Quiz 15
... A) hydrophobic interactions B) nonpolar covalent bonds C) ionic bonds D) hydrogen bonds E) peptide bonds 8. A hydrophilic R-group of an amino acid in hemoglobin would NOT be attracted to: A) the water molecules surrounding hemoglobin. B) a hydrophobic amino acid R group of hemoglobin. C) a charged a ...
... A) hydrophobic interactions B) nonpolar covalent bonds C) ionic bonds D) hydrogen bonds E) peptide bonds 8. A hydrophilic R-group of an amino acid in hemoglobin would NOT be attracted to: A) the water molecules surrounding hemoglobin. B) a hydrophobic amino acid R group of hemoglobin. C) a charged a ...
Molecules of Life
... • The final twists and folds that lead to this shape are the result of polarity differences in regions of the polypeptide ...
... • The final twists and folds that lead to this shape are the result of polarity differences in regions of the polypeptide ...
AS-biology answers
... The amino acids are joined together in a long (polypeptide) chain (1). The sequence of amino acids is the proteins primary structure (1). The amino acid chain / polypeptide coils in a certain way (1). The way its coiled is the proteins secondary structure (1). The coiled chain is itself folded into ...
... The amino acids are joined together in a long (polypeptide) chain (1). The sequence of amino acids is the proteins primary structure (1). The amino acid chain / polypeptide coils in a certain way (1). The way its coiled is the proteins secondary structure (1). The coiled chain is itself folded into ...
Powerpoint
... contains the information to code for one complete protein PROTEINS are made up of a chain of amino acids Proteins determine many of the traits in an organism ...
... contains the information to code for one complete protein PROTEINS are made up of a chain of amino acids Proteins determine many of the traits in an organism ...
Transcription and Translation Work Sheet:
... Abbreviations for the 20 different amino acids: Phenylalanine-Phe, Leucine-Leu, Isoleucine-Ile, Methionine-Met, Valine-Val, Serine-Ser, Proline-Pro, Threonine-Thr, Alanine-Ala, Tyrosine-Tyr, Histidine-His, Glutamine-Gin, Asparagine-Asn, Lysine-Lys, Aspartate-Asp, Glutamate-Glu, Cysteine-Cys, Tryptop ...
... Abbreviations for the 20 different amino acids: Phenylalanine-Phe, Leucine-Leu, Isoleucine-Ile, Methionine-Met, Valine-Val, Serine-Ser, Proline-Pro, Threonine-Thr, Alanine-Ala, Tyrosine-Tyr, Histidine-His, Glutamine-Gin, Asparagine-Asn, Lysine-Lys, Aspartate-Asp, Glutamate-Glu, Cysteine-Cys, Tryptop ...
Lecture 5
... How much is there? Remember, most of the methods we’ve talked about for observing proteins are not quantitative. So no matter what happens, we are likely only going to be able to get a relative ...
... How much is there? Remember, most of the methods we’ve talked about for observing proteins are not quantitative. So no matter what happens, we are likely only going to be able to get a relative ...
Biochemistry
... (membranes) water resistant Found in cell membranes •Steroids and Hormones – produce body changes such as puberty Found in cholesterol, testosterone, estrogen ...
... (membranes) water resistant Found in cell membranes •Steroids and Hormones – produce body changes such as puberty Found in cholesterol, testosterone, estrogen ...
ReviewExamIII
... Why do glycolysis and the Krebs Cycle stop running when oxygen is lacking? How does fermentation allow glycolysis to start up again even in the absence of oxygen? Where in aerobic cellular respiration is the most carbon dioxide released (What set of reactions and where in the cell? What are the prod ...
... Why do glycolysis and the Krebs Cycle stop running when oxygen is lacking? How does fermentation allow glycolysis to start up again even in the absence of oxygen? Where in aerobic cellular respiration is the most carbon dioxide released (What set of reactions and where in the cell? What are the prod ...
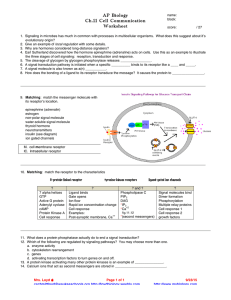
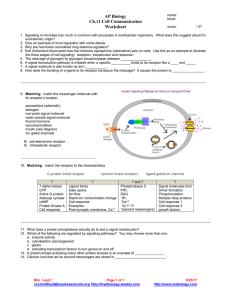
POGIL “Cellular Communication” KEY
... 10. The researcher could develop a medicine that blocks the receptor on the cell that normally receives the signal. Another possible solution could be to develop a medicine that prevents the release of the signal. 11. Develop a medicine that mimics the signal (ligand) or a medicine that makes the ce ...
... 10. The researcher could develop a medicine that blocks the receptor on the cell that normally receives the signal. Another possible solution could be to develop a medicine that prevents the release of the signal. 11. Develop a medicine that mimics the signal (ligand) or a medicine that makes the ce ...
Biochemistry
... • Monomer Nucleotide • Polymers nucleic acid – DNA deoxyribonucleic acid (genetic info.) – RNA ribonucleic acid (directs protein ...
... • Monomer Nucleotide • Polymers nucleic acid – DNA deoxyribonucleic acid (genetic info.) – RNA ribonucleic acid (directs protein ...
Automated Microscopy, Machine Learning, Systems Biology, and
... (without using colocalization!) Examination of proteins for which methods disagree suggests machine classifier is correct in at least some cases Shann-Ching (Sam) Chen & Geoff Gordon ...
