Ch. 8 notes
... THIRD LINE OF DEFENSE • ANTIBODIES – PROTEINS MADE BY THE IMMUNE SYSTEM – SOME ARE ATTACHED TO CERTAIN TYPE OF WHITE BLOOD CELLS – OTHERS FLOAT AROUND IN THE BLOOD ...
... THIRD LINE OF DEFENSE • ANTIBODIES – PROTEINS MADE BY THE IMMUNE SYSTEM – SOME ARE ATTACHED TO CERTAIN TYPE OF WHITE BLOOD CELLS – OTHERS FLOAT AROUND IN THE BLOOD ...
The Immune System and Infertility
... In the ejaculate, sperm antibodies can cause infertility by affecting sperm mobility or binding to the egg, although it is still unclear what level of antibodies is significant to warrant treatment. It is now known that immunosuppressive therapy (e.g. Prednisolone tablets) does not improve fertility ...
... In the ejaculate, sperm antibodies can cause infertility by affecting sperm mobility or binding to the egg, although it is still unclear what level of antibodies is significant to warrant treatment. It is now known that immunosuppressive therapy (e.g. Prednisolone tablets) does not improve fertility ...
Document
... lymphocytes, T-cells and the B-cells. These two cells have different functions and actions. B cells are more like central control centers: they do not attack pathogens, but remain in the lymphatic tissue to produce a large amount of antibodies to be sent through the bloodstream to attack invaders, b ...
... lymphocytes, T-cells and the B-cells. These two cells have different functions and actions. B cells are more like central control centers: they do not attack pathogens, but remain in the lymphatic tissue to produce a large amount of antibodies to be sent through the bloodstream to attack invaders, b ...
Veterinary Immunology
... • T and B cells recognize antigen differently: • B cells recognize intact antigen (not processed) They recognize a wide variety of chemical types: protein, carbohydrate, etc… via membrane‐bound antibody molecules • T cells (TH and TC) – recognize only peptides (processed proteins) o Antigen must ...
... • T and B cells recognize antigen differently: • B cells recognize intact antigen (not processed) They recognize a wide variety of chemical types: protein, carbohydrate, etc… via membrane‐bound antibody molecules • T cells (TH and TC) – recognize only peptides (processed proteins) o Antigen must ...
Document
... Purification of Ab mostly with Protein A or G Glycosylation is different in plants β 1,2 Xylose and α 1,3 fucose Retain in ER, only mannose is attached –Shorter half-life of Ab ...
... Purification of Ab mostly with Protein A or G Glycosylation is different in plants β 1,2 Xylose and α 1,3 fucose Retain in ER, only mannose is attached –Shorter half-life of Ab ...
Supplementary Figure Legends Supplementary Figure S1. Both
... Supplementary Figure S1. Both LIMD2 (rAb) and LIMD2 (mAb) detected the exogenous and endogenous LIMD2 protein in cell lines and human cancer specimens. A, The His-tagged and GST-tagged full-length LIMD2 proteins were used to produce polyclonal and monoclonal antibodies, respectively. B & C, The L ...
... Supplementary Figure S1. Both LIMD2 (rAb) and LIMD2 (mAb) detected the exogenous and endogenous LIMD2 protein in cell lines and human cancer specimens. A, The His-tagged and GST-tagged full-length LIMD2 proteins were used to produce polyclonal and monoclonal antibodies, respectively. B & C, The L ...
Regulatory T
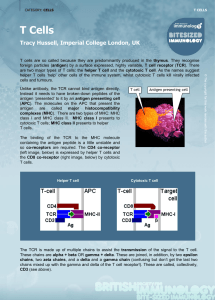
... Unlike antibody, the TCR cannot bind antigen directly. Instead it needs to have broken-down peptides of the antigen ‘presented’ to it by an antigen presenting cell (APC). The molecules on the APC that present the antigen are called major histocompatibility complexes (MHC). There are two types of MHC ...
... Unlike antibody, the TCR cannot bind antigen directly. Instead it needs to have broken-down peptides of the antigen ‘presented’ to it by an antigen presenting cell (APC). The molecules on the APC that present the antigen are called major histocompatibility complexes (MHC). There are two types of MHC ...
Immunology
... phagocytosis by opsonization. Two pathways: classic and alternative. Pyrogens - secreted by macrophages and signal the body to increase temperature; high body temperature inhibits microbial multiplication and enhances body repair processes. ...
... phagocytosis by opsonization. Two pathways: classic and alternative. Pyrogens - secreted by macrophages and signal the body to increase temperature; high body temperature inhibits microbial multiplication and enhances body repair processes. ...
CELLS& ORGANS OF IMMUNE MECHANISM.
... • Success of organ transplant is in large part determined by the compatibility of MHC genes of the donor and recipient. ...
... • Success of organ transplant is in large part determined by the compatibility of MHC genes of the donor and recipient. ...
Anti-Human IL-13-169Tm
... nonglycosylated protein with a molecular weight of 12 kDa. The IL-13 gene is located in the same region as the genes encoding IL-3, IL-4, IL-5 and GM-CSF. IL-13 shares 30% amino acid sequence homology with IL-4 and can induce similar processes. IL-13 has a diverse range of biological effects includi ...
