Quiz 2
... - RNA – transcription and sequences of amino acides during translation – segment of DNA (genes) 2. Proteins are polymers with important roles both in structure and metabolism. Describe important aspects of this macromolecule. - Functions: Enzymes, Defensive, Hormonal and regulatory, receptors, stora ...
... - RNA – transcription and sequences of amino acides during translation – segment of DNA (genes) 2. Proteins are polymers with important roles both in structure and metabolism. Describe important aspects of this macromolecule. - Functions: Enzymes, Defensive, Hormonal and regulatory, receptors, stora ...
A1985ASW1100001
... group’s in vitro rat-liver system, I uncovered the mechanism of amino acid activation in 1955. The enzymic activity was concentrated in a “soluble” cellular fraction obtained by adjusting cell sap to pH 5 and redissolving the precipitate. In the presence of ATP and amino acids, the fraction vigorous ...
... group’s in vitro rat-liver system, I uncovered the mechanism of amino acid activation in 1955. The enzymic activity was concentrated in a “soluble” cellular fraction obtained by adjusting cell sap to pH 5 and redissolving the precipitate. In the presence of ATP and amino acids, the fraction vigorous ...
ReliaTech GmbH Recombinant Human p16
... inhibiting cyclin dependent kinase-4 (CDK4) and CDK6. p16-INK4a inhibits CDK activity by binding to the CDK molecules in a manner that interferes with their ability to interact with cyclin D. This activity has the effect of suppressing tumor formation and growth, and of inducing replicative senescen ...
... inhibiting cyclin dependent kinase-4 (CDK4) and CDK6. p16-INK4a inhibits CDK activity by binding to the CDK molecules in a manner that interferes with their ability to interact with cyclin D. This activity has the effect of suppressing tumor formation and growth, and of inducing replicative senescen ...
poly=many
... As polysaccharides, saccharide means sugar, poly means many. So polysaccharides means many sugars, and ...
... As polysaccharides, saccharide means sugar, poly means many. So polysaccharides means many sugars, and ...
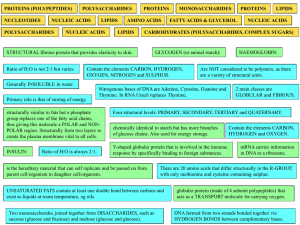
biol 3 biomolecules table activity
... chemically identical to starch but has more branches of glucose chains. Also used for energy storage. Y-shaped globular protein that is involved in the immune response by specifically binding to foreign substances. ...
... chemically identical to starch but has more branches of glucose chains. Also used for energy storage. Y-shaped globular protein that is involved in the immune response by specifically binding to foreign substances. ...
1. Identify the structural formula. Use these choices - burgess
... 17. All organic compounds are compounds that contain oxygen. _false - carbon_ 18. Isomers are organic molecules that have the same chemical formula, but different structural formulas. _true_ ...
... 17. All organic compounds are compounds that contain oxygen. _false - carbon_ 18. Isomers are organic molecules that have the same chemical formula, but different structural formulas. _true_ ...
Exercise 1. a) The authors would like to study the membrane bound
... When Zn2+ binds to CH1, a molten globule structure is formed which is then further stabilized to a well-structured protein complex together with the target protein HIF. Note that all three methods were required to solve the problem! Exercise 4. a) The spectrum is recorded with NMR (nuclear magnetic ...
... When Zn2+ binds to CH1, a molten globule structure is formed which is then further stabilized to a well-structured protein complex together with the target protein HIF. Note that all three methods were required to solve the problem! Exercise 4. a) The spectrum is recorded with NMR (nuclear magnetic ...
Biosynthesis of non-amino acids from amino acid precursors
... Transported as alanine or glutamine. Released as Urea (see above). Pool of glutamine in blood serves several functions Provides ammonia for excretion of H in urine as NH4+ Fuel for gut, kidney, cells of immune Source of N for rapidly dividng cells Formation of glutamine from gluatamate a ...
... Transported as alanine or glutamine. Released as Urea (see above). Pool of glutamine in blood serves several functions Provides ammonia for excretion of H in urine as NH4+ Fuel for gut, kidney, cells of immune Source of N for rapidly dividng cells Formation of glutamine from gluatamate a ...
Hoku`s Slides
... Library-on-library cleavage profiling Double-stranded target pool is used to stain yeast Cleavable targets on cleaving enzymes are cut, rest remain intact Biotinylated linker is ligated to cleaved targets ...
... Library-on-library cleavage profiling Double-stranded target pool is used to stain yeast Cleavable targets on cleaving enzymes are cut, rest remain intact Biotinylated linker is ligated to cleaved targets ...
