Geneticseasy
... 1. Which members of the family above are afflicted with Huntington’s Disease? _________________________________ 2. There are no carriers for Huntington’s Disease- you either have it or you don’t. With this in mind, is Huntington’s disease caused by a dominant or recessive trait? ____________________ ...
... 1. Which members of the family above are afflicted with Huntington’s Disease? _________________________________ 2. There are no carriers for Huntington’s Disease- you either have it or you don’t. With this in mind, is Huntington’s disease caused by a dominant or recessive trait? ____________________ ...
AP CHEMISTRY – Source: 1999 AP Exam, Also Data Base of MC
... 26. According to the rate law for the reaction, an increase in the concentration of hydronium ion has what effect on this reaction? (A) The rate of reaction increases. (B) The rate of reaction decreases. (C) The value of the equilibrium constant increases. (D) The value of the equilibrium constant ...
... 26. According to the rate law for the reaction, an increase in the concentration of hydronium ion has what effect on this reaction? (A) The rate of reaction increases. (B) The rate of reaction decreases. (C) The value of the equilibrium constant increases. (D) The value of the equilibrium constant ...
A Tn 10-lacZ-kanR-URA3 Gene Fusion Transposon for Insertion Mutagenesis and Fusion Analysis of Yeast and Bacterial Genes.
... plasmids were introduced into E. coli strain NK5830 (recA56 suo lacproXII1, Arg-, Ara-, NalR,RifR/F’ laciq L8 pro) (FOSTER et al. 1981) carrying a pACYCl84 derivative, pNK629, that produces a high, IPTG-inducible level of TnlO transposase function (WAYet al. 1984). pNK629 carries a selectable TetR m ...
... plasmids were introduced into E. coli strain NK5830 (recA56 suo lacproXII1, Arg-, Ara-, NalR,RifR/F’ laciq L8 pro) (FOSTER et al. 1981) carrying a pACYCl84 derivative, pNK629, that produces a high, IPTG-inducible level of TnlO transposase function (WAYet al. 1984). pNK629 carries a selectable TetR m ...
Biomarkery a mechanismy toxicity
... - Competitive vs. non-competitive: active site vs. side domains - Specific affinity – inhibition (effective) concentration - What enzymes are known to be selectively affected ? ...
... - Competitive vs. non-competitive: active site vs. side domains - Specific affinity – inhibition (effective) concentration - What enzymes are known to be selectively affected ? ...
Mapping Enzyme Active Sites in Complex Proteomes
... probes have been developed that target, for example, serine hydrolases5,7 and cysteine proteases.8 In each of these cases, the designed probes have been shown to label their target enzymes in an activity-based manner, distinguishing, for example, active enzymes from their inactive zymogens and/or in ...
... probes have been developed that target, for example, serine hydrolases5,7 and cysteine proteases.8 In each of these cases, the designed probes have been shown to label their target enzymes in an activity-based manner, distinguishing, for example, active enzymes from their inactive zymogens and/or in ...
This article was published in an Elsevier journal. The attached copy
... 2000). A defective lambda prophage supplies the function that protects and recombines linear DNA. This system is highly efficient and allows recombination between homologies as short as 40 bp. The first step in making each VZV ORF deletion was to amplify the KanR cassette containing 40-bp flanking s ...
... 2000). A defective lambda prophage supplies the function that protects and recombines linear DNA. This system is highly efficient and allows recombination between homologies as short as 40 bp. The first step in making each VZV ORF deletion was to amplify the KanR cassette containing 40-bp flanking s ...
Document
... along to future generations, and express that information as it carries out all the processes of life. The major steps involved in handling genetic information are illustrated by the central dogma of molecular biology (Figure I-1-1). Genetic information is stored in the base sequence of DNA molecule ...
... along to future generations, and express that information as it carries out all the processes of life. The major steps involved in handling genetic information are illustrated by the central dogma of molecular biology (Figure I-1-1). Genetic information is stored in the base sequence of DNA molecule ...
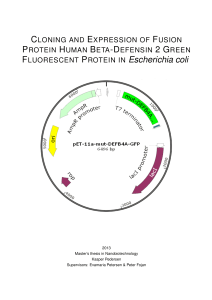
FLUORESCENT PROTEIN IN Escherichia coli
... AMPs are an essential part of the innate immune system, hence their description as host defence peptides. The innate immune system evolved 2.6 billion years ago, and is present in all living organisms [Gordon et al., 2005]. It is the front-line defense against infections, and it is very rapid compar ...
... AMPs are an essential part of the innate immune system, hence their description as host defence peptides. The innate immune system evolved 2.6 billion years ago, and is present in all living organisms [Gordon et al., 2005]. It is the front-line defense against infections, and it is very rapid compar ...
Chance and Natural Selection
... conceptsof chance variation.)But perhapsthe most importantthing to consideris whatis distinguishablyDarwinianaboutthe notionof chance variation.And thatis, I think,best broughtout simply in contrastto the use and disuse theoriesof evolution,from which Darwinwantedto distancehimself. 3. Chance in Mod ...
