Polymerase Chain Reaction
... to amplify the DNA of a pathogen so it can be sequenced. This can enable scientists to pinpoint the source of some serious outbreaks of infection. ...
... to amplify the DNA of a pathogen so it can be sequenced. This can enable scientists to pinpoint the source of some serious outbreaks of infection. ...
Bio 139 Exam Review Outline: Exam #3
... LacZ is a structural gene (what does that mean?) that codes for beta-galactosidase. What is a promoter? (regulatory gene where RNA polymerase binds and initiates transcription) Does its DNA sequence code for a protein? (no) What is an operator? (regulatory gene which controls expression of structura ...
... LacZ is a structural gene (what does that mean?) that codes for beta-galactosidase. What is a promoter? (regulatory gene where RNA polymerase binds and initiates transcription) Does its DNA sequence code for a protein? (no) What is an operator? (regulatory gene which controls expression of structura ...
Chapters 5-8a
... 2. The amount of energy it takes to get a chemical reaction going is known as a. starting energy b. ATP c. activation energy d. denaturation 3. When a protein’s three-dimensional structure has been altered to the extent that it no longer functions, it has been a. denatured b. killed c. anabolized d. ...
... 2. The amount of energy it takes to get a chemical reaction going is known as a. starting energy b. ATP c. activation energy d. denaturation 3. When a protein’s three-dimensional structure has been altered to the extent that it no longer functions, it has been a. denatured b. killed c. anabolized d. ...
Chromatin Structure and Function
... that move down the DNA and open or restore nucleosomes, and allow other DNA-binding proteins to bind, e.g., DNA and RNA polymerases and Transcription Factors ...
... that move down the DNA and open or restore nucleosomes, and allow other DNA-binding proteins to bind, e.g., DNA and RNA polymerases and Transcription Factors ...
Evolution and Genetics
... Antibiotic-resistant strains of microorganisms that cause diseases, such as tuberculosis, are increasing in number due to natural selection ...
... Antibiotic-resistant strains of microorganisms that cause diseases, such as tuberculosis, are increasing in number due to natural selection ...
DNA Workshop - Mrs. Sills` Science Site
... How many seconds does it take to create a protein chain that is 400 _______________________________ ...
... How many seconds does it take to create a protein chain that is 400 _______________________________ ...
SNC2D Genes - Malvern Science
... Food for thought.. (don’t write) • How do we communicate to each other? • What does each of the following mean? – kobo – meti – etwar ...
... Food for thought.. (don’t write) • How do we communicate to each other? • What does each of the following mean? – kobo – meti – etwar ...
Dna rEPLICATION - Manning`s Science
... called ORIGINS OF REPLICATION -the structure of 2 unwound DNA strands is referred to as a replication fork ...
... called ORIGINS OF REPLICATION -the structure of 2 unwound DNA strands is referred to as a replication fork ...
Molecular genetics
... group) is added to the 5’ end of RNA after splicing. RNA cap determines the site of translation. PolyA tailing is the process by which a long tail of Adenine residue is added to the 3’ end of m-RNA during splicing. Ribozymes are RNA molecules act as enzymes. RNase P is a Ribozyme. 9. Recombinant DNA ...
... group) is added to the 5’ end of RNA after splicing. RNA cap determines the site of translation. PolyA tailing is the process by which a long tail of Adenine residue is added to the 3’ end of m-RNA during splicing. Ribozymes are RNA molecules act as enzymes. RNase P is a Ribozyme. 9. Recombinant DNA ...
Topic 4: Genetics - Peoria Public Schools
... genes. Not only did the project strive to find the total genes but it attempted to find each gene’s location and each gene’s base sequence. 64. Benefits of the Human Genome Project include the ability to study how genes influence human development, the easier identification of genetic diseases, and ...
... genes. Not only did the project strive to find the total genes but it attempted to find each gene’s location and each gene’s base sequence. 64. Benefits of the Human Genome Project include the ability to study how genes influence human development, the easier identification of genetic diseases, and ...
DNA - The Double Helix
... the production of proteins within the cell. These proteins in turn, form the structural units of cells and control all chemical processes within the cell. Think of proteins as the building blocks for an organism, proteins make up your skin, your hair, parts of individual cells. How you look is large ...
... the production of proteins within the cell. These proteins in turn, form the structural units of cells and control all chemical processes within the cell. Think of proteins as the building blocks for an organism, proteins make up your skin, your hair, parts of individual cells. How you look is large ...
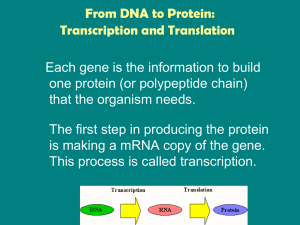
From DNA to Protein: Transcription and Translation
... • mRNA has the nitrogen base uracil instead of thymine. ...
... • mRNA has the nitrogen base uracil instead of thymine. ...
PowerPoint Presentation - No Slide Title
... The restriction-fragment length experiment we looked at before could use PCR instead of a radioactive probe. If we amplify large quantities of the region of interest from a small amount of genomic DNA, and then do the restriction digest, the fragments we are interested in will be the only ones on t ...
... The restriction-fragment length experiment we looked at before could use PCR instead of a radioactive probe. If we amplify large quantities of the region of interest from a small amount of genomic DNA, and then do the restriction digest, the fragments we are interested in will be the only ones on t ...
