Model question Paper- Gene Technology MLAB 475
... Question 6: In 1962 Watson, Crick and Wilkins won the Nobel Prize for their discovery of the structure of DNA. The figure below shows a picture that was shown to Watson by Wilkins in early 1953. Answer the following with respect to ...
... Question 6: In 1962 Watson, Crick and Wilkins won the Nobel Prize for their discovery of the structure of DNA. The figure below shows a picture that was shown to Watson by Wilkins in early 1953. Answer the following with respect to ...
3 - socesbio.c…
... 4. Cut out Introns: Part of the mRNA does not leave the Nucleus. These parts are called INTRONS. There are 5 introns in the mRNA strand. They follow one of two patterns: UAUGCGCGG or UAUGCGGCCCUA. . You must find all FIVE and put a single line through them (see left), because they are not used in ma ...
... 4. Cut out Introns: Part of the mRNA does not leave the Nucleus. These parts are called INTRONS. There are 5 introns in the mRNA strand. They follow one of two patterns: UAUGCGCGG or UAUGCGGCCCUA. . You must find all FIVE and put a single line through them (see left), because they are not used in ma ...
1 - socesbio.c…
... 4. Cut out Introns: Part of the mRNA does not leave the Nucleus. These parts are called INTRONS. There are 5 introns in the mRNA strand. They follow one of two patterns: UAUGCGCGG or UAUGCGGCCCUA. . You must find all FIVE and put a single line through them (see left), because they are not used in ma ...
... 4. Cut out Introns: Part of the mRNA does not leave the Nucleus. These parts are called INTRONS. There are 5 introns in the mRNA strand. They follow one of two patterns: UAUGCGCGG or UAUGCGGCCCUA. . You must find all FIVE and put a single line through them (see left), because they are not used in ma ...
review sheet
... a. Label the diagram with the following terms: hydrogen bond, phosphodiester bond, deoxyribose, phosphate group. (Use each term only once) b. Label ALL the nitrogenous bases present with the appropriate letter (A,C,G,T). c. What part of the DNA molecule actually contains the hereditary information? ...
... a. Label the diagram with the following terms: hydrogen bond, phosphodiester bond, deoxyribose, phosphate group. (Use each term only once) b. Label ALL the nitrogenous bases present with the appropriate letter (A,C,G,T). c. What part of the DNA molecule actually contains the hereditary information? ...
biotech
... RFLPs - Restriction fragment length polymorphisms, generated from differences in VNTR’s & STR’s. Southern blotting: process that reveals sequences and the RFLPs in a DNA sequence. Animation ...
... RFLPs - Restriction fragment length polymorphisms, generated from differences in VNTR’s & STR’s. Southern blotting: process that reveals sequences and the RFLPs in a DNA sequence. Animation ...
THE CELLULAR AND MOLECULAR BASIS OF INHERITANCE
... 1. Sugar: is a five carbon pentose called 2`deoxyribose in which the –OH group on carbon 2 of ribose is replaced by hydrogen 2. Phosphate group there are one, two or three phosphate group attached to the 5` charbon of the sugar • Base a complex molecules containing carbon and nitrogen ring structure ...
... 1. Sugar: is a five carbon pentose called 2`deoxyribose in which the –OH group on carbon 2 of ribose is replaced by hydrogen 2. Phosphate group there are one, two or three phosphate group attached to the 5` charbon of the sugar • Base a complex molecules containing carbon and nitrogen ring structure ...
Infection cycle: DNA viruses
... • Bidirectional replication from single ori (similar to Bacteria) • Early to late strategies – T ags in SV40 enhance first and then suppresses early; – E ag in BPV is an enhancer for late genes – Mutations in T or Eag/transition lead to tumors ...
... • Bidirectional replication from single ori (similar to Bacteria) • Early to late strategies – T ags in SV40 enhance first and then suppresses early; – E ag in BPV is an enhancer for late genes – Mutations in T or Eag/transition lead to tumors ...
Introduction to DNA - University of Dayton
... • From your on-line computer activity, what do you know about the structure of DNA? ...
... • From your on-line computer activity, what do you know about the structure of DNA? ...
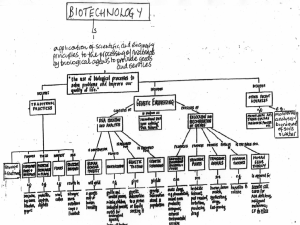
Biotech applic
... A variety of simple to complex products can be made by biological processes, ranging from alcohol, organic acids, to peptides, complex proteins, etc. Some of these compounds can not be made easily by chemical synthesis, for example, monoclonal antibodies E. Multi-step reactions are possible and are ...
