Human CAMP/LL37/FALL39 Antibody
... Please Note: Optimal dilutions should be determined by each laboratory for each application. General Protocols are available in the Technical Information section on our website. ...
... Please Note: Optimal dilutions should be determined by each laboratory for each application. General Protocols are available in the Technical Information section on our website. ...
Anti-SDHA antibody [EPR9043(B)] ab137040 Product datasheet 1 Abreviews 12 Images
... Synthetic peptide (the amino acid sequence is considered to be commercially sensitive) corresponding to Human SDHA aa 550-650. ...
... Synthetic peptide (the amino acid sequence is considered to be commercially sensitive) corresponding to Human SDHA aa 550-650. ...
View PDF
... Describe in detail how enzymes work: Enzymes fit specifically to a substrate like a key fits a lock. The enzyme attached to the substrate and changes it into a new product that can be used by the cell or organism. ...
... Describe in detail how enzymes work: Enzymes fit specifically to a substrate like a key fits a lock. The enzyme attached to the substrate and changes it into a new product that can be used by the cell or organism. ...
Document
... - Isolation of cells Isolation of CD34+ stem cells for autologous/allogeneic transplantation (from peripheral blood!) - Blood group determination (with anti-A, anti-B, and anti-D monoclonals) - Identification of cell surface and intracellular antigens Cell activation state - Targeted chemotherapy CD ...
... - Isolation of cells Isolation of CD34+ stem cells for autologous/allogeneic transplantation (from peripheral blood!) - Blood group determination (with anti-A, anti-B, and anti-D monoclonals) - Identification of cell surface and intracellular antigens Cell activation state - Targeted chemotherapy CD ...
VL 08lecture2008
... The Adaptive Immune response: humoral immunity • How are antibodies made? – B cells • Lymphocytes that make antibodies • Have B cell receptors on surface • 100 million different types of B cells, each with different surface receptors • B cell receptors are so diverse they can recognize every organi ...
... The Adaptive Immune response: humoral immunity • How are antibodies made? – B cells • Lymphocytes that make antibodies • Have B cell receptors on surface • 100 million different types of B cells, each with different surface receptors • B cell receptors are so diverse they can recognize every organi ...
Protein Expression and Purification Service Quotation Request Form
... Which species would you like to use? Mouse Rat Either one What application(s) you would use the antibody for? ELISA WB FC or FACS IF IP IHC ELISA Sandwich Other: If several applications are needed, please mention the preferred one below (if any): What kind of sample will the antibody be used on? Add ...
... Which species would you like to use? Mouse Rat Either one What application(s) you would use the antibody for? ELISA WB FC or FACS IF IP IHC ELISA Sandwich Other: If several applications are needed, please mention the preferred one below (if any): What kind of sample will the antibody be used on? Add ...
... cells is summarized in table 1. After PCR with primers specific for heavy chain consensus sequences [15], using temperature gradient gel electrophoresis, one monoclonal band was detected, which has to be interpreted as monoclonal proliferation of B-blasts [15]. Discussion Pulmonary infections are th ...
Chapter 9
... into an animal. The resulting antibody mixture found in the serum are polyclonal. They recognize multiple antigenic epitopes on the molecule in question. Most of the time these work well for ELISA. Two drawbacks are:(1) the amount of the antibodies may vary from batch to batch and (2) cross ...
... into an animal. The resulting antibody mixture found in the serum are polyclonal. They recognize multiple antigenic epitopes on the molecule in question. Most of the time these work well for ELISA. Two drawbacks are:(1) the amount of the antibodies may vary from batch to batch and (2) cross ...
Immune Strategies to Infection
... derived cytokines, and also CTLs directly killing the infected cell. If the bacteria is non-invasive, then a humoral response (antibody production) is enough to neutralise the toxin. Antibody Humoral immunity is mediated by antibodies. Antibodies prevent infection by blocking the ability of microbes ...
... derived cytokines, and also CTLs directly killing the infected cell. If the bacteria is non-invasive, then a humoral response (antibody production) is enough to neutralise the toxin. Antibody Humoral immunity is mediated by antibodies. Antibodies prevent infection by blocking the ability of microbes ...
19-20_Hypersensitivity-autoimmune
... blood cell autoantibodies in 10-20% of patients taking the drug for longer than 4 months. True autoantibodies: directed against an autoantigen on the red blood cell membrane, not against the drug The target membrane antigen is usually within the Rhesus system • Drug-dependent Abs Penicillin, c ...
... blood cell autoantibodies in 10-20% of patients taking the drug for longer than 4 months. True autoantibodies: directed against an autoantigen on the red blood cell membrane, not against the drug The target membrane antigen is usually within the Rhesus system • Drug-dependent Abs Penicillin, c ...
Apresentação do PowerPoint
... sample. (A) The sample is loaded and voltage is applied. The proteins will migrate to their isoelectric pH, the location at which they have no net charge. (B) The proteins form bands that can be excised and used for further experimentation. ...
... sample. (A) The sample is loaded and voltage is applied. The proteins will migrate to their isoelectric pH, the location at which they have no net charge. (B) The proteins form bands that can be excised and used for further experimentation. ...
Recombinant Human LIF (Carrier-free) - Data Sheets
... Leukemia Inhibitory Factor (LIF) is a member of the IL-6 family of cytokines, based on its helical structure. LIF expression has been observed in various tissues including thymus, lung, and neuronal tissue. Expression has also been reported in T cells, monocytes, astrocytes, osteoblasts, keratinocyt ...
