pdf
... documented in areas where substantial DIN concentrations were measured, including coastal waters (Grosse et al., 2010; Mulholland et al., 2012), the Pacific Ocean (Moisander et al., 2010), and the eastern tropical Atlantic Ocean (Voss et al., 2004). In addition, models suggest that N2 fixation may o ...
... documented in areas where substantial DIN concentrations were measured, including coastal waters (Grosse et al., 2010; Mulholland et al., 2012), the Pacific Ocean (Moisander et al., 2010), and the eastern tropical Atlantic Ocean (Voss et al., 2004). In addition, models suggest that N2 fixation may o ...
Knackstedt, K.A., H.B. Thorpe, C.R. Santangelo, M.A. Balinski, and R
... reports. The availability of multiple inbred strains for class use will increase the likelihood that some students will select two strains with different mean values for the assayed trait. The lab can also be made incrementally more complex at the discretion of the instructor with respect to genetic ...
... reports. The availability of multiple inbred strains for class use will increase the likelihood that some students will select two strains with different mean values for the assayed trait. The lab can also be made incrementally more complex at the discretion of the instructor with respect to genetic ...
The Art of Multiple Sequence Alignment in R - decipher
... maximize scoring metrics in order to accomplish a combination of both structural alignment and evolutionary alignment. The idea is to give the alignment a biological basis even though the molecules that the sequences represent will never meet each other and align under any natural circumstance. The ...
... maximize scoring metrics in order to accomplish a combination of both structural alignment and evolutionary alignment. The idea is to give the alignment a biological basis even though the molecules that the sequences represent will never meet each other and align under any natural circumstance. The ...
Method of Analysis for Feed Enzymes: Methodological Problems?
... xylanase on arabinoxylan, an amylase on starch, a proteinase on protein) even in the presence of other reactants. Furthermore, the substrate needs to be of a defined quality. For example, similar results are obtained from xylanase with xylan substrates extracted from birchwood or from wheat (Table 1 ...
... xylanase on arabinoxylan, an amylase on starch, a proteinase on protein) even in the presence of other reactants. Furthermore, the substrate needs to be of a defined quality. For example, similar results are obtained from xylanase with xylan substrates extracted from birchwood or from wheat (Table 1 ...
N-Terminal Intramolecularly Conserved Histidines of Three Domains
... shown in Figure 2. Both the full-length protein and the one with the 90 N-terminal residues removed (D1,2,391-1241) exhibited a type A pH-activity profile (Figure 2A). Peptides encompassing complete individual domains (D192-486, D2489-862, and D3791-1241) also exhibited type A pH-activity profiles ( ...
... shown in Figure 2. Both the full-length protein and the one with the 90 N-terminal residues removed (D1,2,391-1241) exhibited a type A pH-activity profile (Figure 2A). Peptides encompassing complete individual domains (D192-486, D2489-862, and D3791-1241) also exhibited type A pH-activity profiles ( ...
biology - Kendriya Vidyalaya No.1 Kanchrapara
... 2. Name the group of organisms and the substrate they act on, to produce biogas. 3. Which of the following is a free living bacteria that can fix nitrogen in the soil: (Spirulina, Azospirillium, Sonalika) 4. Which one of the following in the Baker’s yeast used in fermentation? (Saccharum barberi, Sa ...
... 2. Name the group of organisms and the substrate they act on, to produce biogas. 3. Which of the following is a free living bacteria that can fix nitrogen in the soil: (Spirulina, Azospirillium, Sonalika) 4. Which one of the following in the Baker’s yeast used in fermentation? (Saccharum barberi, Sa ...
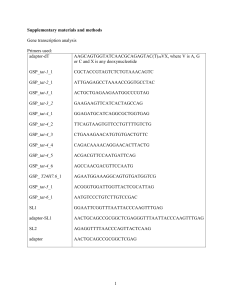
Supplementary Table 1: WormBase IDs and given
... tat-1: amplified near full-length using GSP_tat-1_1 and SL1 (SL2 did not produce a product), sequenced 4 clones fully, 4 partially; 3 ESTs sequenced (yk1228h06, yk34c11, yk1496c06); a singe poly(A) signal inferred from the ESTs; tat-2: amplified near full-length using GSP_tat-2_1 and SL1 (SL2 did no ...
... tat-1: amplified near full-length using GSP_tat-1_1 and SL1 (SL2 did not produce a product), sequenced 4 clones fully, 4 partially; 3 ESTs sequenced (yk1228h06, yk34c11, yk1496c06); a singe poly(A) signal inferred from the ESTs; tat-2: amplified near full-length using GSP_tat-2_1 and SL1 (SL2 did no ...
The coiled-coil of the human Rad50 DNA repair protein contains
... For polymers like DNA, this method yields an average persistence length that is in good agreement with values obtained by other techniques (8). This method has been modified to describe known segments of different persistence length (9). Another method for the determination of overall flexibility of ...