Protein Biosynthesis
... 1. After trypsinogen enters the small intestine, it is converted into its active form, trypsin by enteropeptidase. 2. Now trypsin hydrolyzes more trypsinogen and starts to hydrolyze chymotrpsinogen to active their forms. ...
... 1. After trypsinogen enters the small intestine, it is converted into its active form, trypsin by enteropeptidase. 2. Now trypsin hydrolyzes more trypsinogen and starts to hydrolyze chymotrpsinogen to active their forms. ...
CHAPTER 4 Proteins: Structure, Function, Folding
... Protein Stability and Folding •A protein’s function depends on its three-dimensional structure. •Loss of structural integrity with accompanying loss of activity is called denaturation •Proteins can be denatured by • heat or cold; pH extremes; organic solvents • chaotropic agents: urea and guanidini ...
... Protein Stability and Folding •A protein’s function depends on its three-dimensional structure. •Loss of structural integrity with accompanying loss of activity is called denaturation •Proteins can be denatured by • heat or cold; pH extremes; organic solvents • chaotropic agents: urea and guanidini ...
Attachment 2
... • Does not have a nucleus • Travel in blood to find cuts and scrapes on your skin • “plug” the cuts and scrapes to stop them from bleeding and help ...
... • Does not have a nucleus • Travel in blood to find cuts and scrapes on your skin • “plug” the cuts and scrapes to stop them from bleeding and help ...
Name:______________________________ Biochemistry I-First Exam
... 9. The Gibb’s free energy, ∆G, is negative for a) non-spontaneous processes. b) aspontaneous processes. c) temperature-independent processes. d) none of the above. 10. The most important conclusion from Anfinsen’s work on denaturation and refolding Ribonuclease (RnaseA) was that: a). the conformatio ...
... 9. The Gibb’s free energy, ∆G, is negative for a) non-spontaneous processes. b) aspontaneous processes. c) temperature-independent processes. d) none of the above. 10. The most important conclusion from Anfinsen’s work on denaturation and refolding Ribonuclease (RnaseA) was that: a). the conformatio ...
Document
... Why proteomics? Protein alterations cannot be fully deduced from DNA. RNA expression does not always reflect protein levels: translational control degradation turnover ...
... Why proteomics? Protein alterations cannot be fully deduced from DNA. RNA expression does not always reflect protein levels: translational control degradation turnover ...
About
... Characteristic (ROC) graph it classified correctly 70% of negative instances with having only 35% of positive instances misclassified into the negative class. TP, FP, TN, FN rates as described in solubility section ...
... Characteristic (ROC) graph it classified correctly 70% of negative instances with having only 35% of positive instances misclassified into the negative class. TP, FP, TN, FN rates as described in solubility section ...
Protein Structure
... Denaturing agents include: ◦ Heat, 6 M urea, detergents, Acids, Bases, Salts, Reducing agents, Heavy metals, Alcohol ...
... Denaturing agents include: ◦ Heat, 6 M urea, detergents, Acids, Bases, Salts, Reducing agents, Heavy metals, Alcohol ...
The Chemicals of Life
... Base element for many macromolecules in the body Carbon is a small element that can form 4 stable covalent bonds with other atoms (look at valence electrons). The number of covalent bonds an atom can form is called its bonding capacity. Carbon can bond to other carbon atoms in straight chains, branc ...
... Base element for many macromolecules in the body Carbon is a small element that can form 4 stable covalent bonds with other atoms (look at valence electrons). The number of covalent bonds an atom can form is called its bonding capacity. Carbon can bond to other carbon atoms in straight chains, branc ...
Proteolysis
Proteolysis is the breakdown of proteins into smaller polypeptides or amino acids. Uncatalysed, the hydrolysis of peptide bonds is extremely slow, taking hundreds of years. Proteolysis is typically catalysed by cellular enzymes called proteases, but may also occur by intra-molecular digestion. Low pH or high temperatures can also cause proteolysis non-enzymatically.Proteolysis in organisms serves many purposes; for example, digestive enzymes break down proteins in food to provide amino acids for the organism, while proteolytic processing of a polypeptide chain after its synthesis may be necessary for the production of an active protein. It is also important in the regulation of some physiological and cellular processes, as well as preventing the accumulation of unwanted or abnormal proteins in cells. Consequently, dis-regulation of proteolysis can cause diseases, and is used in some venoms to damage their prey.Proteolysis is important as an analytical tool for studying proteins in the laboratory, as well as industrially, for example in food processing and stain removal.