... Leukemia Inhibitory Factor (LIF) is a member of the IL-6 family of cytokines, based on its helical structure. LIF expression has been observed in various tissues including thymus, lung, and neuronal tissue. Expression has also been reported in T cells, monocytes, astrocytes, osteoblasts, keratinocyt ...
Lymphatic system - s3.amazonaws.com
... The danger the immune system poses to transplanted tissue is that the recipient’s cells may recognize the donor’s tissue a foreign and attempt to destroy transplanted tissue Immunosuppresive drugs are used to reduce rejection of transplanted tissue Interfere with recipient’s immune response by ...
... The danger the immune system poses to transplanted tissue is that the recipient’s cells may recognize the donor’s tissue a foreign and attempt to destroy transplanted tissue Immunosuppresive drugs are used to reduce rejection of transplanted tissue Interfere with recipient’s immune response by ...
anatomy and physiology answers
... A) is based on recognition of antigens that are specific to different pathogens. B) is found only in vertebrate animals. C) depends on a newly infected animalʹs previous exposure to the same pathogen. D) is activated immediately upon infection. E) utilizes highly specific antigen receptors on B cell ...
... A) is based on recognition of antigens that are specific to different pathogens. B) is found only in vertebrate animals. C) depends on a newly infected animalʹs previous exposure to the same pathogen. D) is activated immediately upon infection. E) utilizes highly specific antigen receptors on B cell ...
Read article here
... team and another at Memorial Sloan-Kettering Cancer Center in New York reported that the T cell therapy in their studies put 45 of 75 adults and children with leukemia into complete remission, although some later relapsed. CAR therapy is now the focus of numerous clinical trials. Researchers hope th ...
... team and another at Memorial Sloan-Kettering Cancer Center in New York reported that the T cell therapy in their studies put 45 of 75 adults and children with leukemia into complete remission, although some later relapsed. CAR therapy is now the focus of numerous clinical trials. Researchers hope th ...
Physiology: The Immune System
... grown in the laboratory in pure culture. b. The pathogen is found in the body of a sick organism and not a healthy one. c. If placed in a new host, the cultured pathogens should not cause the same disease. d. The injected pathogen should be isolated from the second host. It should be identical to th ...
... grown in the laboratory in pure culture. b. The pathogen is found in the body of a sick organism and not a healthy one. c. If placed in a new host, the cultured pathogens should not cause the same disease. d. The injected pathogen should be isolated from the second host. It should be identical to th ...
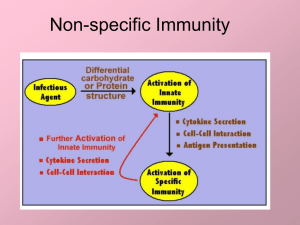
Non-specific Immunity
... • Phagocytosis continues to be common way to kill pathogenic cells in both specific and nonspecific response • Inflammation works to allow both specific and non-specific immune response to accelerate • Fever also allows for better performance in both specific and non-specific function • Specific imm ...
... • Phagocytosis continues to be common way to kill pathogenic cells in both specific and nonspecific response • Inflammation works to allow both specific and non-specific immune response to accelerate • Fever also allows for better performance in both specific and non-specific function • Specific imm ...
Biomolecules PPT
... What is another everyday example you can think of that have monomers and polymers? ...
... What is another everyday example you can think of that have monomers and polymers? ...
Disease Unit Review
... 16. Describe four parts of your body’s first line of defense: a. skin: provides a protective barrier against pathogens b. mucus: traps pathogens and other foreign objects in nose, throat, and eyes. Cilia (tiny hairs) push the pathogens forward to be expelled from the body. c. Digestive fluids: stoma ...
... 16. Describe four parts of your body’s first line of defense: a. skin: provides a protective barrier against pathogens b. mucus: traps pathogens and other foreign objects in nose, throat, and eyes. Cilia (tiny hairs) push the pathogens forward to be expelled from the body. c. Digestive fluids: stoma ...
Specific
... production of a specific defensive response against the particular type of foreign organism or substance that has invaded the body. ...
... production of a specific defensive response against the particular type of foreign organism or substance that has invaded the body. ...
INTEGUMENTARY SYSTEM - Coast Colleges Home Page
... Non-Specific/Innate Defenses Barriers – skin, mucous membranes, tears Phagocytes – Neutrophils, Macrophages Natural Killer Cells – lymphocytes that lyse/kill cancer cells & virus-infected cells Proteins – complement & interferon Inflammation – Redness, Heat, Pain, Swelling Fever ...
... Non-Specific/Innate Defenses Barriers – skin, mucous membranes, tears Phagocytes – Neutrophils, Macrophages Natural Killer Cells – lymphocytes that lyse/kill cancer cells & virus-infected cells Proteins – complement & interferon Inflammation – Redness, Heat, Pain, Swelling Fever ...
Monoclonal antibody

Monoclonal antibodies (mAb or moAb) are monospecific antibodies that are made by identical immune cells that are all clones of a unique parent cell, in contrast to polyclonal antibodies which are made from several different immune cells. Monoclonal antibodies have monovalent affinity, in that they bind to the same epitope.Given almost any substance, it is possible to produce monoclonal antibodies that specifically bind to that substance; they can then serve to detect or purify that substance. This has become an important tool in biochemistry, molecular biology and medicine. When used as medications, the non-proprietary drug name ends in -mab (see ""Nomenclature of monoclonal antibodies""), and many immunotherapy specialists use the word mab anacronymically.

![Anti-SDHA antibody [EPR9043(B)] ab137040 Product datasheet 1 Abreviews 12 Images](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/000030236_1-388d4cb04c9400dad80d1dd049a08d18-300x300.png)