LACZIK_Pharmacology - 4 practice
... Why do antibodies need an Fc region? The (Fab)2 fragment can Detect antigen ...
... Why do antibodies need an Fc region? The (Fab)2 fragment can Detect antigen ...
Genomic Organization
... -Also in cancer cells. The resistant cells after chemotherapy have amplified segments of DNA which carry genes that are resistant to the drugs. Benefit- allows the egg to have a burst of protein synthesis once the egg is fertilized. Makes large amounts of growth possible (protein production) possibl ...
... -Also in cancer cells. The resistant cells after chemotherapy have amplified segments of DNA which carry genes that are resistant to the drugs. Benefit- allows the egg to have a burst of protein synthesis once the egg is fertilized. Makes large amounts of growth possible (protein production) possibl ...
09 Antibodies
... with specific antibody. Haptens are usually small molecules, but some high-molecular-weight nucleic acids, lipids, complex carbohydrates and other substances are haptens as well. Many drugs, eg, penicillins, are haptens, and the catechol in the plant oil that causes poison oak and poison ivy is a ha ...
... with specific antibody. Haptens are usually small molecules, but some high-molecular-weight nucleic acids, lipids, complex carbohydrates and other substances are haptens as well. Many drugs, eg, penicillins, are haptens, and the catechol in the plant oil that causes poison oak and poison ivy is a ha ...
Ab to glomerular basement membrane
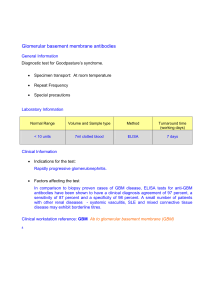
... Glomerular basement membrane antibodies General Information Diagnostic test for Goodpasture’s syndrome. ...
... Glomerular basement membrane antibodies General Information Diagnostic test for Goodpasture’s syndrome. ...
UACA / Nucling (Nuclear Membrane Marker) Antibody
... Regulates the redistribution of APAF1 into the nucleus after proapoptotic stress. Down-regulates the expression of LGALS3 by ...
... Regulates the redistribution of APAF1 into the nucleus after proapoptotic stress. Down-regulates the expression of LGALS3 by ...
Antibodies to Biotherapeutics
... the non-specific background signals initiated by the antibody Fc backbone or other cellular protein interactions, from the target-specific antibody signal. ...
... the non-specific background signals initiated by the antibody Fc backbone or other cellular protein interactions, from the target-specific antibody signal. ...
6.3 Immune system notes
... Skin – contains two primary layers, dermis and epidermis. The underneath layer is dermis and it is alive, the top layer is the epidermis and it is mainly dead cells. This top layer of epidermis is an excellent barrier against most pathogens. Entry points that are not covered by skin are covered by m ...
... Skin – contains two primary layers, dermis and epidermis. The underneath layer is dermis and it is alive, the top layer is the epidermis and it is mainly dead cells. This top layer of epidermis is an excellent barrier against most pathogens. Entry points that are not covered by skin are covered by m ...
Eulji University Hospital
... critically involved in the development of Th1 immune responses. RA is often assumed to be a Th1-mediated disease process. ...
... critically involved in the development of Th1 immune responses. RA is often assumed to be a Th1-mediated disease process. ...
8.2 Structure of DNA
... Antigen: A substance that the body recognizes as foreign and that can evoke an immune response Antibody: A protein produced by certain white blood cells (B lymphocytes, plasma cells) in response to an antigen ...
... Antigen: A substance that the body recognizes as foreign and that can evoke an immune response Antibody: A protein produced by certain white blood cells (B lymphocytes, plasma cells) in response to an antigen ...
CELL BIOLOGY TECHNIQUES
... • Resolution of 0.2µm • Magnification – objective and projection lens • Resolution – D = 0.61λ/N sin α Resolution is improved by using shorter wavelengths or increasing either N or α. ...
... • Resolution of 0.2µm • Magnification – objective and projection lens • Resolution – D = 0.61λ/N sin α Resolution is improved by using shorter wavelengths or increasing either N or α. ...
Deutsche Bank 36th Annual Health Care Conference
... MOR103 A Novel Anti-Inflammatory Antibody The Target GM-CSF – a growth factor and inflammatory mediator ...
... MOR103 A Novel Anti-Inflammatory Antibody The Target GM-CSF – a growth factor and inflammatory mediator ...
Weatherall Institute of Molecular Medicine (WIMM) University of
... Use TIRF to visualize the movement of different fluorescently labeled molecules during T-cell activation ...
... Use TIRF to visualize the movement of different fluorescently labeled molecules during T-cell activation ...
1. Light Chain
... Immunoglobulins bind specifically to one or a few closely related antigens. Each immunoglobulin actually binds to a specific antigenic determinant. Antigen binding by antibodies is the primary function of antibodies and can result in protection of the host. B. Effector Functions Frequently the bindi ...
... Immunoglobulins bind specifically to one or a few closely related antigens. Each immunoglobulin actually binds to a specific antigenic determinant. Antigen binding by antibodies is the primary function of antibodies and can result in protection of the host. B. Effector Functions Frequently the bindi ...
Hypersensitivities
... result from transplant, blood products or pregnancy the other “person” could be an animal, e.g. anti-toxin produced in a horse Examples of Hypersensitivity Diseases – allergy vs autoimmunity vs alloimmunity Type I (IgE) Allergy (environmental antigen): allergic rhinitis, anaphylaxis, asthm ...
... result from transplant, blood products or pregnancy the other “person” could be an animal, e.g. anti-toxin produced in a horse Examples of Hypersensitivity Diseases – allergy vs autoimmunity vs alloimmunity Type I (IgE) Allergy (environmental antigen): allergic rhinitis, anaphylaxis, asthm ...
