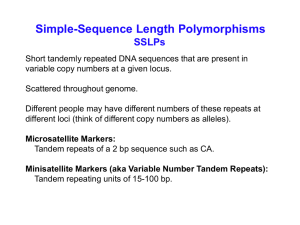
Using microsatellites as molecular markers
... Advantages of SSLPs compared to RFLPs 1. Unlike RFLPs, both microsatellites and minisatellites usually have > 2 alleles. By having more allele possibilities, each allele can be used as a more specific tag. 2. In a population, heterozygosity for a particular RFLP may be low, whereas heterozygosity f ...
... Advantages of SSLPs compared to RFLPs 1. Unlike RFLPs, both microsatellites and minisatellites usually have > 2 alleles. By having more allele possibilities, each allele can be used as a more specific tag. 2. In a population, heterozygosity for a particular RFLP may be low, whereas heterozygosity f ...
Nucleic Acids and Genetics - Travis Science TAKS Practice
... Name the RNA used in transcription. Name the RNA used in translation. III. Protein synthesis: Going from DNA to Protein Transcription - mRNA will leave the nucleus and travel to the ribosomes where proteins are assembled. The ribosome reads the mRNA strand in sets of three bases (codons). These codo ...
... Name the RNA used in transcription. Name the RNA used in translation. III. Protein synthesis: Going from DNA to Protein Transcription - mRNA will leave the nucleus and travel to the ribosomes where proteins are assembled. The ribosome reads the mRNA strand in sets of three bases (codons). These codo ...
BIOCHEMISTRY Nucleic Acids
... • The bases of the separated strands are not connected by hydrogen bonds anymore – they can now pair with free individual nucleotides present in the nucleus (C≡G & A=T) one at a time & form new hydrogen bonds with the old strand (= the template). • The enzyme DNA-polymerase checks if the pairing of ...
... • The bases of the separated strands are not connected by hydrogen bonds anymore – they can now pair with free individual nucleotides present in the nucleus (C≡G & A=T) one at a time & form new hydrogen bonds with the old strand (= the template). • The enzyme DNA-polymerase checks if the pairing of ...
P site
... synthesised in fragments (named the lagging strand). The leading strand only needs one primer while the lagging strand needs quite a few as it is formed in fragments. These fragments are called Okazaki fragments. DNA polymerase I will remove the RNA primers and replace these with DNA. The enzyme DNA ...
... synthesised in fragments (named the lagging strand). The leading strand only needs one primer while the lagging strand needs quite a few as it is formed in fragments. These fragments are called Okazaki fragments. DNA polymerase I will remove the RNA primers and replace these with DNA. The enzyme DNA ...
6.3 Advances in Genetics
... one organism are put into the DNA of another • Genetic engineering can produce and improve medicines and foods. • Genes have been inserted into animals (example- creating blood clotting protein to help people with hemophilia • Genes have been inserted into plants (example- creating crops that are re ...
... one organism are put into the DNA of another • Genetic engineering can produce and improve medicines and foods. • Genes have been inserted into animals (example- creating blood clotting protein to help people with hemophilia • Genes have been inserted into plants (example- creating crops that are re ...
ANSWERS TO REVIEW QUESTIONS
... DNA microarrays are used to evaluate patterns of gene expression. Short nucleic acids serve as probes (DNA) or to silence gene expression (RNAi and microRNAs) ...
... DNA microarrays are used to evaluate patterns of gene expression. Short nucleic acids serve as probes (DNA) or to silence gene expression (RNAi and microRNAs) ...
Final Review
... 25. Explain the process of DNA replication, including what enzymes are involved. 26. Explain the process of protein synthesis, including all key terminology. 27. Define transcription. 28. Define translation. 29. What happens to mRNA before it leaves the nucleus? 30. What is a codon? Anticodon? 31. 3 ...
... 25. Explain the process of DNA replication, including what enzymes are involved. 26. Explain the process of protein synthesis, including all key terminology. 27. Define transcription. 28. Define translation. 29. What happens to mRNA before it leaves the nucleus? 30. What is a codon? Anticodon? 31. 3 ...
DNA Replication, Transcription, and Translation
... single strand of RNA is formed. This RNA is called messenger RNA (mRNA) because it carries DNA’s message for protein synthesis. RNA will not normally contain thymine bases. Instead, every adenine on the DNA will be paired with a uracil base (pyrimidine) on the RNA strand. So, RNA can contain A, U, C ...