... conceptsof chance variation.)But perhapsthe most importantthing to consideris whatis distinguishablyDarwinianaboutthe notionof chance variation.And thatis, I think,best broughtout simply in contrastto the use and disuse theoriesof evolution,from which Darwinwantedto distancehimself. 3. Chance in Mod ...
Cloning in bacteria other than Escherichia coli
... with specialist properties, e.g. regulatable high-level gene expression. However, use of E. coli is not always practicable because it lacks some auxiliary biochemical pathways that are essential for the phenotypic expression of certain functions, e.g. degradation of aromatic compounds, antibiotic sy ...
... with specialist properties, e.g. regulatable high-level gene expression. However, use of E. coli is not always practicable because it lacks some auxiliary biochemical pathways that are essential for the phenotypic expression of certain functions, e.g. degradation of aromatic compounds, antibiotic sy ...
Lampbrush Chromosomes of the Chicken
... of meiotic prophase and are characterized by extensive transcription on the loops. An excellent review of LBC investigations and techniques has just been published by Callan (1986). This reference should be consulted for a more detailed discussion. Despite a century of study, we still know relativel ...
... of meiotic prophase and are characterized by extensive transcription on the loops. An excellent review of LBC investigations and techniques has just been published by Callan (1986). This reference should be consulted for a more detailed discussion. Despite a century of study, we still know relativel ...
genes. Numbers of 6-10 copies per genome have
... genes. Numbers of 6-10 copies per genome have been reported11,13,14. Conversely, the LSU gene encoded by the chloroplast genome is present at several thousand copies per cell15. For this reason, the sequences of SSU genes that allow for light regulation and the coordinate regulation with LSU gene ex ...
... genes. Numbers of 6-10 copies per genome have been reported11,13,14. Conversely, the LSU gene encoded by the chloroplast genome is present at several thousand copies per cell15. For this reason, the sequences of SSU genes that allow for light regulation and the coordinate regulation with LSU gene ex ...
Introduction to Organic Chemistry
... • A fat is constructed from two kinds of smaller molecules, glycerol and fatty acids. • The major function of fats is energy storage. – A gram of fat stores more than twice as much energy as a gram of a polysaccharide. Copyright © 2002 Pearson Education, Inc., publishing as Benjamin Cummings ...
... • A fat is constructed from two kinds of smaller molecules, glycerol and fatty acids. • The major function of fats is energy storage. – A gram of fat stores more than twice as much energy as a gram of a polysaccharide. Copyright © 2002 Pearson Education, Inc., publishing as Benjamin Cummings ...
PDF File
... The role of the cleavage site 2′-hydroxyl in the Tetrahymena group I ribozyme reaction Aiichiro Yoshida1*, Shu-ou Shan2*, Daniel Herschlag2 and Joseph A Piccirilli1 Background: The 2′-hydroxyl of U preceding the cleavage site, U(–1), in the Tetrahymena ribozyme reaction contributes 103-fold to catal ...
... The role of the cleavage site 2′-hydroxyl in the Tetrahymena group I ribozyme reaction Aiichiro Yoshida1*, Shu-ou Shan2*, Daniel Herschlag2 and Joseph A Piccirilli1 Background: The 2′-hydroxyl of U preceding the cleavage site, U(–1), in the Tetrahymena ribozyme reaction contributes 103-fold to catal ...
USMLE Step 1 - Becker Professional Education
... of State Medical Boards (FSMB) and National Board of Medical Examiners® (NBME®). United States Medical Licensing Examination, USMLE, National Board of Medical Examiners, and NBME are registered trademarks of the National Board of Medical Examiners. The National Board of Medical Examiners does not sp ...
... of State Medical Boards (FSMB) and National Board of Medical Examiners® (NBME®). United States Medical Licensing Examination, USMLE, National Board of Medical Examiners, and NBME are registered trademarks of the National Board of Medical Examiners. The National Board of Medical Examiners does not sp ...
Precise insertion and guided editing of higher plant
... hygromycin resistance gene under the control of the maize ubiquitin promoter flanked by 1kb regions of rice genomic DNA known as homology arms (Table S1-2). The Cpf1 genes were codon optimized for monocot plants, including an N-terminal nuclear localization tag, and were expressed by the 2x35S CaMV ...
... hygromycin resistance gene under the control of the maize ubiquitin promoter flanked by 1kb regions of rice genomic DNA known as homology arms (Table S1-2). The Cpf1 genes were codon optimized for monocot plants, including an N-terminal nuclear localization tag, and were expressed by the 2x35S CaMV ...
Organic Chemistry - mscurransclasses
... • A fat is constructed from two kinds of smaller molecules, glycerol and fatty acids. • The major function of fats is energy storage. – A gram of fat stores more than twice as much energy as a gram of a polysaccharide. Copyright © 2002 Pearson Education, Inc., publishing as Benjamin Cummings ...
... • A fat is constructed from two kinds of smaller molecules, glycerol and fatty acids. • The major function of fats is energy storage. – A gram of fat stores more than twice as much energy as a gram of a polysaccharide. Copyright © 2002 Pearson Education, Inc., publishing as Benjamin Cummings ...
