milk (Linzell et al. 1969, Trottier et al. 1997). Intracellular metabolic pathways other than protein synthesis may account for a significant portion of the BCAA taken up by the gland (Hurley & Bryson, ...
... Valine and other BCAA are taken up by the mammary gland in quantities higher than their output in milk (Linzell et al. 1969, Trottier et al. 1997). Intracellular metabolic pathways other than protein synthesis may account for a significant portion of the BCAA taken up by the gland (Hurley & Bryson, ...
Cloning and Functional Characterization of a Phospholipid
... a Glu aligning with this position but instead has Ala or Ser, which have smaller side chains. Lipases, as well as HsLCAT, contain a so-called lid domain which is closed by a disulfide bridge. The lid structure occurs between the two Cys, C74 and C98, at the N- and C- terminal parts of the segment in ...
... a Glu aligning with this position but instead has Ala or Ser, which have smaller side chains. Lipases, as well as HsLCAT, contain a so-called lid domain which is closed by a disulfide bridge. The lid structure occurs between the two Cys, C74 and C98, at the N- and C- terminal parts of the segment in ...
Acetyl CoA - WordPress.com
... The increased cytosolic Ca++ that occurs during activation of muscle contraction can lead to Ca++ uptake by mitochondria. The higher Ca++ stimulates the phosphatase, & dephosphorylation activates Pyruvate Dehydrogenase. Thus mitochondrial metabolism may be stimulated during exercise. ...
... The increased cytosolic Ca++ that occurs during activation of muscle contraction can lead to Ca++ uptake by mitochondria. The higher Ca++ stimulates the phosphatase, & dephosphorylation activates Pyruvate Dehydrogenase. Thus mitochondrial metabolism may be stimulated during exercise. ...
SUGAR AND ACID METABOLISM IN CITRUS FRUIT 1
... of this compound that can be readily measured. Known effects of arsenate on metabolic pathways may therefore be occurring only in peel and leaves. In addition, transport of labeled materials frM peel to pulp has been measured, and high levels of organic acids occur in peel. Lastly, an enzyme known t ...
... of this compound that can be readily measured. Known effects of arsenate on metabolic pathways may therefore be occurring only in peel and leaves. In addition, transport of labeled materials frM peel to pulp has been measured, and high levels of organic acids occur in peel. Lastly, an enzyme known t ...
CV Protection in the EMPA-REG OUTCOME Trial: A
... cotransporter 2 (SGLT2) in patients with type 2 diabetes and high CV risk have raised the possibility that mechanisms other than those observed in the trialdmodest improvement in glycemic control, small decrease in body weight, and persistent reductions in blood pressure and uric acid leveldmay be a ...
... cotransporter 2 (SGLT2) in patients with type 2 diabetes and high CV risk have raised the possibility that mechanisms other than those observed in the trialdmodest improvement in glycemic control, small decrease in body weight, and persistent reductions in blood pressure and uric acid leveldmay be a ...
Gustatory Responses of Eel Palatine Receptors to Amino Acids and
... various amino acids and carboxylic acids, the extent of cross-adaptation between these stimuli was examined. A method similar to that of Smith and Frank (1972) who examined the extent of cross-adaptation between salts in the rat chorda tympani nerve was employed. The experiments were carried out as ...
... various amino acids and carboxylic acids, the extent of cross-adaptation between these stimuli was examined. A method similar to that of Smith and Frank (1972) who examined the extent of cross-adaptation between salts in the rat chorda tympani nerve was employed. The experiments were carried out as ...
Cellular Respiration and Fermentation
... combines O2 with hydrogens (that is, electrons and protons) to form water. (See figure on next slide.) Which choice correctly describes the ultimate source of these hydrogens? a) The electrons are taken directly from the carbons of glucose, but the protons (H+) are taken from bulk water. b) These hy ...
... combines O2 with hydrogens (that is, electrons and protons) to form water. (See figure on next slide.) Which choice correctly describes the ultimate source of these hydrogens? a) The electrons are taken directly from the carbons of glucose, but the protons (H+) are taken from bulk water. b) These hy ...
Enzymes - CEA Workshop Teacher Notes.pptx
... to assist enzyme acJvity • A coenzyme will bind to a protein to form an acJve enzyme • Coenzymes osen help by carrying a group of atoms to the acJve site which are then transferred to the su ...
... to assist enzyme acJvity • A coenzyme will bind to a protein to form an acJve enzyme • Coenzymes osen help by carrying a group of atoms to the acJve site which are then transferred to the su ...