Bioanalytical chemistry
... There are 3 types of "particles" commonly used in agglutination tests: 1) erythrocytes (RBCs), 2) bacterial cells (often stained to make the clumps visible), 3) latex particles (the antigens are chemically attached prior to running the test). The agglutination or precipitation reaction is affected by ...
... There are 3 types of "particles" commonly used in agglutination tests: 1) erythrocytes (RBCs), 2) bacterial cells (often stained to make the clumps visible), 3) latex particles (the antigens are chemically attached prior to running the test). The agglutination or precipitation reaction is affected by ...
Immuno Revision Notes
... ↓ Phagocyte recruitment ↑WCC (neutrophils) Lmyphocyte SequestraIon, cytotoxicity, reduced cytokine gene expression Block Purine synthesis (T>B) Blocks DNA replication (B>T) ...
... ↓ Phagocyte recruitment ↑WCC (neutrophils) Lmyphocyte SequestraIon, cytotoxicity, reduced cytokine gene expression Block Purine synthesis (T>B) Blocks DNA replication (B>T) ...
Document
... viruses. They grab onto them and hook them up together so that they can be easily phagocytized. D. Fever - Infection causes lymphocytes to make interleukin-1 that causes the body’s temperature set point to increase. This causes the liver and spleen to hold onto iron, reducing its levels in the blood ...
... viruses. They grab onto them and hook them up together so that they can be easily phagocytized. D. Fever - Infection causes lymphocytes to make interleukin-1 that causes the body’s temperature set point to increase. This causes the liver and spleen to hold onto iron, reducing its levels in the blood ...
ReliaTech GmbH Recombinant Human p16
... p16-INK4a is a nuclear protein that regulates the cell cycle by inhibiting cyclin dependent kinase-4 (CDK4) and CDK6. p16-INK4a inhibits CDK activity by binding to the CDK molecules in a manner that interferes with their ability to interact with cyclin D. This activity has the effect of suppressing ...
... p16-INK4a is a nuclear protein that regulates the cell cycle by inhibiting cyclin dependent kinase-4 (CDK4) and CDK6. p16-INK4a inhibits CDK activity by binding to the CDK molecules in a manner that interferes with their ability to interact with cyclin D. This activity has the effect of suppressing ...
Materials and Methods - Welcome to the Biology Department
... Lactococcus lactis • Gram positive, cocci, 0.5-1.5μm • Used in the production of fermented milk products (buttermilk, cheese, etc…) • Noninvasive (can’t multiply in vivo), nonpathogenic • Can serve as an antigen delivery vehicle ...
... Lactococcus lactis • Gram positive, cocci, 0.5-1.5μm • Used in the production of fermented milk products (buttermilk, cheese, etc…) • Noninvasive (can’t multiply in vivo), nonpathogenic • Can serve as an antigen delivery vehicle ...
Exam 2
... segment on light chain codes for variable region (rearranges second), VDJ on heavy chain codes for variable region (rearranges first); ...
... segment on light chain codes for variable region (rearranges second), VDJ on heavy chain codes for variable region (rearranges first); ...
Document
... system response. Antigens are often naturally occurring molecules (protein, glycoprotein, or polysaccharide) on the surface of cells and viruses C. Pathogen: any antigen that causes a disruption in homeostasis a.k.a. normal, disease free, functions D. Antibody: a protein produced specifically in res ...
... system response. Antigens are often naturally occurring molecules (protein, glycoprotein, or polysaccharide) on the surface of cells and viruses C. Pathogen: any antigen that causes a disruption in homeostasis a.k.a. normal, disease free, functions D. Antibody: a protein produced specifically in res ...
Watching Class II MHC molecules move Hidde L. Ploegh
... approach to their study. Direct imaging has cast a new light on such interactions, as testified by the broad acceptance of the concept of an immunological synapse. Most of the detailed imaging experiments reported concern surface molecules on the T cell, while relatively little work has been done on ...
... approach to their study. Direct imaging has cast a new light on such interactions, as testified by the broad acceptance of the concept of an immunological synapse. Most of the detailed imaging experiments reported concern surface molecules on the T cell, while relatively little work has been done on ...
factors
... Type III – Immune-complexmediated reactions • Caused by antigen-antibody complexes formed in circulation and deposited in vessel walls or other tissues • Not organ specific • Effects caused by activation of complement – chemotaxis of neutrophils ...
... Type III – Immune-complexmediated reactions • Caused by antigen-antibody complexes formed in circulation and deposited in vessel walls or other tissues • Not organ specific • Effects caused by activation of complement – chemotaxis of neutrophils ...
HIPC-Ontologies - Buffalo Ontology Site
... tools have been developed for modeling immune functions, ranging from single receptor signaling to cell dynamics; each modeling initiative employs its own vocabularies and formats to represent the models, so data and tools are difficult to compare or aggregate • Project Goals: Create a controlled vo ...
... tools have been developed for modeling immune functions, ranging from single receptor signaling to cell dynamics; each modeling initiative employs its own vocabularies and formats to represent the models, so data and tools are difficult to compare or aggregate • Project Goals: Create a controlled vo ...
Monoclonal antibody

Monoclonal antibodies (mAb or moAb) are monospecific antibodies that are made by identical immune cells that are all clones of a unique parent cell, in contrast to polyclonal antibodies which are made from several different immune cells. Monoclonal antibodies have monovalent affinity, in that they bind to the same epitope.Given almost any substance, it is possible to produce monoclonal antibodies that specifically bind to that substance; they can then serve to detect or purify that substance. This has become an important tool in biochemistry, molecular biology and medicine. When used as medications, the non-proprietary drug name ends in -mab (see ""Nomenclature of monoclonal antibodies""), and many immunotherapy specialists use the word mab anacronymically.