... single strand of RNA is formed. This RNA is called messenger RNA (mRNA) because it carries DNA’s message for protein synthesis. RNA will not normally contain thymine bases. Instead, every adenine on the DNA will be paired with a uracil base (pyrimidine) on the RNA strand. So, RNA can contain A, U, C ...
Biology 3201 - novacentral.ca
... 4. Gel Electrophoresis (see fig 18.11, p. 617) → gel electrophoresis: method in which molecules travel through a gel subjected to an electric current. It is used to replicate molecules according to mass and charge, and enable fragments of DNA to be separated for analysis → DNA fingerprint: pattern o ...
... 4. Gel Electrophoresis (see fig 18.11, p. 617) → gel electrophoresis: method in which molecules travel through a gel subjected to an electric current. It is used to replicate molecules according to mass and charge, and enable fragments of DNA to be separated for analysis → DNA fingerprint: pattern o ...
03 Biotechnology Note
... Recombinant DNA – a fragment of DNA composed of sequences originating from at least 2 different sources – scientists use this DNA to mess with (manipulate) genes and proteins ...
... Recombinant DNA – a fragment of DNA composed of sequences originating from at least 2 different sources – scientists use this DNA to mess with (manipulate) genes and proteins ...
File
... individual cells differentiate and become specialized in structure and function. Differentiation happens due to selective gene expression – some genes are turned off, some are ...
... individual cells differentiate and become specialized in structure and function. Differentiation happens due to selective gene expression – some genes are turned off, some are ...
Level 3 Biology (90715) 2011 Assessment Schedule
... mRNA is read via translation at the site of the ribosome (rRNA), where codon sequences are translated via tRNA into a chain of amino acids. tRNA attach to specific amino acids and contain an anti codon, complementary to the codons of the mRNA. AND The final protein / order in which the amino acids a ...
... mRNA is read via translation at the site of the ribosome (rRNA), where codon sequences are translated via tRNA into a chain of amino acids. tRNA attach to specific amino acids and contain an anti codon, complementary to the codons of the mRNA. AND The final protein / order in which the amino acids a ...
Insects and genetics
... 5. Tendency of varieties to depart from original type f. Walter Flemming 6. Mitosis 2. The process by which those individuals with heritable traits conferring survival produce more offspring than do individuals lacking such traits is called ___________ _____________. 3. Describe 2 entomological phen ...
... 5. Tendency of varieties to depart from original type f. Walter Flemming 6. Mitosis 2. The process by which those individuals with heritable traits conferring survival produce more offspring than do individuals lacking such traits is called ___________ _____________. 3. Describe 2 entomological phen ...
Assessment Schedule
... mRNA is read via translation at the site of the ribosome (rRNA), where codon sequences are translated via tRNA into a chain of amino acids. tRNA attach to specific amino acids and contain an anti codon, complementary to the codons of the mRNA. AND The final protein / order in which the amino acids a ...
... mRNA is read via translation at the site of the ribosome (rRNA), where codon sequences are translated via tRNA into a chain of amino acids. tRNA attach to specific amino acids and contain an anti codon, complementary to the codons of the mRNA. AND The final protein / order in which the amino acids a ...
Human Genetic Variation - Mediapolis Community School
... • Genes are pieces of DNA, and most genes contain information for making a specific protein. • Genes exist in 2 forms at each location on a chromosome. These are called alleles. • Alleles can be dominant or recessive. ...
... • Genes are pieces of DNA, and most genes contain information for making a specific protein. • Genes exist in 2 forms at each location on a chromosome. These are called alleles. • Alleles can be dominant or recessive. ...
Nucleotides Base Pair By Hydrogen bonds
... • G1 phase is a period of cellular growth preceding DNA synthesis. Cells that have stopped cycling, such as muscle and nerve cells, are said to be in a special state called Go. • S phase is the period of time during which DNA replication occurs. At the end of S phase, each chromosome has doubled its ...
... • G1 phase is a period of cellular growth preceding DNA synthesis. Cells that have stopped cycling, such as muscle and nerve cells, are said to be in a special state called Go. • S phase is the period of time during which DNA replication occurs. At the end of S phase, each chromosome has doubled its ...
