macromolecule notes
... 2. Carbohydrates are the ________________ source of short term _________________. ii. The building blocks (or monomers) of carbohydrates are monosaccharides. iii. Monosaccharides are _____________ ____________ (saccharide = sugar). Examples: 1. Glucose: commonly found in _________________ of animals ...
... 2. Carbohydrates are the ________________ source of short term _________________. ii. The building blocks (or monomers) of carbohydrates are monosaccharides. iii. Monosaccharides are _____________ ____________ (saccharide = sugar). Examples: 1. Glucose: commonly found in _________________ of animals ...
Homework1
... Identify whether each of the following covalent bonds, C-O, C-H, N-H and O-H is polar or nonpolar, and explain how these different characteristics relate to the electronegativity of each atom involved in the bond. ...
... Identify whether each of the following covalent bonds, C-O, C-H, N-H and O-H is polar or nonpolar, and explain how these different characteristics relate to the electronegativity of each atom involved in the bond. ...
Chemistry of Life - Bilkent University
... • High-density lipoproteins (HDL) form a class of lipoproteins, varying somewhat in their size (8-11 nm in diameter) and contents, that carry cholesterol from the body's tissues to the liver. • Generally, LDL transports cholesterol and triglycerides away from cells and tissues that produce more than ...
... • High-density lipoproteins (HDL) form a class of lipoproteins, varying somewhat in their size (8-11 nm in diameter) and contents, that carry cholesterol from the body's tissues to the liver. • Generally, LDL transports cholesterol and triglycerides away from cells and tissues that produce more than ...
RER - Botanik in Bonn
... Sey 1p (yeast) and RHD 3 (Arabidopsis) plant homologue of atlastin Lnp1p (protein of lunapark family) – localises the ER network in yeast and ...
... Sey 1p (yeast) and RHD 3 (Arabidopsis) plant homologue of atlastin Lnp1p (protein of lunapark family) – localises the ER network in yeast and ...
Problem Set 5, 7.06, Spring 2003 1. In order to please your
... • An arginine residue at amino acid 47 and a lysine residue at position 74 • No other arginine or lysine residues • Only 3 cysteine residues at positions 36, 58, and 143 • Only 3 asparagine residues at positions 30, 52, and 110 • There are no O-linked sugars in this protein • A signal sequence at th ...
... • An arginine residue at amino acid 47 and a lysine residue at position 74 • No other arginine or lysine residues • Only 3 cysteine residues at positions 36, 58, and 143 • Only 3 asparagine residues at positions 30, 52, and 110 • There are no O-linked sugars in this protein • A signal sequence at th ...
3 Amino acids and crude protein - DLG
... has the great advantage that it is possible to derive recommendations concerning the supply of protein, energy and minerals from identical original data. A further advantage is the fact that unlike metabolism trials, experimental animals are kept without restriction of movements or limitation of tim ...
... has the great advantage that it is possible to derive recommendations concerning the supply of protein, energy and minerals from identical original data. A further advantage is the fact that unlike metabolism trials, experimental animals are kept without restriction of movements or limitation of tim ...
Purification and Reengineering of Plastic
... belonging to the Streptomyces species Aim 2: To enhance the biodegradability of the ...
... belonging to the Streptomyces species Aim 2: To enhance the biodegradability of the ...
PE 690 weight training PPt
... • Body either excrete it, turn it to fat, or use it for energy. • Types of protein (whey, casein, soy, rice) • The major proteins in milk are casein and whey. These two milk proteins are both excellent sources, but they differ in one important aspect—whey is a fast-digesting protein and casein is a ...
... • Body either excrete it, turn it to fat, or use it for energy. • Types of protein (whey, casein, soy, rice) • The major proteins in milk are casein and whey. These two milk proteins are both excellent sources, but they differ in one important aspect—whey is a fast-digesting protein and casein is a ...
Télécharger la version pdf
... During their life, plants constantly renew themselves. They sprout new leaves in the spring and shed them in the fall. No longer needed, damaged or dead organs such as blossoms and leaves are also cast off by a process known as abscission. By doing so, plants conserve energy and prepare for the next ...
... During their life, plants constantly renew themselves. They sprout new leaves in the spring and shed them in the fall. No longer needed, damaged or dead organs such as blossoms and leaves are also cast off by a process known as abscission. By doing so, plants conserve energy and prepare for the next ...
File
... that is also the start code. So every protein starts with methionine when it is translated » Now, the ribosome moves over one codon a new tRNA will attach to the A site. » Note that the first amino acid left the tRNA and attached to the next one ...
... that is also the start code. So every protein starts with methionine when it is translated » Now, the ribosome moves over one codon a new tRNA will attach to the A site. » Note that the first amino acid left the tRNA and attached to the next one ...
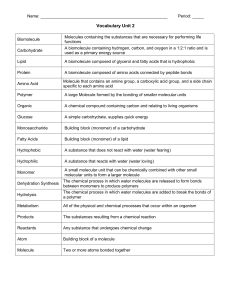
Name: Period: _____ Vocabulary Unit 2 Biomolecule Molecules
... A small molecular unit that can be chemically combined with other small molecular units to form a larger molecule ...
... A small molecular unit that can be chemically combined with other small molecular units to form a larger molecule ...
enzyme
... • SA 2-4 page 53 #1-5 • Start looking at the back of the sheet to review for the test next week ...
... • SA 2-4 page 53 #1-5 • Start looking at the back of the sheet to review for the test next week ...
Document
... chain of amino acids held together by a peptide bond. This chain may be 10’s, 100’s, or even 1000’s long and has a specific function (i.e. tubulin microtubules, catalase in cells, helicase to unwind DNA, etc.). There are only 20 amino acids; we are able to make 12 in our bodies (termed nonessential) ...