... For polymers like DNA, this method yields an average persistence length that is in good agreement with values obtained by other techniques (8). This method has been modified to describe known segments of different persistence length (9). Another method for the determination of overall flexibility of ...
(Enzymes Lecture Notes).
... the formation of products. The products are released from the enzyme surface to regenerate the enzyme for another reaction cycle. The active site has a unique geometric shape that is complementary to the geometric shape of a substrate molecule, similar to the fit of puzzle pieces. This means that en ...
... the formation of products. The products are released from the enzyme surface to regenerate the enzyme for another reaction cycle. The active site has a unique geometric shape that is complementary to the geometric shape of a substrate molecule, similar to the fit of puzzle pieces. This means that en ...
Chapter 1: An Introduction to Chemistry
... of the genetic information that transmits the characteristic of red hair from parent to child? ...
... of the genetic information that transmits the characteristic of red hair from parent to child? ...
Artemis Reference
... them names by going to EDIT and AUTOMATICALLY CREATE GENE NAMES. Then go to the write menu and you can create a file of the protein sequences, nucleotide sequences, or the upstream and downstream sequences. Try this and look at the files you create. ...
... them names by going to EDIT and AUTOMATICALLY CREATE GENE NAMES. Then go to the write menu and you can create a file of the protein sequences, nucleotide sequences, or the upstream and downstream sequences. Try this and look at the files you create. ...
Kinetics of Enzyme-Catalyzed Reactions
... effects by means of enzyme inhibition. Enzyme inhibitors fall into two broad classes: 1. Those causing irreversible inactivation of enzymes: Inhibitors of the first class usually cause an inactivating, covalent modification of enzyme structure . Cyanide is a classic example of an irreversible enzyme ...
... effects by means of enzyme inhibition. Enzyme inhibitors fall into two broad classes: 1. Those causing irreversible inactivation of enzymes: Inhibitors of the first class usually cause an inactivating, covalent modification of enzyme structure . Cyanide is a classic example of an irreversible enzyme ...
Translation Section 1 From Genes to Proteins Chapter 10
... Decoding the Information in DNA, continued • RNA differs from DNA in three ways: 1. RNA consists of a single strand of nucleotides instead of the two strands found in DNA. 2. RNA nucleotides contain the five-carbon sugar ribose rather than the sugar deoxyribose, which is found in DNA nucleotides. 3. ...
... Decoding the Information in DNA, continued • RNA differs from DNA in three ways: 1. RNA consists of a single strand of nucleotides instead of the two strands found in DNA. 2. RNA nucleotides contain the five-carbon sugar ribose rather than the sugar deoxyribose, which is found in DNA nucleotides. 3. ...
DNA Evolution 3.1 Troubleshooting and Debugging Guide
... DNA Evolution binaries and logging basics .................................................................... 5 Enable logging ................................................................................................................................. 5 Turning on logging ..................... ...
... DNA Evolution binaries and logging basics .................................................................... 5 Enable logging ................................................................................................................................. 5 Turning on logging ..................... ...
Proteinases as catalysts in peptide synthesis
... Several longer peptides have been successfully obtained using pepsin as a catalyst. It was observed, however, that these syntheses might be complicated by the enzyme entrapment into the gel of the peptide formed in the course of the synthesis. Further collapse of the gel leads to the enzyme inclusio ...
... Several longer peptides have been successfully obtained using pepsin as a catalyst. It was observed, however, that these syntheses might be complicated by the enzyme entrapment into the gel of the peptide formed in the course of the synthesis. Further collapse of the gel leads to the enzyme inclusio ...
Sequence analysis of 16S rRNA, gyrB and catA genes and DNA
... approximately 1200 bp PCR product besides the approximately 1500 bp specific product, making direct sequencing impossible. Sequence analyses gave interesting results. The reported 0.2 % difference between 16S rRNA gene sequences of type strains of R. qingshengii and R. jialingiae was not found, beca ...
... approximately 1200 bp PCR product besides the approximately 1500 bp specific product, making direct sequencing impossible. Sequence analyses gave interesting results. The reported 0.2 % difference between 16S rRNA gene sequences of type strains of R. qingshengii and R. jialingiae was not found, beca ...
Moving one DNA double helix through another by a type II DNA
... multiple loops, the problem of separating its strands is not all that different from that for a covalently closed DNA ring. Therefore, it would appear that during evolution, as DNA became very long or circular, a solution must be found for the disentanglement of its topologically intertwined strands ...
... multiple loops, the problem of separating its strands is not all that different from that for a covalently closed DNA ring. Therefore, it would appear that during evolution, as DNA became very long or circular, a solution must be found for the disentanglement of its topologically intertwined strands ...
Multiregional origin of B chromosomes in the grasshopper
... genome, albeit intra- or interspecifically. Although the intraspecific hypothesis likely applies to many, perhaps most, B chromosomes, there is sound evidence that some of them have arisen through interspecific hybridization (see McAllister and Werren 1997; Perfectti and Werren 2001). In every case, ...