... A variety of simple to complex products can be made by biological processes, ranging from alcohol, organic acids, to peptides, complex proteins, etc. Some of these compounds can not be made easily by chemical synthesis, for example, monoclonal antibodies E. Multi-step reactions are possible and are ...
2.5 Genetics - Elaine Galvin
... To establish presence or absence of gene(s) The process of producing mRNA using DNA as a template. The process of making a protein using the mRNA code a template ...
... To establish presence or absence of gene(s) The process of producing mRNA using DNA as a template. The process of making a protein using the mRNA code a template ...
DNA Transcription and Translation
... nucleus so that the cell can make a protein out of the information obtained from the DNA in the gene Every 3 nitrogen bases in the DNA that makes up a gene is called a codon, and codes for a specific amino acid DNA does not leave the nucleus so a carrier molecule called messanger RNA (mRNA) i ...
... nucleus so that the cell can make a protein out of the information obtained from the DNA in the gene Every 3 nitrogen bases in the DNA that makes up a gene is called a codon, and codes for a specific amino acid DNA does not leave the nucleus so a carrier molecule called messanger RNA (mRNA) i ...
042310_recombinant_DNA2
... copies could be generated) • A recognition sequence for a restriction enzyme (so that we can introduce our DNA of interest) • Reporter genes (to confirm we have successfully introduced the vector into the host cell) • Small size in comparison with host’s chromosomes (for easy manipulation) ...
... copies could be generated) • A recognition sequence for a restriction enzyme (so that we can introduce our DNA of interest) • Reporter genes (to confirm we have successfully introduced the vector into the host cell) • Small size in comparison with host’s chromosomes (for easy manipulation) ...
Genetically modified foods by Tim Harding B.Sc
... plant and animal breeding (long-term) mutagenesis (hit or miss) genetic engineering (short-term) ...
... plant and animal breeding (long-term) mutagenesis (hit or miss) genetic engineering (short-term) ...
16.6 * Locating and Sequencing Genes
... template, countless nucleotides, and a good supply of the specific terminator nucleotide. Due to this, you get a variety of ‘partially completed’ DNA strands, because they have been ‘terminated’ at different points. ...
... template, countless nucleotides, and a good supply of the specific terminator nucleotide. Due to this, you get a variety of ‘partially completed’ DNA strands, because they have been ‘terminated’ at different points. ...
Recitation 10 Solutions
... mRNA found in the nucleus and therefore contains only the expressed genes of an organism. In eukaryotic cells the mature mRNA is already spliced, hence the cDNA produced lacks introns and can be readily expressed in a bacterial cell. While information in cDNA libraries is a powerful and useful tool ...
... mRNA found in the nucleus and therefore contains only the expressed genes of an organism. In eukaryotic cells the mature mRNA is already spliced, hence the cDNA produced lacks introns and can be readily expressed in a bacterial cell. While information in cDNA libraries is a powerful and useful tool ...
Biology Chapters 8 and 9 Test Review
... o DNA cannot exit the nucleus but the RNA must exit its nucleolus o Initiation RNA Polymerase binds to the promoter region using transcription factors, proteins that tell it where to begin. DNA is unzipped and unraveled, breaking H bonds between the nitrogen bases. o Elongation From RNA nucleo ...
... o DNA cannot exit the nucleus but the RNA must exit its nucleolus o Initiation RNA Polymerase binds to the promoter region using transcription factors, proteins that tell it where to begin. DNA is unzipped and unraveled, breaking H bonds between the nitrogen bases. o Elongation From RNA nucleo ...
Gene Expression (Epigenetics)
... Morphogenesis 1. Cytoplasmic determinants are maternal substances in the egg that influence early development (uneven in early cells) 2. Cell-cell signals are molecules made by cells (external hormones) that influence other cells (induction) – Determination is the series of events that lead to cell ...
... Morphogenesis 1. Cytoplasmic determinants are maternal substances in the egg that influence early development (uneven in early cells) 2. Cell-cell signals are molecules made by cells (external hormones) that influence other cells (induction) – Determination is the series of events that lead to cell ...
md 2 bbq
... The mother tells you that the girl’s skin is becoming red and scaling with only minimal sun exposure. She began to nitice this pahenomenon when the child was 7 months old. Now the girl’s skin is thin and hyperpigmented. The patient has few nevi on her hands that have been rapidly enlarging. The defe ...
... The mother tells you that the girl’s skin is becoming red and scaling with only minimal sun exposure. She began to nitice this pahenomenon when the child was 7 months old. Now the girl’s skin is thin and hyperpigmented. The patient has few nevi on her hands that have been rapidly enlarging. The defe ...
