Chapter 5 Proteins - Liberty Public Schools
... proteins; form shape of cells and tissues. Ex. Collagen-the most abundant protein of vertebrates. 2. Globular Proteins- have specific shapes for their functions. Ex. Enzymes and antibodies. ...
... proteins; form shape of cells and tissues. Ex. Collagen-the most abundant protein of vertebrates. 2. Globular Proteins- have specific shapes for their functions. Ex. Enzymes and antibodies. ...
Biochemistry Lecture 4 9/6/01
... • Basic structural units of proteins • All have 3 common functional grps: – -NH2, -COOH, -H ...
... • Basic structural units of proteins • All have 3 common functional grps: – -NH2, -COOH, -H ...
You Light Up My Life - Hillsborough Community College
... • It delivers electrons to mitochondrial membrane • Membrane proteins shuttle electrons to NAD+ or FAD inside mitochondrion • Electrons given to FAD yield less ATP than those given to NAD+ ...
... • It delivers electrons to mitochondrial membrane • Membrane proteins shuttle electrons to NAD+ or FAD inside mitochondrion • Electrons given to FAD yield less ATP than those given to NAD+ ...
Flashback - Max-Planck
... this way, glycolysis brought Meyerhof back to the beginnings of his physiological research. The productive working relationship between Lohmann and Meyerhof came to an abrupt end due to the changed political circumstances of Nazi Germany. On November 16, 1935, Meyerhof received a letter from Baden’s ...
... this way, glycolysis brought Meyerhof back to the beginnings of his physiological research. The productive working relationship between Lohmann and Meyerhof came to an abrupt end due to the changed political circumstances of Nazi Germany. On November 16, 1935, Meyerhof received a letter from Baden’s ...
harvesting chemical energy
... 3. The citric acid cycle completes the energy-yielding oxidation of organic molecules. ...
... 3. The citric acid cycle completes the energy-yielding oxidation of organic molecules. ...
Model Description Sheet
... countries, as it kills approximately 2 million people each year according to the World Health Organization. Because of overuse and increasing resistance to current antibiotics, researchers are working to develop new drugs to more effectively treat tuberculosis. M. tuberculosis alpha-isopropylmalate ...
... countries, as it kills approximately 2 million people each year according to the World Health Organization. Because of overuse and increasing resistance to current antibiotics, researchers are working to develop new drugs to more effectively treat tuberculosis. M. tuberculosis alpha-isopropylmalate ...
09 Respiration
... – an agent that closely mimics the structure of glucose but is not metabolized – an agent that reacts with NADH and oxidizes it to NAD+ – an agent that inhibits the formation of acetyl coenzyme A ...
... – an agent that closely mimics the structure of glucose but is not metabolized – an agent that reacts with NADH and oxidizes it to NAD+ – an agent that inhibits the formation of acetyl coenzyme A ...
Ch 14 Digestive System
... In your groups…you will come up with a definition (using YOUR WORDS) and a colored picture of it happening in the body. You will be presenting this to the class. YOU MAY NOT USE BOOKS!!!! ...
... In your groups…you will come up with a definition (using YOUR WORDS) and a colored picture of it happening in the body. You will be presenting this to the class. YOU MAY NOT USE BOOKS!!!! ...
Bchm2000_P1 - U of L Class Index
... any disulfide bonds. There are two possible results: case 1: two or more bands are present and indicate the protein has multiple subunits case 2: one band is present. This is an inconclusive result as the sample may have one subunit or be composed of multiple identical subunits To resolve case 2, us ...
... any disulfide bonds. There are two possible results: case 1: two or more bands are present and indicate the protein has multiple subunits case 2: one band is present. This is an inconclusive result as the sample may have one subunit or be composed of multiple identical subunits To resolve case 2, us ...
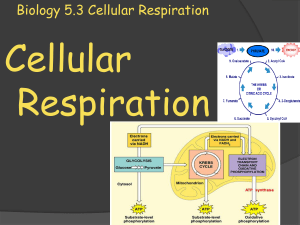
Biology 5.3 Cellular Respiration
... Stage 2: Aerobic respiration occurs: this is when oxygen is present, pyruvate and NADH make more ATP. ...
... Stage 2: Aerobic respiration occurs: this is when oxygen is present, pyruvate and NADH make more ATP. ...
Energy Transformation — Cellular Respiration
... perfringens and C. sporogenes are the two anaerobic bacteria associated with the disease gas gangrene. A gangrenous wound is a foul-smelling infection resulting from the fermentation activities of those two bacteria. Because many disease-causing organisms are prokaryotic and have somewhat different ...
... perfringens and C. sporogenes are the two anaerobic bacteria associated with the disease gas gangrene. A gangrenous wound is a foul-smelling infection resulting from the fermentation activities of those two bacteria. Because many disease-causing organisms are prokaryotic and have somewhat different ...
