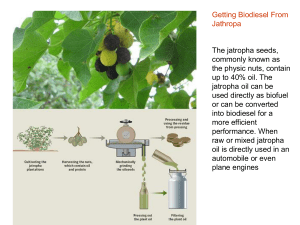
Lecture Powerpoint Here
... DNA is genetic material now DNA-to-RNA-to-protein system is complex! RNA may have been first genetic material ...
... DNA is genetic material now DNA-to-RNA-to-protein system is complex! RNA may have been first genetic material ...
Quiz 3 Key - UW Canvas
... NOTE: This key is for version A – look carefully if you have version B! 1. (4 pts) For each of the following molecules or structures, write the letter for the category of biological macromolecule it is or is made of. IF IT CONSISTS OF TWO TYPES, write both letters. Categories may be used once, more ...
... NOTE: This key is for version A – look carefully if you have version B! 1. (4 pts) For each of the following molecules or structures, write the letter for the category of biological macromolecule it is or is made of. IF IT CONSISTS OF TWO TYPES, write both letters. Categories may be used once, more ...
Chapter 13: The Genetic Code and Transcription
... Three other codons serve as termination codons (UAG, UAA, and UGA) but do not code for an amino acid. They are not recognized by the tRNA performing translation, so the process ends when they are reached. 13.8 Transcription synthesizes RNA on a DNA template During the studies of DNA, it was clea ...
... Three other codons serve as termination codons (UAG, UAA, and UGA) but do not code for an amino acid. They are not recognized by the tRNA performing translation, so the process ends when they are reached. 13.8 Transcription synthesizes RNA on a DNA template During the studies of DNA, it was clea ...
DNA functions worksheet
... A. it stays in the nucleus and is copied by DNA B. it carries amino acids to the growing polypeptide chain C. it makes up the ribosomes and provides the site for protein synthesis D. it is transcribed from the DNA and carries the information to the ribosome 6. Read the following DNA sequence left to ...
... A. it stays in the nucleus and is copied by DNA B. it carries amino acids to the growing polypeptide chain C. it makes up the ribosomes and provides the site for protein synthesis D. it is transcribed from the DNA and carries the information to the ribosome 6. Read the following DNA sequence left to ...
Genetics Study Guide
... What do the squares in the above pedigree represent? Males or Females How many people in the above example are carriers of albinism, but are not albino? ___ ...
... What do the squares in the above pedigree represent? Males or Females How many people in the above example are carriers of albinism, but are not albino? ___ ...
MUTATIONS
... DNA just happen. Our DNA can change without warning, which changes the genes and how they behave. Factors that cause changes in our DNA: Errors when DNA is copied for new cells Environmental factors change DNA (nicotine, sunlight, x-rays, chemicals Mutations are inherited from the parents ...
... DNA just happen. Our DNA can change without warning, which changes the genes and how they behave. Factors that cause changes in our DNA: Errors when DNA is copied for new cells Environmental factors change DNA (nicotine, sunlight, x-rays, chemicals Mutations are inherited from the parents ...
1. Diagram the biosynthetic pathway fiom UMP),
... a pH gradient across the inner membrane (outside more acidic than inside). The tendency of protons to diffuse back into the matrix is the driving force for ATP synthesis by ATP synthase. During oxidative phosphorylation by a suspension of mitochondria in a medium of pH 7.4, the pH of the matrix has ...
... a pH gradient across the inner membrane (outside more acidic than inside). The tendency of protons to diffuse back into the matrix is the driving force for ATP synthesis by ATP synthase. During oxidative phosphorylation by a suspension of mitochondria in a medium of pH 7.4, the pH of the matrix has ...
Genetics
... broad definition = a change that does not change the function of the encoded protein • by this definition a silent mutation could be any of these types of base substitions, as long as the function of the protein (phenotype) was not affected) ...
... broad definition = a change that does not change the function of the encoded protein • by this definition a silent mutation could be any of these types of base substitions, as long as the function of the protein (phenotype) was not affected) ...
