1 Biology - Organic Chemistry Notes Name Date Organic Chemistry
... proteins. Protein molecules are long, usually folded chains made from 20 different kinds of amino acids in a specific sequence. This sequence influences the shape of the protein. The shape of the protein, in tern determines its function. -------------------------------------------------------------- ...
... proteins. Protein molecules are long, usually folded chains made from 20 different kinds of amino acids in a specific sequence. This sequence influences the shape of the protein. The shape of the protein, in tern determines its function. -------------------------------------------------------------- ...
Topics that we have covered
... 1. Turn assignments in on time! No late work will be accepted unless accompanied by a excused absence note. 2. Attendance policy: 3 UE tardies = Detention, 5 UE tadies = Detention with VP. Call home for each unexcused absence. You must be in I203 in order to be counted as present. If you have an exc ...
... 1. Turn assignments in on time! No late work will be accepted unless accompanied by a excused absence note. 2. Attendance policy: 3 UE tardies = Detention, 5 UE tadies = Detention with VP. Call home for each unexcused absence. You must be in I203 in order to be counted as present. If you have an exc ...
Monoclonal antibodies
... antibody-producing Bcells are taken from the mouse’s spleen. The mouse cells and tumor cells are mixed together in ...
... antibody-producing Bcells are taken from the mouse’s spleen. The mouse cells and tumor cells are mixed together in ...
EOC Review Answer Key- Friday
... 2. Why did the large dark molecules NOT move to the left? Too large for membrane pores 3. How is the semi-permeable membrane like a cell membrane? Allows some substances to pass and not ...
... 2. Why did the large dark molecules NOT move to the left? Too large for membrane pores 3. How is the semi-permeable membrane like a cell membrane? Allows some substances to pass and not ...
The subject of the offer are unique sequences of single
... In addition to the above applications, DNA aptamers can be used as molecules with attached tags, especially fluorescent, and in particular to label the molecular targets containing His‐Tag. This type of molecules can be successfully used e.g. to study the interaction be ...
... In addition to the above applications, DNA aptamers can be used as molecules with attached tags, especially fluorescent, and in particular to label the molecular targets containing His‐Tag. This type of molecules can be successfully used e.g. to study the interaction be ...
A) chemical bonds between carbon atoms are formed during
... • ribosome • site of protein synthesis • amino acid — used to make proteins • nucleus — the ribosome gets instructions from the nucleus determining which proteins are produced by the cell ...
... • ribosome • site of protein synthesis • amino acid — used to make proteins • nucleus — the ribosome gets instructions from the nucleus determining which proteins are produced by the cell ...
Biomolecules Discussion
... Shmoop Editorial Team. (November 11, 2008).Biomolecules and the Chemistry of Life. Retrieved April 6, 2013, from http://www.shmoop.com/biomolecules/ ...
... Shmoop Editorial Team. (November 11, 2008).Biomolecules and the Chemistry of Life. Retrieved April 6, 2013, from http://www.shmoop.com/biomolecules/ ...
Translation PPT
... “Clover leaf” structure anticodon on “clover leaf” end amino acid attached on 3 end ...
... “Clover leaf” structure anticodon on “clover leaf” end amino acid attached on 3 end ...
Transformation
... Transformation :is a process in which cells take up foreign DNA from their environment. bacteria take up exogenous (foreign) DNA and produce the genetic products (proteins) encoded in the foreign DNA. Under proper conditions, a cell that is incubated with plasmid DNA can absorb the plasmid into i ...
... Transformation :is a process in which cells take up foreign DNA from their environment. bacteria take up exogenous (foreign) DNA and produce the genetic products (proteins) encoded in the foreign DNA. Under proper conditions, a cell that is incubated with plasmid DNA can absorb the plasmid into i ...
Organic Macromolecules
... plate for 48hrs at 37 C, you notice that there was not any growth. Explain why this may have occurred. ...
... plate for 48hrs at 37 C, you notice that there was not any growth. Explain why this may have occurred. ...