1. Under influence of what hormone the absorbtion of Na+ increases
... Bile forming Concentration of bile Excretion of bile There are investigated fermentative qualities of pancreatic juice.After the incubation of juice and substance for 15 min ( 37C ) the products of hydrolysis gave the positive Felling’s reaction.The action of what ferments of juice is the cause of ...
... Bile forming Concentration of bile Excretion of bile There are investigated fermentative qualities of pancreatic juice.After the incubation of juice and substance for 15 min ( 37C ) the products of hydrolysis gave the positive Felling’s reaction.The action of what ferments of juice is the cause of ...
electron transport
... Gradient: The Mitchell Hypothesis • Peter Mitchell proposed a novel idea—a proton gradient across the inner membrane could be used to drive ATP synthesis • The proton gradient is created by the proteins of the electron-transport pathway (Figure 20.19) • This mechanism stores the energy of electron t ...
... Gradient: The Mitchell Hypothesis • Peter Mitchell proposed a novel idea—a proton gradient across the inner membrane could be used to drive ATP synthesis • The proton gradient is created by the proteins of the electron-transport pathway (Figure 20.19) • This mechanism stores the energy of electron t ...
Metabolism
... Chemical Reactions in the Body • Plants use the sun’s energy to make carbohydrate from carbon dioxide and water. • This is called photosynthesis. • Humans and animals eat the plants and use the carbohydrate as fuel for their bodies. • During digestion, the energy-yielding nutrients are broken down ...
... Chemical Reactions in the Body • Plants use the sun’s energy to make carbohydrate from carbon dioxide and water. • This is called photosynthesis. • Humans and animals eat the plants and use the carbohydrate as fuel for their bodies. • During digestion, the energy-yielding nutrients are broken down ...
6 Energy and Metabolism
... the mitochondria. Here, the NADH molecules from glycolysis and the TCA cycle are oxidized back to NAD so glycolysis can continue. It also generates 3 more ATP. When this system is performing in the presence of oxygen, oxygen is consumed and the waste product is water. When it is done anaerobically ( ...
... the mitochondria. Here, the NADH molecules from glycolysis and the TCA cycle are oxidized back to NAD so glycolysis can continue. It also generates 3 more ATP. When this system is performing in the presence of oxygen, oxygen is consumed and the waste product is water. When it is done anaerobically ( ...
"Amino Acids of the 21st Century" (7) –The
... acids and the enormous effort required to assess the actions exerted by different amounts of the various amino acids. The authors prepared a supplement of a mixture of 12 types of amino acids (Amino Vital Pro, AVP) containing as main ingredients BCAA, arginine, and glutamine, then undertook studies ...
... acids and the enormous effort required to assess the actions exerted by different amounts of the various amino acids. The authors prepared a supplement of a mixture of 12 types of amino acids (Amino Vital Pro, AVP) containing as main ingredients BCAA, arginine, and glutamine, then undertook studies ...
Who Wants To Be A Biologist?
... FADH2 donates electrons further down the ETC than NADH. This means the ATP yield for every FADH2 is only about 2 ATP, as opposed to 3 ATP per molecule of NADH. ...
... FADH2 donates electrons further down the ETC than NADH. This means the ATP yield for every FADH2 is only about 2 ATP, as opposed to 3 ATP per molecule of NADH. ...
Cellular Respiration
... glycolysis ◦ If the supply of NAD+ runs out, then glycolysis would have to stop. ◦ Fermentation occurs as simply a means of recycling the NAD+, so that glycolysis can occur ...
... glycolysis ◦ If the supply of NAD+ runs out, then glycolysis would have to stop. ◦ Fermentation occurs as simply a means of recycling the NAD+, so that glycolysis can occur ...
Citric acid cycle - Imperial College London
... converted into acetyl-CoA by decarboxylation and enters the citric acid cycle. In protein catabolism, proteins are broken down by proteases into their constituent amino acids. The carbon backbone of these amino acids can become a source of energy by being converted to acetyl-CoA and entering into th ...
... converted into acetyl-CoA by decarboxylation and enters the citric acid cycle. In protein catabolism, proteins are broken down by proteases into their constituent amino acids. The carbon backbone of these amino acids can become a source of energy by being converted to acetyl-CoA and entering into th ...
Pyropheophytin a accompanies pheophytin a in darkened light
... Metabolites of 1,2,4-Trihydroxybenzene from Fruiting Bodies of Gomphiaius maculatus and G. glutinosus (Boletales) (N) ...
... Metabolites of 1,2,4-Trihydroxybenzene from Fruiting Bodies of Gomphiaius maculatus and G. glutinosus (Boletales) (N) ...
Reaction of glycolysis
... •This reaction is catalyzed by phosphoglyceromutase •Mutase is an enzyme that catalyzes the intramolecular shift of a chemical group from one position to another within the same molecule such as phosphoryl group ...
... •This reaction is catalyzed by phosphoglyceromutase •Mutase is an enzyme that catalyzes the intramolecular shift of a chemical group from one position to another within the same molecule such as phosphoryl group ...