Name
... 14. Segment of DNA recognized by restriction enzymes? 15. Fragments produced by restriction enzymes are called? 16. What is the purpose of PCR? ...
... 14. Segment of DNA recognized by restriction enzymes? 15. Fragments produced by restriction enzymes are called? 16. What is the purpose of PCR? ...
elife-14258-supp2
... were fragmented using Covaris g-TUBEs and further processed by end-repair and dA tailing using the NEBNext Ultra II End Repair/dA-tailing Module. The sequencing libraries were prepared according to version 6 of Oxford Nanopore Technologies Protocol (MAP006). DNA concentration was measured by Qubit F ...
... were fragmented using Covaris g-TUBEs and further processed by end-repair and dA tailing using the NEBNext Ultra II End Repair/dA-tailing Module. The sequencing libraries were prepared according to version 6 of Oxford Nanopore Technologies Protocol (MAP006). DNA concentration was measured by Qubit F ...
Isolation of DNA from 96 Well Plates
... 6. Add 100 μl/well NaCl/Ethanol (@ -20oC). The salt precipitates, so keep the mixture well mixed. Incubate at -20oC for at least 30 minutes until precipitated DNA is visible as long threads under tissue culture microscope. 7. Quickly invert plate over sink to dump out liquid then blot on paper towel ...
... 6. Add 100 μl/well NaCl/Ethanol (@ -20oC). The salt precipitates, so keep the mixture well mixed. Incubate at -20oC for at least 30 minutes until precipitated DNA is visible as long threads under tissue culture microscope. 7. Quickly invert plate over sink to dump out liquid then blot on paper towel ...
Supplementary Methods
... RT-PCR Extraction of total RNA, synthesis of cDNA, and PCR were carried out as described previously4. Total RNA was extracted from tissues and contaminating genomic DNA was removed by treating with 5 u of RNase-free DNase-I (Ambion)/10 µg of RNA. cDNA was synthesized using the first-strand Superscri ...
... RT-PCR Extraction of total RNA, synthesis of cDNA, and PCR were carried out as described previously4. Total RNA was extracted from tissues and contaminating genomic DNA was removed by treating with 5 u of RNase-free DNase-I (Ambion)/10 µg of RNA. cDNA was synthesized using the first-strand Superscri ...
Deoxyribozyme
_DNAzyme.png?width=300)
Deoxyribozymes, also called DNA enzymes, DNAzymes, or catalytic DNA, are DNA oligonucleotides that are capable of catalyzing specific chemical reactions, similar to the action of other biological enzymes, such as proteins or ribozymes (enzymes composed of RNA).However, in contrast to the abundance of protein enzymes in biological systems and the discovery of biological ribozymes in the 1980s,there are no known naturally occurring deoxyribozymes.Deoxyribozymes should not be confused with DNA aptamers which are oligonucleotides that selectively bind a target ligand, but do not catalyze a subsequent chemical reaction.With the exception of ribozymes, nucleic acid molecules within cells primarily serve as storage of genetic information due to its ability to form complementary base pairs, which allows for high-fidelity copying and transfer of genetic information. In contrast, nucleic acid molecules are more limited in their catalytic ability, in comparison to protein enzymes, to just three types of interactions: hydrogen bonding, pi stacking, and metal-ion coordination. This is due to the limited number of functional groups of the nucleic acid monomers: while proteins are built from up to twenty different amino acids with various functional groups, nucleic acids are built from just four chemically similar nucleobases. In addition, DNA lacks the 2'-hydroxyl group found in RNA which limits the catalytic competency of deoxyribozymes even in comparison to ribozymes.In addition to the inherent inferiority of DNA catalytic activity, the apparent lack of naturally occurring deoxyribozymes may also be due to the primarily double-stranded conformation of DNA in biological systems which would limit its physical flexibility and ability to form tertiary structures, and so would drastically limit the ability of double-stranded DNA to act as a catalyst; though there are a few known instances of biological single-stranded DNA such as multicopy single-stranded DNA (msDNA), certain viral genomes, and the replication fork formed during DNA replication. Further structural differences between DNA and RNA may also play a role in the lack of biological deoxyribozymes, such as the additional methyl group of the DNA base thymidine compared to the RNA base uracil or the tendency of DNA to adopt the B-form helix while RNA tends to adopt the A-form helix. However, it has also been shown that DNA can form structures that RNA cannot, which suggests that, though there are differences in structures that each can form, neither is inherently more or less catalytic due to their possible structural motifs.