macromoleculeppt
... Are often very large polymers of many amino acids (monomers) linked together to form POLYPEPTIDES Proteins are built by condensation reactions forming peptide bonds. ...
... Are often very large polymers of many amino acids (monomers) linked together to form POLYPEPTIDES Proteins are built by condensation reactions forming peptide bonds. ...
Modification of Genes and Proteins - sharonap-cellrepro-p2
... and binds to DNA RNA polymerase bonds to DNA RNA polymerase separates strands and strings together complementary nucleotides (using U instead of T) Primary transcript has been created when terminator region is reached ...
... and binds to DNA RNA polymerase bonds to DNA RNA polymerase separates strands and strings together complementary nucleotides (using U instead of T) Primary transcript has been created when terminator region is reached ...
Outline of MALDI mass spectrometric analysis
... regulatory proteins are seldom detected when total cell lysates are analyzed. ...
... regulatory proteins are seldom detected when total cell lysates are analyzed. ...
Genetic encoding of the post-translational modification 2
... (Mm) (see the ESI†). These included the wild-type enzymes and variants that have been shown to have relaxed substrate specificity towards other, larger unnatural amino acids. The screen utilized an expression plasmid for superfolder green fluorescent protein (sfGFP) containing an amber stop codon, T ...
... (Mm) (see the ESI†). These included the wild-type enzymes and variants that have been shown to have relaxed substrate specificity towards other, larger unnatural amino acids. The screen utilized an expression plasmid for superfolder green fluorescent protein (sfGFP) containing an amber stop codon, T ...
Most molecules of human vasopressin have a net charge of _____
... b. The net (average) charge of protein Z at neutral pH is: c. The predominant charge state of protein Z at pH 8.0 is: d. The net (average) charge of protein Z at pH 8.0 is: ...
... b. The net (average) charge of protein Z at neutral pH is: c. The predominant charge state of protein Z at pH 8.0 is: d. The net (average) charge of protein Z at pH 8.0 is: ...
( 2 points each).
... In order to prevent the process of either crenation or hemolysis with red blood cells an intravenous solution concentration should be ________ to the concentration of blood. A) hypotonic B) hypertonic C) isotonic* D) all of these ...
... In order to prevent the process of either crenation or hemolysis with red blood cells an intravenous solution concentration should be ________ to the concentration of blood. A) hypotonic B) hypertonic C) isotonic* D) all of these ...
Bioinformatics in Computer Sciences at NJIT
... • DNA can be represented as strings consisting of four letters: A, C, G, and T. They could be very long, e.g. thousands and even millions of letters • Proteins are also represented as strings of 20 letters (each letter is an amino acid). Their 3-D structure determines the function to a large extent. ...
... • DNA can be represented as strings consisting of four letters: A, C, G, and T. They could be very long, e.g. thousands and even millions of letters • Proteins are also represented as strings of 20 letters (each letter is an amino acid). Their 3-D structure determines the function to a large extent. ...
Possible Test 1 Questions
... 1) Glycosyl hydrolases comprise the largest enzyme family in the world. This group has evolved a wide array of three-dimensional topologies to facilitate the binding of all possible carbohydrate polymers and position the catalytic amino acids in place to hydrolyze the glycosidic bond between adjacen ...
... 1) Glycosyl hydrolases comprise the largest enzyme family in the world. This group has evolved a wide array of three-dimensional topologies to facilitate the binding of all possible carbohydrate polymers and position the catalytic amino acids in place to hydrolyze the glycosidic bond between adjacen ...
a. carbohydrates - Valhalla High School
... 3. List the 4 most common elements found in living things. 4. Explain the differences between inorganic and organic compounds. 5. Understand that water is the most important inorganic compound for organisms. 6. State the functions of carbohydrates. 7. Understand that monosaccharides (i.e., glucose) ...
... 3. List the 4 most common elements found in living things. 4. Explain the differences between inorganic and organic compounds. 5. Understand that water is the most important inorganic compound for organisms. 6. State the functions of carbohydrates. 7. Understand that monosaccharides (i.e., glucose) ...
3 MoleculesCells
... molecule? What two important functional groups are part of this molecule? What is a side group (variable group) and how is this group important in the folding of a protein? Why aren't the carboxyl and amino groups of the amino acid important in driving folding reactions? ...
... molecule? What two important functional groups are part of this molecule? What is a side group (variable group) and how is this group important in the folding of a protein? Why aren't the carboxyl and amino groups of the amino acid important in driving folding reactions? ...
Close Reading for Macromolecules
... (contain at least one double bond). A carboxyl functional group (-COOH) is found on the end of the fatty acid that does NOT attach to glycerol. CIRCLE AND LABEL the carboxyl groups in the 2 fatty acids on this worksheet. Color the fatty acid chains the same colors for carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen as ...
... (contain at least one double bond). A carboxyl functional group (-COOH) is found on the end of the fatty acid that does NOT attach to glycerol. CIRCLE AND LABEL the carboxyl groups in the 2 fatty acids on this worksheet. Color the fatty acid chains the same colors for carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen as ...
Protein_hierarchy
... chain folds, the hydrophobic R-groups tend to be close to each other in the interior of the folded chain, whereas hydrophilic R-groups tend to be on the outside, attracted to water. ...
... chain folds, the hydrophobic R-groups tend to be close to each other in the interior of the folded chain, whereas hydrophilic R-groups tend to be on the outside, attracted to water. ...
Amino Acids, Peptides and Proteins
... 3. You have an 28 amino acid long peptide that contains three cysteines. Explain why when examining the structure of this peptide the same two cysteines were involved in a disulfide bond, but not the other one. ...