... nonglycosylated protein with a molecular weight of 12 kDa. The IL-13 gene is located in the same region as the genes encoding IL-3, IL-4, IL-5 and GM-CSF. IL-13 shares 30% amino acid sequence homology with IL-4 and can induce similar processes. IL-13 has a diverse range of biological effects includi ...
What could have caused this?
... What is happening in your lymph nodes during the inflammatory response? • Preparing the 3rd line of defense to attack the pathogen! • B cells and T cells • Specific Defense ...
... What is happening in your lymph nodes during the inflammatory response? • Preparing the 3rd line of defense to attack the pathogen! • B cells and T cells • Specific Defense ...
Cells of the innate immune system
... • Secreted antibodies by plasma cells, 109 different specificities! • 5 classes (isotypes: IgM, IgD, IgG, IgA, IgE) • Effector functions eliminate antigen ...
... • Secreted antibodies by plasma cells, 109 different specificities! • 5 classes (isotypes: IgM, IgD, IgG, IgA, IgE) • Effector functions eliminate antigen ...
Immunity and Microbes
... Silver, mercury, copper and others are heavy metals that are good antiseptics/disinfectants. These are useful metals but are used with caution as they can be toxic. ...
... Silver, mercury, copper and others are heavy metals that are good antiseptics/disinfectants. These are useful metals but are used with caution as they can be toxic. ...
Use of virus-like particles for therapeutic vaccination
... 4) Mouse anti-MSP1 3) MSP1-Qb [Qb]=[1 mg/ml] (titration) 2) Rabbit anti-Qb polyclonal serum 1) Goat anti-rabbit IgG ...
... 4) Mouse anti-MSP1 3) MSP1-Qb [Qb]=[1 mg/ml] (titration) 2) Rabbit anti-Qb polyclonal serum 1) Goat anti-rabbit IgG ...
ORGANIZATION OF THE IMMUNE SYSTEM
... QUESTION: How can so many different pathogens and other structures be recognized by antibodies? What drives and How the production of antibodies? ...
... QUESTION: How can so many different pathogens and other structures be recognized by antibodies? What drives and How the production of antibodies? ...
Bacteria vs. Viruses
... A. Bacteria are living organisms (have DNA): they can control functions and replicate on their own ...
... A. Bacteria are living organisms (have DNA): they can control functions and replicate on their own ...
The Human Body Systems
... b) Antibodies are proteins that react with antigens (foreign molecules that have attacked the body) to deactivate them. (1) T Cells – Identify one kind of pathogen from another – (a) Over 10 million T Cells in your body, each able to recognize different types of proteins (Antigens) found on the cell ...
... b) Antibodies are proteins that react with antigens (foreign molecules that have attacked the body) to deactivate them. (1) T Cells – Identify one kind of pathogen from another – (a) Over 10 million T Cells in your body, each able to recognize different types of proteins (Antigens) found on the cell ...
Hypersensitivities
... Clinically hypersensitivity gives rise to two categories. o Allergies o Autoimmune disease Allergy Deleterious effects of hypersensitivity to environmental (exogenous) antigens There is an exaggerated inflammatory response to an environmental agent An antigen that generates an allergic react ...
... Clinically hypersensitivity gives rise to two categories. o Allergies o Autoimmune disease Allergy Deleterious effects of hypersensitivity to environmental (exogenous) antigens There is an exaggerated inflammatory response to an environmental agent An antigen that generates an allergic react ...
Monoclonal antibodies as enhancers of the host`s immunoresponse
... may also enhance various immune effector functions which can mediate tumour cell destruction. Immune functions which spontaneously might kill tumour cells include antibodies, unspecific cytotoxic cells (monocytes/macrophages, NK cells, granulocytes, eosinophils) and specific killer cells (various T ...
... may also enhance various immune effector functions which can mediate tumour cell destruction. Immune functions which spontaneously might kill tumour cells include antibodies, unspecific cytotoxic cells (monocytes/macrophages, NK cells, granulocytes, eosinophils) and specific killer cells (various T ...
The Avian Immune System - EDIS
... lymphokines (over 90 different ones have been identified); others directly destroy disease organisms; some T-cells act to enhance the response of B-cells, macrophages, or other T-cells (helpers); and others inhibit the activity of these cells (suppressors). The cellular system was identified when it ...
... lymphokines (over 90 different ones have been identified); others directly destroy disease organisms; some T-cells act to enhance the response of B-cells, macrophages, or other T-cells (helpers); and others inhibit the activity of these cells (suppressors). The cellular system was identified when it ...
Monoclonal antibody

Monoclonal antibodies (mAb or moAb) are monospecific antibodies that are made by identical immune cells that are all clones of a unique parent cell, in contrast to polyclonal antibodies which are made from several different immune cells. Monoclonal antibodies have monovalent affinity, in that they bind to the same epitope.Given almost any substance, it is possible to produce monoclonal antibodies that specifically bind to that substance; they can then serve to detect or purify that substance. This has become an important tool in biochemistry, molecular biology and medicine. When used as medications, the non-proprietary drug name ends in -mab (see ""Nomenclature of monoclonal antibodies""), and many immunotherapy specialists use the word mab anacronymically.