[001-072] pierce student man
... d. Some RNA molecules are longer than normal. e. RNA is copied from both DNA strands. Explain your reasoning for accepting or rejecting each of these five options. ***9. Enhancers are sequences that affect initiation of transcription occurring at genes that are hundreds or thousands of nucleotides a ...
... d. Some RNA molecules are longer than normal. e. RNA is copied from both DNA strands. Explain your reasoning for accepting or rejecting each of these five options. ***9. Enhancers are sequences that affect initiation of transcription occurring at genes that are hundreds or thousands of nucleotides a ...
Chapter 13: Genetic Engineering
... DNA Extraction – Chemical procedure (we’ll do this) Restriction enzymes – molecular scissors that cut DNA at specific nucleotide sequences Gel Electrophoresis – method to analyze fragments of DNA cut by restriction enzymes through a gel made of agarose (molecular sieve) DNA Ligase – molecular glue t ...
... DNA Extraction – Chemical procedure (we’ll do this) Restriction enzymes – molecular scissors that cut DNA at specific nucleotide sequences Gel Electrophoresis – method to analyze fragments of DNA cut by restriction enzymes through a gel made of agarose (molecular sieve) DNA Ligase – molecular glue t ...
Central Dogma of Biology Nucleic Acids
... structure. DNA is stable. • Requires enzyme/ATP to split apart, to do its thing: replicate, transcribe. • RNA more flexible than DNA (lack of an OH-bond in RNA!), can do catalysis as well as store information. • RNA not as stable as DNA, therefore not as good at genetic/ information storage. • Life ...
... structure. DNA is stable. • Requires enzyme/ATP to split apart, to do its thing: replicate, transcribe. • RNA more flexible than DNA (lack of an OH-bond in RNA!), can do catalysis as well as store information. • RNA not as stable as DNA, therefore not as good at genetic/ information storage. • Life ...
Name
... 15. Translation of mRNA in a ribosome proceeds __. a. from the middle simultaneously toward the 3' and 5' ends b. from either the 5' or 3' end, depending on the enzymes present c. from the 5' end to the 3' end d. from the 3' end to the 5' end 16. Most inborn disorders of metabolism associated with ...
... 15. Translation of mRNA in a ribosome proceeds __. a. from the middle simultaneously toward the 3' and 5' ends b. from either the 5' or 3' end, depending on the enzymes present c. from the 5' end to the 3' end d. from the 3' end to the 5' end 16. Most inborn disorders of metabolism associated with ...
Semiconservative
... • Uncoiling- unwinding of DNA from histones • Unzipping- breaking hydrogen bonds between base pairs allowing strands to separate • Addition of nucleotides- each parent strand is used as the template for synthesis of daughter strands. Read 3’-5’, synthesis 5’3’ ...
... • Uncoiling- unwinding of DNA from histones • Unzipping- breaking hydrogen bonds between base pairs allowing strands to separate • Addition of nucleotides- each parent strand is used as the template for synthesis of daughter strands. Read 3’-5’, synthesis 5’3’ ...
Genetic Engineering
... They are named from the organism from which it was isolated. EcoR1 E – genus name, Escherichia co – species, coli R - strain 1 - number Cut only at a very specific sequence of DNA nucleotide bases and leave sticky ends. ...
... They are named from the organism from which it was isolated. EcoR1 E – genus name, Escherichia co – species, coli R - strain 1 - number Cut only at a very specific sequence of DNA nucleotide bases and leave sticky ends. ...
Test Review on DNA Structure, DNA Replication
... Understand that the nitrogen base is the part of the nucleotide that forms the genetic code, and be able to name the four possible nitrogen bases in a DNA nucleotide. Know how the nucleotides are organized in the strands Know the complementary nitrogen base pairings ...
... Understand that the nitrogen base is the part of the nucleotide that forms the genetic code, and be able to name the four possible nitrogen bases in a DNA nucleotide. Know how the nucleotides are organized in the strands Know the complementary nitrogen base pairings ...