1 BIOS 1300 SI SI WORKSHEET 8 (Chapter 3 Cont.) SI Leader
... - Alteration of mRNA ends: the 5’ end receives a _____________ and the 3’ end receives a ___________________ that have 3 important functions: 1. Facilitate export of mature mRNA from _____________________. 2. Protect mRNA from degradation by _____________________. 3. Help __________________ attach ...
... - Alteration of mRNA ends: the 5’ end receives a _____________ and the 3’ end receives a ___________________ that have 3 important functions: 1. Facilitate export of mature mRNA from _____________________. 2. Protect mRNA from degradation by _____________________. 3. Help __________________ attach ...
Proteins
... individual cells differentiate and become specialized in structure and function. Differentiation happens due to selective gene expression – some genes are turned off, some are ...
... individual cells differentiate and become specialized in structure and function. Differentiation happens due to selective gene expression – some genes are turned off, some are ...
Molecular Basis for Relationship between Genotype and Phenotype
... part of TFIID complex, must bind to promoter before other GTFs and RNA polymerase II can form preinitiation complex (PIC). Phosphorylation of carboxyl tail domain (CTD), the protein tail of b subunit of RNA polymerase II, allows separation of RNA polymerase II from GTFs to start transcription. ...
... part of TFIID complex, must bind to promoter before other GTFs and RNA polymerase II can form preinitiation complex (PIC). Phosphorylation of carboxyl tail domain (CTD), the protein tail of b subunit of RNA polymerase II, allows separation of RNA polymerase II from GTFs to start transcription. ...
Instructor`s Answer Key
... 5. Fats and oils are two types of triglycerides. Fats tend to be solid at normal temperatures and are composed primarily of triglycerides that are mostly saturated with hydrogen ions (no double bonds). Oils tend to be liquid in form and are composed primarily of triglycerides unsaturated with hydrog ...
... 5. Fats and oils are two types of triglycerides. Fats tend to be solid at normal temperatures and are composed primarily of triglycerides that are mostly saturated with hydrogen ions (no double bonds). Oils tend to be liquid in form and are composed primarily of triglycerides unsaturated with hydrog ...
Deoxyribozyme
_DNAzyme.png?width=300)
Deoxyribozymes, also called DNA enzymes, DNAzymes, or catalytic DNA, are DNA oligonucleotides that are capable of catalyzing specific chemical reactions, similar to the action of other biological enzymes, such as proteins or ribozymes (enzymes composed of RNA).However, in contrast to the abundance of protein enzymes in biological systems and the discovery of biological ribozymes in the 1980s,there are no known naturally occurring deoxyribozymes.Deoxyribozymes should not be confused with DNA aptamers which are oligonucleotides that selectively bind a target ligand, but do not catalyze a subsequent chemical reaction.With the exception of ribozymes, nucleic acid molecules within cells primarily serve as storage of genetic information due to its ability to form complementary base pairs, which allows for high-fidelity copying and transfer of genetic information. In contrast, nucleic acid molecules are more limited in their catalytic ability, in comparison to protein enzymes, to just three types of interactions: hydrogen bonding, pi stacking, and metal-ion coordination. This is due to the limited number of functional groups of the nucleic acid monomers: while proteins are built from up to twenty different amino acids with various functional groups, nucleic acids are built from just four chemically similar nucleobases. In addition, DNA lacks the 2'-hydroxyl group found in RNA which limits the catalytic competency of deoxyribozymes even in comparison to ribozymes.In addition to the inherent inferiority of DNA catalytic activity, the apparent lack of naturally occurring deoxyribozymes may also be due to the primarily double-stranded conformation of DNA in biological systems which would limit its physical flexibility and ability to form tertiary structures, and so would drastically limit the ability of double-stranded DNA to act as a catalyst; though there are a few known instances of biological single-stranded DNA such as multicopy single-stranded DNA (msDNA), certain viral genomes, and the replication fork formed during DNA replication. Further structural differences between DNA and RNA may also play a role in the lack of biological deoxyribozymes, such as the additional methyl group of the DNA base thymidine compared to the RNA base uracil or the tendency of DNA to adopt the B-form helix while RNA tends to adopt the A-form helix. However, it has also been shown that DNA can form structures that RNA cannot, which suggests that, though there are differences in structures that each can form, neither is inherently more or less catalytic due to their possible structural motifs.