... (without using colocalization!) Examination of proteins for which methods disagree suggests machine classifier is correct in at least some cases Shann-Ching (Sam) Chen & Geoff Gordon ...
File - Peterson Biology
... 3. tRNA brings correct amino acid (methionine) to the ribosome. Each tRNA carries one type of amino acid. The anticodon (three nitrogen bases on tRNA) must ...
... 3. tRNA brings correct amino acid (methionine) to the ribosome. Each tRNA carries one type of amino acid. The anticodon (three nitrogen bases on tRNA) must ...
Slide 1
... In this study we investigated ubiquitin, HSC70, and HSP70 in intact and severed ventral nerve cords of the crayfish, Procambarus Clarkii. Ubiquitin is a highly conserved protein that is found in all eukaryotic cells. The ubiquitin-proteasome pathway plays a very important part in the active break do ...
... In this study we investigated ubiquitin, HSC70, and HSP70 in intact and severed ventral nerve cords of the crayfish, Procambarus Clarkii. Ubiquitin is a highly conserved protein that is found in all eukaryotic cells. The ubiquitin-proteasome pathway plays a very important part in the active break do ...
Structural Genomics - University of Houston
... Hydrophobic effects force global protein conformation. ...
... Hydrophobic effects force global protein conformation. ...
PPT
... structure, but not all proteins have quaternary structure. • Quaternary structure is the arrangement of subunits that form a larger protein. • Subunits are polypeptides that have primary, secondary, and tertiary structure. ...
... structure, but not all proteins have quaternary structure. • Quaternary structure is the arrangement of subunits that form a larger protein. • Subunits are polypeptides that have primary, secondary, and tertiary structure. ...
1 - edl.io
... 26. What are two examples of carbohydrates found in plants? 27. What is the chemical formula for glucose? 28. What happens during hydrolysis? During dehydration synthesis? 29. Draw each of the following parts of a protein: Amino group, Carboxyl group, R-group: 30. What is a polypeptide? 31. What do ...
... 26. What are two examples of carbohydrates found in plants? 27. What is the chemical formula for glucose? 28. What happens during hydrolysis? During dehydration synthesis? 29. Draw each of the following parts of a protein: Amino group, Carboxyl group, R-group: 30. What is a polypeptide? 31. What do ...
Latinos take on bigger role in Obama inauguration
... 2) The secondary structure of a protein is the local folding patterns within short segments of each polypeptide due to hydrogen bonding (weak chemical bonds). 3) The tertiary structure of a protein is the local folding patterns that result from interactions between amino acid side chains (parts of a ...
... 2) The secondary structure of a protein is the local folding patterns within short segments of each polypeptide due to hydrogen bonding (weak chemical bonds). 3) The tertiary structure of a protein is the local folding patterns that result from interactions between amino acid side chains (parts of a ...
Peptide Structure: The Building Blocks of Life
... • Non-Polar – Hydrophobic Acidic vs. Non-acidic vs. Basic o This property is determined by comparison to water ...
... • Non-Polar – Hydrophobic Acidic vs. Non-acidic vs. Basic o This property is determined by comparison to water ...
Biomolecules - Cloudfront.net
... It’s important to have lots of protein in your diet! Proteins in foods such as meats, soybeans, & nuts are broken down into amino acids. Without protein, your body can’t function perfectly.. This is why it’s important for vegetarians to find protein from non-animal sources. ...
... It’s important to have lots of protein in your diet! Proteins in foods such as meats, soybeans, & nuts are broken down into amino acids. Without protein, your body can’t function perfectly.. This is why it’s important for vegetarians to find protein from non-animal sources. ...
Chapter 5: What are the major types of organic molecules?
... peptide bonds are called a polypeptide D. the sequence of amino acids determine the structure (and thus the properties) of a protein E. proteins have 4 levels of organization or structure 1. primary structure (1) of a protein is the sequence of amino acids in the peptide chain 2. secondary structur ...
... peptide bonds are called a polypeptide D. the sequence of amino acids determine the structure (and thus the properties) of a protein E. proteins have 4 levels of organization or structure 1. primary structure (1) of a protein is the sequence of amino acids in the peptide chain 2. secondary structur ...
Substrate Metabolism – Rest vs Stress
... - rest = basal metabolic rate + minimal exercise - major stress = 50% burn - aim = to preserve plasma glucose levels for brain metabolism. REST - least expensive form of energy production utilized: carbohydrate -> fat -> protein in decreasing ratios. Carbohydrate Sources ...
... - rest = basal metabolic rate + minimal exercise - major stress = 50% burn - aim = to preserve plasma glucose levels for brain metabolism. REST - least expensive form of energy production utilized: carbohydrate -> fat -> protein in decreasing ratios. Carbohydrate Sources ...
Proteolysis
Proteolysis is the breakdown of proteins into smaller polypeptides or amino acids. Uncatalysed, the hydrolysis of peptide bonds is extremely slow, taking hundreds of years. Proteolysis is typically catalysed by cellular enzymes called proteases, but may also occur by intra-molecular digestion. Low pH or high temperatures can also cause proteolysis non-enzymatically.Proteolysis in organisms serves many purposes; for example, digestive enzymes break down proteins in food to provide amino acids for the organism, while proteolytic processing of a polypeptide chain after its synthesis may be necessary for the production of an active protein. It is also important in the regulation of some physiological and cellular processes, as well as preventing the accumulation of unwanted or abnormal proteins in cells. Consequently, dis-regulation of proteolysis can cause diseases, and is used in some venoms to damage their prey.Proteolysis is important as an analytical tool for studying proteins in the laboratory, as well as industrially, for example in food processing and stain removal.