Slide 1
... recombinant plasmids in a particular colony of bacteria • cDNA libraries contain all the gene that there are cDNA for ...
... recombinant plasmids in a particular colony of bacteria • cDNA libraries contain all the gene that there are cDNA for ...
Amal Awwad 23 Abd Alraheem Jerdaneh st. Amman, Jordan
... Studied the formation of G-quadruplexes in more than 500 DNA and RNA aptamer sequences. Aptamers are single stranded RNA or DNA oligonucleotides that bind with high affinity and specificity to unique targets such as peptides, cells, organelles and viruses. The main purpose of the project was to stud ...
... Studied the formation of G-quadruplexes in more than 500 DNA and RNA aptamer sequences. Aptamers are single stranded RNA or DNA oligonucleotides that bind with high affinity and specificity to unique targets such as peptides, cells, organelles and viruses. The main purpose of the project was to stud ...
No Slide Title
... 1. Heat the mixture. Just before the boiling point of water, the DNA will become single-stranded. 2. Cool the mixture. As the mixture cools, the primer will bind to the DNA and the polymerase will synthesize a new strand for each strand of DNA. 3. Repeat steps 1 and 2 until a sufficient amount of th ...
... 1. Heat the mixture. Just before the boiling point of water, the DNA will become single-stranded. 2. Cool the mixture. As the mixture cools, the primer will bind to the DNA and the polymerase will synthesize a new strand for each strand of DNA. 3. Repeat steps 1 and 2 until a sufficient amount of th ...
Human Genetics and Genetic Technology Test Review Jeopardy
... How the DNA fragments are divided once the gel is finished running ...
... How the DNA fragments are divided once the gel is finished running ...
Deoxyribozyme
_DNAzyme.png?width=300)
Deoxyribozymes, also called DNA enzymes, DNAzymes, or catalytic DNA, are DNA oligonucleotides that are capable of catalyzing specific chemical reactions, similar to the action of other biological enzymes, such as proteins or ribozymes (enzymes composed of RNA).However, in contrast to the abundance of protein enzymes in biological systems and the discovery of biological ribozymes in the 1980s,there are no known naturally occurring deoxyribozymes.Deoxyribozymes should not be confused with DNA aptamers which are oligonucleotides that selectively bind a target ligand, but do not catalyze a subsequent chemical reaction.With the exception of ribozymes, nucleic acid molecules within cells primarily serve as storage of genetic information due to its ability to form complementary base pairs, which allows for high-fidelity copying and transfer of genetic information. In contrast, nucleic acid molecules are more limited in their catalytic ability, in comparison to protein enzymes, to just three types of interactions: hydrogen bonding, pi stacking, and metal-ion coordination. This is due to the limited number of functional groups of the nucleic acid monomers: while proteins are built from up to twenty different amino acids with various functional groups, nucleic acids are built from just four chemically similar nucleobases. In addition, DNA lacks the 2'-hydroxyl group found in RNA which limits the catalytic competency of deoxyribozymes even in comparison to ribozymes.In addition to the inherent inferiority of DNA catalytic activity, the apparent lack of naturally occurring deoxyribozymes may also be due to the primarily double-stranded conformation of DNA in biological systems which would limit its physical flexibility and ability to form tertiary structures, and so would drastically limit the ability of double-stranded DNA to act as a catalyst; though there are a few known instances of biological single-stranded DNA such as multicopy single-stranded DNA (msDNA), certain viral genomes, and the replication fork formed during DNA replication. Further structural differences between DNA and RNA may also play a role in the lack of biological deoxyribozymes, such as the additional methyl group of the DNA base thymidine compared to the RNA base uracil or the tendency of DNA to adopt the B-form helix while RNA tends to adopt the A-form helix. However, it has also been shown that DNA can form structures that RNA cannot, which suggests that, though there are differences in structures that each can form, neither is inherently more or less catalytic due to their possible structural motifs.









![[001-072] pierce student man](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/022334386_1-9de543484cd36eb36195da727e3238d8-300x300.png)