Extend Your Understanding of the Bacterial
... move recombinant plasmids containing DNA from two or more species into bacterial cells to produce many copies of the recombinant plasmid or to produce large amounts of the recombinant protein(s). Through these technologies scientists use bacteria as mini factories to produce specific DNA molecules a ...
... move recombinant plasmids containing DNA from two or more species into bacterial cells to produce many copies of the recombinant plasmid or to produce large amounts of the recombinant protein(s). Through these technologies scientists use bacteria as mini factories to produce specific DNA molecules a ...
Istituto d`Istruzione Superiore “F. Alderisio”
... Istituto d’Istruzione Superiore “F. Alderisio”- Stigliano Programma svolto progetto CLIL (Content and Language Integrated Learning) Prof. Nunzia Carusio ...
... Istituto d’Istruzione Superiore “F. Alderisio”- Stigliano Programma svolto progetto CLIL (Content and Language Integrated Learning) Prof. Nunzia Carusio ...
3. Protein Structure and Function – Bio 20-1
... 7. Signaling and response (inter and intracellular) ...
... 7. Signaling and response (inter and intracellular) ...
Protein synthesis and Enzyme test review
... 15. How many nitrogen bases make up a codon? three 16. How many codons are in a strand of DNA that has 60 nucleotides? 20 17. How many codons would be necessary to code for a strand of protein that has 15 amino acids? 5 18. List the 3 parts of the RNA nucleotide. = Sugar (ribose), phosphate, nitroge ...
... 15. How many nitrogen bases make up a codon? three 16. How many codons are in a strand of DNA that has 60 nucleotides? 20 17. How many codons would be necessary to code for a strand of protein that has 15 amino acids? 5 18. List the 3 parts of the RNA nucleotide. = Sugar (ribose), phosphate, nitroge ...
Chapter 39 – Plant Responses to Stimuli Signal Transduction
... Chemical signal that coordinates different parts of an organism o Growth, development, & responses to stimuli Reception Internal & external signals are detected by receptors Proteins that change in response to specific stimuli o Can be in membrane or cytoplasm Transduction Second messengers ...
... Chemical signal that coordinates different parts of an organism o Growth, development, & responses to stimuli Reception Internal & external signals are detected by receptors Proteins that change in response to specific stimuli o Can be in membrane or cytoplasm Transduction Second messengers ...
Food - cbbiology
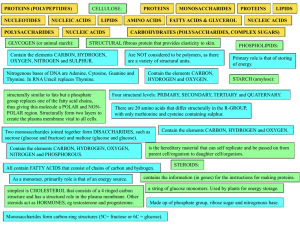
... Carbohydrates and lipids: broken down in respiration to give energy Proteins: 1. Act as enzymes to control metabolic reactions 2. Act as antibodies to fight infection. 3. Some proteins are hormones that can regulate body reactions. Vitamin C: 1. Helps form connective tissue (surrounds body structure ...
... Carbohydrates and lipids: broken down in respiration to give energy Proteins: 1. Act as enzymes to control metabolic reactions 2. Act as antibodies to fight infection. 3. Some proteins are hormones that can regulate body reactions. Vitamin C: 1. Helps form connective tissue (surrounds body structure ...
File
... linear chain of amino acids. This polypeptide lacks any developed threedimensional structure (the left hand side of the neighboring figure). Amino acids interact with each other to produce a well-defined three-dimensional structure, the folded protein (the right hand side of the figure), known as th ...
... linear chain of amino acids. This polypeptide lacks any developed threedimensional structure (the left hand side of the neighboring figure). Amino acids interact with each other to produce a well-defined three-dimensional structure, the folded protein (the right hand side of the figure), known as th ...
Transcription/Translation foldable
... foldable Fold your paper so the two ends meet in the middle. Label Transcription on one side and Translation on the other. ...
... foldable Fold your paper so the two ends meet in the middle. Label Transcription on one side and Translation on the other. ...
file (4.1 MB, ppt)
... In globular proteins, tertiary interactions are frequently stabilized by the sequestration of hydrophobic amino acid residues in the protein core, from which water is excluded, and by the consequent enrichment of charged or hydrophilic residues on the protein's water-exposed surface. In secreted pro ...
... In globular proteins, tertiary interactions are frequently stabilized by the sequestration of hydrophobic amino acid residues in the protein core, from which water is excluded, and by the consequent enrichment of charged or hydrophilic residues on the protein's water-exposed surface. In secreted pro ...
Chapter 4 - Evangel University
... ___ structure: the ________________ of amino acids in a polypeptide chain, read from the N-terminal end to the C-terminal end ___ structure: the ______________ ______________ arrangements (conformations) in localized regions of a polypeptide chain; refers only to interactions of the peptide backbone ...
... ___ structure: the ________________ of amino acids in a polypeptide chain, read from the N-terminal end to the C-terminal end ___ structure: the ______________ ______________ arrangements (conformations) in localized regions of a polypeptide chain; refers only to interactions of the peptide backbone ...
Slide 1 - Denton ISD
... Nitrogenous bases of DNA are Adenine, Cytosine, Guanine and Thymine. In RNA Uracil replaces Thymine. structurally similar to fats but a phosphate group replaces one of the fatty acid chains, thus giving this molecule a POLAR and NONPOLAR region. Structurally form two layers to create the plasma memb ...
... Nitrogenous bases of DNA are Adenine, Cytosine, Guanine and Thymine. In RNA Uracil replaces Thymine. structurally similar to fats but a phosphate group replaces one of the fatty acid chains, thus giving this molecule a POLAR and NONPOLAR region. Structurally form two layers to create the plasma memb ...