A new avenue for combating the deterioration in blood stem cells
... cancer patients undergoing treatment. The study will be published this week in the journal Nature Communications. ...
... cancer patients undergoing treatment. The study will be published this week in the journal Nature Communications. ...
Chapter 7: Microbial Genetics
... When stretched out, this single DNA molecule is about 1mm long (~1000 times longer than cell) This immense molecule fits compactly into the cell nucleoid by twisting around itself (supercoiling) Supercoiled DNA DNA can be supercoiled in either a positive or negative direction ...
... When stretched out, this single DNA molecule is about 1mm long (~1000 times longer than cell) This immense molecule fits compactly into the cell nucleoid by twisting around itself (supercoiling) Supercoiled DNA DNA can be supercoiled in either a positive or negative direction ...
Ways Cells Divide
... – Reproduction is clonal (no variation in offspring) • Single, circular bacterial chromosome is replicated • Replication begins at the origin of replication and proceeds in two directions to site of termination • New chromosomes are partitioned to opposite ends of the cell • Septum forms to divide t ...
... – Reproduction is clonal (no variation in offspring) • Single, circular bacterial chromosome is replicated • Replication begins at the origin of replication and proceeds in two directions to site of termination • New chromosomes are partitioned to opposite ends of the cell • Septum forms to divide t ...
interactive_textbook reading
... energy and nutrients to live and grow. However, not all organisms get food in the same way. There are three ways in which organisms can get food. Some organisms, such as plants, are producers. Producers make their own food using energy from their environment. For example, plants, and some bacteria a ...
... energy and nutrients to live and grow. However, not all organisms get food in the same way. There are three ways in which organisms can get food. Some organisms, such as plants, are producers. Producers make their own food using energy from their environment. For example, plants, and some bacteria a ...
PowerPoint
... – Van der Waals forces (transient, weak electrical attraction of one atom for another) – Hydrophobic (clustering of nonpolar groups) – Hydrogen bonding ...
... – Van der Waals forces (transient, weak electrical attraction of one atom for another) – Hydrophobic (clustering of nonpolar groups) – Hydrogen bonding ...
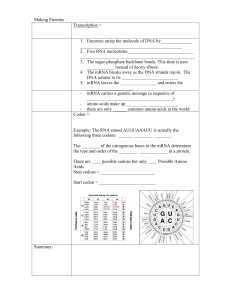
DNA Transcription
... The ________ of the nitrogenous bases in the mRNA determines the type and order of the ________ ____________ in a protein. There are ____ possible codons but only ____ Possible Amino Acids Stop codons = ________________________ Start codon = _________________________ ...
... The ________ of the nitrogenous bases in the mRNA determines the type and order of the ________ ____________ in a protein. There are ____ possible codons but only ____ Possible Amino Acids Stop codons = ________________________ Start codon = _________________________ ...
Holiday Packet 2
... shown in the diagram. Based on these results, which statement correctly predicts what will happen to red blood cells when they are placed in a beaker containing a water solution in which the salt concentration is much higher than the salt concentration in the red blood cells? a. The red blood cells ...
... shown in the diagram. Based on these results, which statement correctly predicts what will happen to red blood cells when they are placed in a beaker containing a water solution in which the salt concentration is much higher than the salt concentration in the red blood cells? a. The red blood cells ...
Simple Sugars
... 3. If you have excess glucose in your blood, your liver would build some the glucose into ……………… (poly saccharide) ...
... 3. If you have excess glucose in your blood, your liver would build some the glucose into ……………… (poly saccharide) ...
Biology EOCT Practice Questions Part 2
... that have both parents’ DNA. B. A cell from one parent undergoes mitotic cell division, producing offspring cells that have only half of the parent’s DNA. C. Cells in the parents undergo meiosis, producing haploid gametes that meet up during fertilization to produce a diploid individual. D. Cells th ...
... that have both parents’ DNA. B. A cell from one parent undergoes mitotic cell division, producing offspring cells that have only half of the parent’s DNA. C. Cells in the parents undergo meiosis, producing haploid gametes that meet up during fertilization to produce a diploid individual. D. Cells th ...