Chapter Outline
... • Proteins that exhibit electrophoretic variation are polymorphic if at least two of the variants have polymorphic if at least two of the variants have frequencies greater than 1% in the population. • Proteins that do not exhibit electrophoretic variation are monomorphic. • The proportion of gene ...
... • Proteins that exhibit electrophoretic variation are polymorphic if at least two of the variants have polymorphic if at least two of the variants have frequencies greater than 1% in the population. • Proteins that do not exhibit electrophoretic variation are monomorphic. • The proportion of gene ...
introduction - Journal | Unair
... of this experiment showed that in samples from nonspecific urethritis patients there was a specific band of Chlamydia trachomatis in agarose with Silver Nitrate staining. The sensitivity of PCR method using Amplicor (Roche) was obtained because a little target DNA could be amplified significantly. A ...
... of this experiment showed that in samples from nonspecific urethritis patients there was a specific band of Chlamydia trachomatis in agarose with Silver Nitrate staining. The sensitivity of PCR method using Amplicor (Roche) was obtained because a little target DNA could be amplified significantly. A ...
Lesson Overview - Dr. Thornton`s Courses
... To find the GFP gene, Prasher compared part of the amino acid sequence of the GFP protein to a genetic code table and was able to predict a probable mRNA base sequence that would code for this sequence of amino acids. Next, Prasher used a complementary base sequence to “attract” an mRNA that matched ...
... To find the GFP gene, Prasher compared part of the amino acid sequence of the GFP protein to a genetic code table and was able to predict a probable mRNA base sequence that would code for this sequence of amino acids. Next, Prasher used a complementary base sequence to “attract” an mRNA that matched ...
Ribosomes: Cashing in on crystals
... density map and a complete atomic model may be available in the near future. A similar level of atomic detail is seen in the 5.5 Å resolution map of the 30S ribosomal subunit from the bacterium Thermus thermophilus. Clemons et al. [3] produced a map of the small subunit with the characteristic shape ...
... density map and a complete atomic model may be available in the near future. A similar level of atomic detail is seen in the 5.5 Å resolution map of the 30S ribosomal subunit from the bacterium Thermus thermophilus. Clemons et al. [3] produced a map of the small subunit with the characteristic shape ...
Major Contributing Factor in Increased Antibiotic Resistance
... stationary phase that survived treatment with erthyomycin was lower than that of those treated with nafcillin indicating that erythromycin was more effective against slowgrowing bacteria, Nafcillin, on the other hand, was much more effective against rapidly growing bacteria as indicated by the small ...
... stationary phase that survived treatment with erthyomycin was lower than that of those treated with nafcillin indicating that erythromycin was more effective against slowgrowing bacteria, Nafcillin, on the other hand, was much more effective against rapidly growing bacteria as indicated by the small ...
Deoxyribozyme
_DNAzyme.png?width=300)
Deoxyribozymes, also called DNA enzymes, DNAzymes, or catalytic DNA, are DNA oligonucleotides that are capable of catalyzing specific chemical reactions, similar to the action of other biological enzymes, such as proteins or ribozymes (enzymes composed of RNA).However, in contrast to the abundance of protein enzymes in biological systems and the discovery of biological ribozymes in the 1980s,there are no known naturally occurring deoxyribozymes.Deoxyribozymes should not be confused with DNA aptamers which are oligonucleotides that selectively bind a target ligand, but do not catalyze a subsequent chemical reaction.With the exception of ribozymes, nucleic acid molecules within cells primarily serve as storage of genetic information due to its ability to form complementary base pairs, which allows for high-fidelity copying and transfer of genetic information. In contrast, nucleic acid molecules are more limited in their catalytic ability, in comparison to protein enzymes, to just three types of interactions: hydrogen bonding, pi stacking, and metal-ion coordination. This is due to the limited number of functional groups of the nucleic acid monomers: while proteins are built from up to twenty different amino acids with various functional groups, nucleic acids are built from just four chemically similar nucleobases. In addition, DNA lacks the 2'-hydroxyl group found in RNA which limits the catalytic competency of deoxyribozymes even in comparison to ribozymes.In addition to the inherent inferiority of DNA catalytic activity, the apparent lack of naturally occurring deoxyribozymes may also be due to the primarily double-stranded conformation of DNA in biological systems which would limit its physical flexibility and ability to form tertiary structures, and so would drastically limit the ability of double-stranded DNA to act as a catalyst; though there are a few known instances of biological single-stranded DNA such as multicopy single-stranded DNA (msDNA), certain viral genomes, and the replication fork formed during DNA replication. Further structural differences between DNA and RNA may also play a role in the lack of biological deoxyribozymes, such as the additional methyl group of the DNA base thymidine compared to the RNA base uracil or the tendency of DNA to adopt the B-form helix while RNA tends to adopt the A-form helix. However, it has also been shown that DNA can form structures that RNA cannot, which suggests that, though there are differences in structures that each can form, neither is inherently more or less catalytic due to their possible structural motifs.