... genome, albeit intra- or interspecifically. Although the intraspecific hypothesis likely applies to many, perhaps most, B chromosomes, there is sound evidence that some of them have arisen through interspecific hybridization (see McAllister and Werren 1997; Perfectti and Werren 2001). In every case, ...
Non-random Allelic Variation
... – a derived character that evolved in response to a specific selective agent (although traits evolve from pre-existing ones and selective agents change in time) or – a feature that is maintained because of natural selection for its function preadaptation – a trait that fortuitously serves a new func ...
... – a derived character that evolved in response to a specific selective agent (although traits evolve from pre-existing ones and selective agents change in time) or – a feature that is maintained because of natural selection for its function preadaptation – a trait that fortuitously serves a new func ...
An Efficient Oxidation of Benzoins to Benzils by Manganese (II
... or complexity of workup. ere still appears a need either to improve the existing oxidation methods or to introduce novel reagents to permit better selectivity under milder conditions and with easy work-up procedures [12]. Transition metal catalysts supported by Schiff base ligands have assumed a pro ...
... or complexity of workup. ere still appears a need either to improve the existing oxidation methods or to introduce novel reagents to permit better selectivity under milder conditions and with easy work-up procedures [12]. Transition metal catalysts supported by Schiff base ligands have assumed a pro ...
Geneticseasy
... 1. Which members of the family above are afflicted with Huntington’s Disease? _________________________________ 2. There are no carriers for Huntington’s Disease- you either have it or you don’t. With this in mind, is Huntington’s disease caused by a dominant or recessive trait? ____________________ ...
... 1. Which members of the family above are afflicted with Huntington’s Disease? _________________________________ 2. There are no carriers for Huntington’s Disease- you either have it or you don’t. With this in mind, is Huntington’s disease caused by a dominant or recessive trait? ____________________ ...
Molecular Biology - Intro
... high degree of purity – characterized transforming factor using highly purified enzymes – found transforming factor to be DNA ...
... high degree of purity – characterized transforming factor using highly purified enzymes – found transforming factor to be DNA ...
Chapt. 14 Eukaryotic mRNA processing I: splicing 14.1 Genes are in
... • U2 snRNA base-pairs with conserved sequence at splicing branchpoint • Essential for splicing • U2 also forms base pairs with U6 – Helps orient snRNPs for splicing • 5’-end of U2 interacts with 3’-end of U6 – important in splicing in mammalian cells, not ...
... • U2 snRNA base-pairs with conserved sequence at splicing branchpoint • Essential for splicing • U2 also forms base pairs with U6 – Helps orient snRNPs for splicing • 5’-end of U2 interacts with 3’-end of U6 – important in splicing in mammalian cells, not ...
Deoxyribozyme
_DNAzyme.png?width=300)
Deoxyribozymes, also called DNA enzymes, DNAzymes, or catalytic DNA, are DNA oligonucleotides that are capable of catalyzing specific chemical reactions, similar to the action of other biological enzymes, such as proteins or ribozymes (enzymes composed of RNA).However, in contrast to the abundance of protein enzymes in biological systems and the discovery of biological ribozymes in the 1980s,there are no known naturally occurring deoxyribozymes.Deoxyribozymes should not be confused with DNA aptamers which are oligonucleotides that selectively bind a target ligand, but do not catalyze a subsequent chemical reaction.With the exception of ribozymes, nucleic acid molecules within cells primarily serve as storage of genetic information due to its ability to form complementary base pairs, which allows for high-fidelity copying and transfer of genetic information. In contrast, nucleic acid molecules are more limited in their catalytic ability, in comparison to protein enzymes, to just three types of interactions: hydrogen bonding, pi stacking, and metal-ion coordination. This is due to the limited number of functional groups of the nucleic acid monomers: while proteins are built from up to twenty different amino acids with various functional groups, nucleic acids are built from just four chemically similar nucleobases. In addition, DNA lacks the 2'-hydroxyl group found in RNA which limits the catalytic competency of deoxyribozymes even in comparison to ribozymes.In addition to the inherent inferiority of DNA catalytic activity, the apparent lack of naturally occurring deoxyribozymes may also be due to the primarily double-stranded conformation of DNA in biological systems which would limit its physical flexibility and ability to form tertiary structures, and so would drastically limit the ability of double-stranded DNA to act as a catalyst; though there are a few known instances of biological single-stranded DNA such as multicopy single-stranded DNA (msDNA), certain viral genomes, and the replication fork formed during DNA replication. Further structural differences between DNA and RNA may also play a role in the lack of biological deoxyribozymes, such as the additional methyl group of the DNA base thymidine compared to the RNA base uracil or the tendency of DNA to adopt the B-form helix while RNA tends to adopt the A-form helix. However, it has also been shown that DNA can form structures that RNA cannot, which suggests that, though there are differences in structures that each can form, neither is inherently more or less catalytic due to their possible structural motifs.