... 3. You have an 28 amino acid long peptide that contains three cysteines. Explain why when examining the structure of this peptide the same two cysteines were involved in a disulfide bond, but not the other one. ...
The Biochemistry of Movement
... acids within the protein polypeptide. While there are only 20 amino acids, the variety of combinations that can be created from them leads to a huge number of proteins. For convenience, amino acids are often indicated by the three-letter codes listed in Table 28.6. The code for a very small protein ...
... acids within the protein polypeptide. While there are only 20 amino acids, the variety of combinations that can be created from them leads to a huge number of proteins. For convenience, amino acids are often indicated by the three-letter codes listed in Table 28.6. The code for a very small protein ...
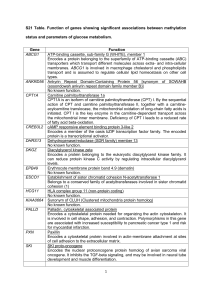
S21 Table. Function of genes showing significant associations
... Belongs to the system L family of plasma membrane carrier proteins that transport large neutral amino acids (3). Sterol regulatory element binding transcription factor 1 Encodes a transcription factor binding to the sterol regulatory element-1, which is a decamer flanking the low density lipoprotein ...
... Belongs to the system L family of plasma membrane carrier proteins that transport large neutral amino acids (3). Sterol regulatory element binding transcription factor 1 Encodes a transcription factor binding to the sterol regulatory element-1, which is a decamer flanking the low density lipoprotein ...
PROTEIN SYNTHESIS
... The ribosome “reads” each codon. Each codon tells the ribosome (look at the genetic code chart) which amino acid is needed. A tRNA (transfer RNA) molecule brings that amino acid to the ribosome. o GCU codes for alanine o AAG codes for o CGA codes for o UUA codes for o UAG codes for The ribosome conn ...
... The ribosome “reads” each codon. Each codon tells the ribosome (look at the genetic code chart) which amino acid is needed. A tRNA (transfer RNA) molecule brings that amino acid to the ribosome. o GCU codes for alanine o AAG codes for o CGA codes for o UUA codes for o UAG codes for The ribosome conn ...
PowerPoint Rubric: Biochemistry worksheet
... 14. Which type of lipoproteins are considered “good” and which are considered “bad”? Explain. Low Density lipoproteins (LDL)- lethal cholesterol, clogs arteries. High Density lipoproteins (HDL) –healthy cholesterol, remove cholesterol from arteries and return it to the liver. ...
... 14. Which type of lipoproteins are considered “good” and which are considered “bad”? Explain. Low Density lipoproteins (LDL)- lethal cholesterol, clogs arteries. High Density lipoproteins (HDL) –healthy cholesterol, remove cholesterol from arteries and return it to the liver. ...
Compare and contrast organic molecules and inorganic - bl-whs
... considered the foundation of lipids, proteins and nucleic acids. By adding elements such as nitrogen and phosphorus to the long carbon chains, these types of molecules can be produced. ...
... considered the foundation of lipids, proteins and nucleic acids. By adding elements such as nitrogen and phosphorus to the long carbon chains, these types of molecules can be produced. ...
Answers for extension worksheet – Option C
... amino acids, which are then deaminated (the NH2 group is removed). The remainder of the molecule enters the respiratory process. Some amino acids are converted to pyruvate, others enter the Krebs cycle. In either case, ATP is synthesised in the usual way. This only occurs during starvation because t ...
... amino acids, which are then deaminated (the NH2 group is removed). The remainder of the molecule enters the respiratory process. Some amino acids are converted to pyruvate, others enter the Krebs cycle. In either case, ATP is synthesised in the usual way. This only occurs during starvation because t ...
Protein Synthesis: Translation
... 3) A transfer RNA with an amino acids is called a charged amino acid. (An enzyme and ATP bind to the correct amino acid to the transfer RNA molecule. At that point it is ready to carry the amino acid to its correct place in the growing polypeptide chain.) ...
... 3) A transfer RNA with an amino acids is called a charged amino acid. (An enzyme and ATP bind to the correct amino acid to the transfer RNA molecule. At that point it is ready to carry the amino acid to its correct place in the growing polypeptide chain.) ...
Steps of Translation
... 2. A tRNA carrying an amino acid approaches 3. The Anticodon on the tRNA pairs with codon 4. The tRNA drops off it’s amino acid 5. An enzyme forms a peptide bond between amino acids 6. This process continues to form a protein until a STOP codon is reached and then the new protein is released. ...
... 2. A tRNA carrying an amino acid approaches 3. The Anticodon on the tRNA pairs with codon 4. The tRNA drops off it’s amino acid 5. An enzyme forms a peptide bond between amino acids 6. This process continues to form a protein until a STOP codon is reached and then the new protein is released. ...
Proteolysis
Proteolysis is the breakdown of proteins into smaller polypeptides or amino acids. Uncatalysed, the hydrolysis of peptide bonds is extremely slow, taking hundreds of years. Proteolysis is typically catalysed by cellular enzymes called proteases, but may also occur by intra-molecular digestion. Low pH or high temperatures can also cause proteolysis non-enzymatically.Proteolysis in organisms serves many purposes; for example, digestive enzymes break down proteins in food to provide amino acids for the organism, while proteolytic processing of a polypeptide chain after its synthesis may be necessary for the production of an active protein. It is also important in the regulation of some physiological and cellular processes, as well as preventing the accumulation of unwanted or abnormal proteins in cells. Consequently, dis-regulation of proteolysis can cause diseases, and is used in some venoms to damage their prey.Proteolysis is important as an analytical tool for studying proteins in the laboratory, as well as industrially, for example in food processing and stain removal.