Day 6 Carlow Bioinformatics
... • Database now huge so prob of finding any short motif is high. • Many copies of ELVIS hiding in UniProt • May be more than 1 motif defining a family • A great first attempt and still useful but too crude ...
... • Database now huge so prob of finding any short motif is high. • Many copies of ELVIS hiding in UniProt • May be more than 1 motif defining a family • A great first attempt and still useful but too crude ...
protein - Portal UniMAP
... Unlike fibrous proteins which only play a structural function, globular proteins can act as: 1) Enzymes, by catalyzing organic reactions taking place in the organism in mild conditions and with a great specificity. 2) Messengers, by transmitting messages to regulate biological processes. This funct ...
... Unlike fibrous proteins which only play a structural function, globular proteins can act as: 1) Enzymes, by catalyzing organic reactions taking place in the organism in mild conditions and with a great specificity. 2) Messengers, by transmitting messages to regulate biological processes. This funct ...
Expression system
... • Used to aid purification of foreign proteins, often by affinity chromatography • Often a rare protease cut site is added to the fusion partner • Eg., For small peptides poly-arginine,Histidine tail ...
... • Used to aid purification of foreign proteins, often by affinity chromatography • Often a rare protease cut site is added to the fusion partner • Eg., For small peptides poly-arginine,Histidine tail ...
CHEM 210(Biochemistry)
... biochemistry of pH and buffers. Structure and function of enzymes including enzyme kinetics and glycogen synthesis and degradation, and insulin and glycogenesis. DNA replication, transcription, translation, protein synthesis by RNA molecules and regulation of gene expression. Cell membrane structure ...
... biochemistry of pH and buffers. Structure and function of enzymes including enzyme kinetics and glycogen synthesis and degradation, and insulin and glycogenesis. DNA replication, transcription, translation, protein synthesis by RNA molecules and regulation of gene expression. Cell membrane structure ...
Type III Secretion System
... This ring of helices is a model of the molecular needle of type III secretion system. The model is a combination of the crystal structure of the single subunit and 3D reconstruction of the needle from electron microscopy. ...
... This ring of helices is a model of the molecular needle of type III secretion system. The model is a combination of the crystal structure of the single subunit and 3D reconstruction of the needle from electron microscopy. ...
20141203103493
... Proteosomes-control how long protein lasts-mainly work on intracellularly produced proteins ex. Cyclins, remove transcription factors, recycle amino acids (Lysosomes work on extracellularly produced proteins) ...
... Proteosomes-control how long protein lasts-mainly work on intracellularly produced proteins ex. Cyclins, remove transcription factors, recycle amino acids (Lysosomes work on extracellularly produced proteins) ...
To the protocol
... the blood stream. The active site of trypsin, as well as of any other enzyme, has two distinct functions; to bind the substrate in the active site, and to perform the catalysis. Trypsin has a preference to degrade peptides and proteins adjacent to basic amino acids, that is arginine or lysine. This ...
... the blood stream. The active site of trypsin, as well as of any other enzyme, has two distinct functions; to bind the substrate in the active site, and to perform the catalysis. Trypsin has a preference to degrade peptides and proteins adjacent to basic amino acids, that is arginine or lysine. This ...
Protein Synthesis
... The sequence (order) of bases in a strand of DNA makes the code for building proteins. EX: The three bases “CCA” form the code for the amino acid proline. A long string of amino acids forms a protein. Each gene is usually a set of instructions for making a protein. Proteins are responsible for most ...
... The sequence (order) of bases in a strand of DNA makes the code for building proteins. EX: The three bases “CCA” form the code for the amino acid proline. A long string of amino acids forms a protein. Each gene is usually a set of instructions for making a protein. Proteins are responsible for most ...
Audesirk, Biology: Life on Earth 7e
... 14) You go the store and buy some lard for cooking. You notice when you get home that the lard is solid at room temperature. What does this tell you about the fats in lard? A) The fats in lard are not organic molecules C) The fats are mostly phospholipids B) The lard is composed of saturated fats D) ...
... 14) You go the store and buy some lard for cooking. You notice when you get home that the lard is solid at room temperature. What does this tell you about the fats in lard? A) The fats in lard are not organic molecules C) The fats are mostly phospholipids B) The lard is composed of saturated fats D) ...
Ligand Binding - Stroud
... • Thermodynamics of Protein Assembly • Structural Change on complexation • Empirical fitting of Atomic Interactions with Free Energy of Association • Estimate of free energy of H bonds and charge interactions in protein complexes and role of hydrophobic effect _______________________________________ ...
... • Thermodynamics of Protein Assembly • Structural Change on complexation • Empirical fitting of Atomic Interactions with Free Energy of Association • Estimate of free energy of H bonds and charge interactions in protein complexes and role of hydrophobic effect _______________________________________ ...
Proteolysis
Proteolysis is the breakdown of proteins into smaller polypeptides or amino acids. Uncatalysed, the hydrolysis of peptide bonds is extremely slow, taking hundreds of years. Proteolysis is typically catalysed by cellular enzymes called proteases, but may also occur by intra-molecular digestion. Low pH or high temperatures can also cause proteolysis non-enzymatically.Proteolysis in organisms serves many purposes; for example, digestive enzymes break down proteins in food to provide amino acids for the organism, while proteolytic processing of a polypeptide chain after its synthesis may be necessary for the production of an active protein. It is also important in the regulation of some physiological and cellular processes, as well as preventing the accumulation of unwanted or abnormal proteins in cells. Consequently, dis-regulation of proteolysis can cause diseases, and is used in some venoms to damage their prey.Proteolysis is important as an analytical tool for studying proteins in the laboratory, as well as industrially, for example in food processing and stain removal.