Drag and Drop Protein Synthesis Name Period Type in the following
... 3. If a DNA sequence consists of 12 nucleotides, how many mRNA codons will there be? 4. The enzyme that creates mRNA from a DNA sequence is called: 5. Each codon of mRNA (hence each triplet in DNA) codes for one: 6. The specific amino acid carried by a tRNA is determined it's: 7. True or False? When ...
... 3. If a DNA sequence consists of 12 nucleotides, how many mRNA codons will there be? 4. The enzyme that creates mRNA from a DNA sequence is called: 5. Each codon of mRNA (hence each triplet in DNA) codes for one: 6. The specific amino acid carried by a tRNA is determined it's: 7. True or False? When ...
Introducing Genetics
... found that the amount of T and A are always equal, as are the amount of C and G. This has led to the conclusion that within the double helix A always pairs with T and C always pairs with G so that if one strand of DNA had the sequence “CCGAAT” then the other strand would be the converse of that code ...
... found that the amount of T and A are always equal, as are the amount of C and G. This has led to the conclusion that within the double helix A always pairs with T and C always pairs with G so that if one strand of DNA had the sequence “CCGAAT” then the other strand would be the converse of that code ...
Lecture_12_Jan 29_2015 Plasmodium_invasion
... channel on the PVM has been implicated in the acquistion of nutrients. Others have proposed a direct connection to the host plasma via a 'parasitophorous duct‘. Presumably the parasite plasma membrane has transporters which are typical of other eukaryotes. ...
... channel on the PVM has been implicated in the acquistion of nutrients. Others have proposed a direct connection to the host plasma via a 'parasitophorous duct‘. Presumably the parasite plasma membrane has transporters which are typical of other eukaryotes. ...
Bio-Ch-8-Mouse
... If the concentration of a sugar solution is lower outside the cell than inside the cell, which of the following will happen by osmosis? ...
... If the concentration of a sugar solution is lower outside the cell than inside the cell, which of the following will happen by osmosis? ...
Languages of a Cell and the History of the
... cell –DNA (English), RNA (Spanish), and proteins (Japanese). Explaining the similarities of verbal languages we know with the languages the cell uses helps the students visualize the similarities. For example, DNA is the universal language of all cells. In the world English is basically the universa ...
... cell –DNA (English), RNA (Spanish), and proteins (Japanese). Explaining the similarities of verbal languages we know with the languages the cell uses helps the students visualize the similarities. For example, DNA is the universal language of all cells. In the world English is basically the universa ...
Cell-penetrating peptide

Cell-penetrating peptides (CPPs) are short peptides that facilitate cellular uptake of various molecular cargo (from nanosize particles to small chemical molecules and large fragments of DNA). The ""cargo"" is associated with the peptides either through chemical linkage via covalent bonds or through non-covalent interactions. The function of the CPPs are to deliver the cargo into cells, a process that commonly occurs through endocytosis with the cargo delivered to the endosomes of living mammalian cells.CPPs hold great potential as in vitro and in vivo delivery vectors for use in research and medicine. Current use is limited by a lack of cell specificity in CPP-mediated cargo delivery and insufficient understanding of the modes of their uptake.CPPs typically have an amino acid composition that either contains a high relative abundance of positively charged amino acids such as lysine or arginine or has sequences that contain an alternating pattern of polar/charged amino acids and non-polar, hydrophobic amino acids. These two types of structures are referred to as polycationic or amphipathic, respectively. A third class of CPPs are the hydrophobic peptides, containing only apolar residues, with low net chargeor have hydrophobic amino acid groups that are crucial for cellular uptake.The first CPP was discovered independently by two laboratories in 1988, when it was found that the trans-activating transcriptional activator (TAT) from human immunodeficiency virus 1 (HIV-1) could be efficiently taken up from the surrounding media by numerous cell types in culture. Since then, the number of known CPPs has expanded considerably and small molecule synthetic analogues with more effective protein transduction properties have been generated.