Biotechnology & Genetic Engineering
... – 3. Making copies • Polymerase chain reaction is used to make many copies of a particular gene ...
... – 3. Making copies • Polymerase chain reaction is used to make many copies of a particular gene ...
Clike here - University of Evansville Faculty Web sites
... The restriction-fragment length experiment we looked at before could use PCR instead of a radioactive probe. If we amplify large quantities of the region of interest from a small amount of genomic DNA, and then do the restriction digest, the fragments we are interested in will be the only ones on t ...
... The restriction-fragment length experiment we looked at before could use PCR instead of a radioactive probe. If we amplify large quantities of the region of interest from a small amount of genomic DNA, and then do the restriction digest, the fragments we are interested in will be the only ones on t ...
Cell Cycle Quiz key
... D. The nucleus translates the ribosomal RNA for the enzymes to be synthesized in mitochondria. 15. _____During a stage of protein synthesis, codons in mRNA molecules are used to specify the sequence of amino acids in polypeptide chains. What is this process called? A. transcription B. gene expressio ...
... D. The nucleus translates the ribosomal RNA for the enzymes to be synthesized in mitochondria. 15. _____During a stage of protein synthesis, codons in mRNA molecules are used to specify the sequence of amino acids in polypeptide chains. What is this process called? A. transcription B. gene expressio ...
Human Alu Insertion Polymorphism Experiment
... Polymerase Chain Reaction: another method of DNA amplification ...
... Polymerase Chain Reaction: another method of DNA amplification ...
geneticsresearchmoleculargens
... October/early November) on Nov. 20, 2012 (will postpone a week if needed). It includes the technical and practical aspects of work we will have done at the lab, as well as some understanding of techniques we did not do at the lab. Even though I will not start using these notes full-bore (NO PUN INTE ...
... October/early November) on Nov. 20, 2012 (will postpone a week if needed). It includes the technical and practical aspects of work we will have done at the lab, as well as some understanding of techniques we did not do at the lab. Even though I will not start using these notes full-bore (NO PUN INTE ...
genome that an organism carries in its DNA. analysis of chromosomes.
... • Klinefelter’s syndrome occurs in about 1 out of 1,000 males. ...
... • Klinefelter’s syndrome occurs in about 1 out of 1,000 males. ...
I.
... I. Questions (50%) 1. What would happen if the different tRNAs in cells could bind to just any amino acid? How does the specificity of tRNA for particular amino acids maintain the integrity of the genetic information? (10%) ...
... I. Questions (50%) 1. What would happen if the different tRNAs in cells could bind to just any amino acid? How does the specificity of tRNA for particular amino acids maintain the integrity of the genetic information? (10%) ...
3rd- 9 Weeks Test Review
... eukaryotic cells); ü This is known as gene expression. ü For transcription to occur, the DNA helix unzips itself, and the DNA is transcribed into mRNA. 2. Translation is the process of synthesizing (creating) proteins from the RNA template. ü The mRNA from transcription carries genetic information f ...
... eukaryotic cells); ü This is known as gene expression. ü For transcription to occur, the DNA helix unzips itself, and the DNA is transcribed into mRNA. 2. Translation is the process of synthesizing (creating) proteins from the RNA template. ü The mRNA from transcription carries genetic information f ...
Deoxyribozyme
_DNAzyme.png?width=300)
Deoxyribozymes, also called DNA enzymes, DNAzymes, or catalytic DNA, are DNA oligonucleotides that are capable of catalyzing specific chemical reactions, similar to the action of other biological enzymes, such as proteins or ribozymes (enzymes composed of RNA).However, in contrast to the abundance of protein enzymes in biological systems and the discovery of biological ribozymes in the 1980s,there are no known naturally occurring deoxyribozymes.Deoxyribozymes should not be confused with DNA aptamers which are oligonucleotides that selectively bind a target ligand, but do not catalyze a subsequent chemical reaction.With the exception of ribozymes, nucleic acid molecules within cells primarily serve as storage of genetic information due to its ability to form complementary base pairs, which allows for high-fidelity copying and transfer of genetic information. In contrast, nucleic acid molecules are more limited in their catalytic ability, in comparison to protein enzymes, to just three types of interactions: hydrogen bonding, pi stacking, and metal-ion coordination. This is due to the limited number of functional groups of the nucleic acid monomers: while proteins are built from up to twenty different amino acids with various functional groups, nucleic acids are built from just four chemically similar nucleobases. In addition, DNA lacks the 2'-hydroxyl group found in RNA which limits the catalytic competency of deoxyribozymes even in comparison to ribozymes.In addition to the inherent inferiority of DNA catalytic activity, the apparent lack of naturally occurring deoxyribozymes may also be due to the primarily double-stranded conformation of DNA in biological systems which would limit its physical flexibility and ability to form tertiary structures, and so would drastically limit the ability of double-stranded DNA to act as a catalyst; though there are a few known instances of biological single-stranded DNA such as multicopy single-stranded DNA (msDNA), certain viral genomes, and the replication fork formed during DNA replication. Further structural differences between DNA and RNA may also play a role in the lack of biological deoxyribozymes, such as the additional methyl group of the DNA base thymidine compared to the RNA base uracil or the tendency of DNA to adopt the B-form helix while RNA tends to adopt the A-form helix. However, it has also been shown that DNA can form structures that RNA cannot, which suggests that, though there are differences in structures that each can form, neither is inherently more or less catalytic due to their possible structural motifs.