... chain of amino acids held together by a peptide bond. This chain may be 10’s, 100’s, or even 1000’s long and has a specific function (i.e. tubulin microtubules, catalase in cells, helicase to unwind DNA, etc.). There are only 20 amino acids; we are able to make 12 in our bodies (termed nonessential) ...
Lecture 1: Overview of bioinformatics
... Protein structure prediction When a protein is manufactured in the cell, it assumes a characteristic 3D structure or fold. It is very costly to determine the 3D structure of a protein experimentally (by NMR or X-ray crystallography). It would be much cheaper if we could predict the 3D structure of ...
... Protein structure prediction When a protein is manufactured in the cell, it assumes a characteristic 3D structure or fold. It is very costly to determine the 3D structure of a protein experimentally (by NMR or X-ray crystallography). It would be much cheaper if we could predict the 3D structure of ...
structural
... III. Lipids A. Fats - structure -unsaturated fats (no double bonds) Plant and fish oils Kinked; don’t pack – liquid at room temperature. “Hydrogenation” can make them saturated and solid, but the process also produces trans-fats (trans conformation around double bond) which may contribute MORE to a ...
... III. Lipids A. Fats - structure -unsaturated fats (no double bonds) Plant and fish oils Kinked; don’t pack – liquid at room temperature. “Hydrogenation” can make them saturated and solid, but the process also produces trans-fats (trans conformation around double bond) which may contribute MORE to a ...
BIO 315 Exam I (F2014)
... to H2O2. Overexpression of this enzyme or the transcriptional regulator of starvation/stress response genes (Sirt1) also extend life/health span in a variety of species, presumably by reducing the amount of these destructive species in cells. Because this transcriptional activator is dependent on th ...
... to H2O2. Overexpression of this enzyme or the transcriptional regulator of starvation/stress response genes (Sirt1) also extend life/health span in a variety of species, presumably by reducing the amount of these destructive species in cells. Because this transcriptional activator is dependent on th ...
41475 - Cell Signaling Technology
... proteins (H2A, H2B, H3, and H4), is the primary building block of chromatin. Originally thought to function as a static scaffold for DNA packaging, histones have now been shown to be dynamic proteins, undergoing multiple types of post-translational modifications, including acetylation, phosphorylati ...
... proteins (H2A, H2B, H3, and H4), is the primary building block of chromatin. Originally thought to function as a static scaffold for DNA packaging, histones have now been shown to be dynamic proteins, undergoing multiple types of post-translational modifications, including acetylation, phosphorylati ...
methods - Nature
... However, by switching expression vectors, either protein can be expressed and labeled first or both proteins can be labeled using different labeling strategies. STINT-NMR can be performed in different ways to achieve the ratios of interactor to target necessary for a complete structural titration. T ...
... However, by switching expression vectors, either protein can be expressed and labeled first or both proteins can be labeled using different labeling strategies. STINT-NMR can be performed in different ways to achieve the ratios of interactor to target necessary for a complete structural titration. T ...
ENZYMES: THE MAJESTIC MOLECULES OF LIFE Part
... substrate, and a catalytic site at which the conversion of the bound substrate takes place. However, this functional differentiation is somewhat arbitrary, since the binding of a substrate at the contact site does not leave unaffected the specificity and the rate of substrate conversion at the catal ...
... substrate, and a catalytic site at which the conversion of the bound substrate takes place. However, this functional differentiation is somewhat arbitrary, since the binding of a substrate at the contact site does not leave unaffected the specificity and the rate of substrate conversion at the catal ...
chapter 3
... 3. Where stereoisomers of biomolecules are possible, only one is usually found in most organisms; for example, only the L amino acids occur in proteins. What problems would occur if, for example, the amino acids in the body proteins of herbivores were in the L isomer form, whereas the amino acids in ...
... 3. Where stereoisomers of biomolecules are possible, only one is usually found in most organisms; for example, only the L amino acids occur in proteins. What problems would occur if, for example, the amino acids in the body proteins of herbivores were in the L isomer form, whereas the amino acids in ...
MCB Lecture 7 – Peroxisomes
... The Peroxisome can be biosynthetic. What is one of the important molecules it synthesizes? o It undergoes Plasmalogen synthesis, which is used in Myelin Sheaths of Axons The Peroxisome is also degradative. What is one of the important molecules it breaks down? o VLCFA (Very Long Chain Fatty Acids) W ...
... The Peroxisome can be biosynthetic. What is one of the important molecules it synthesizes? o It undergoes Plasmalogen synthesis, which is used in Myelin Sheaths of Axons The Peroxisome is also degradative. What is one of the important molecules it breaks down? o VLCFA (Very Long Chain Fatty Acids) W ...
Slide 1
... body Examples (that were not mentioned in class or text) of a solution, a colloid, a suspension and a homogenous mixture with the reasons why. ...
... body Examples (that were not mentioned in class or text) of a solution, a colloid, a suspension and a homogenous mixture with the reasons why. ...
Proteolysis
Proteolysis is the breakdown of proteins into smaller polypeptides or amino acids. Uncatalysed, the hydrolysis of peptide bonds is extremely slow, taking hundreds of years. Proteolysis is typically catalysed by cellular enzymes called proteases, but may also occur by intra-molecular digestion. Low pH or high temperatures can also cause proteolysis non-enzymatically.Proteolysis in organisms serves many purposes; for example, digestive enzymes break down proteins in food to provide amino acids for the organism, while proteolytic processing of a polypeptide chain after its synthesis may be necessary for the production of an active protein. It is also important in the regulation of some physiological and cellular processes, as well as preventing the accumulation of unwanted or abnormal proteins in cells. Consequently, dis-regulation of proteolysis can cause diseases, and is used in some venoms to damage their prey.Proteolysis is important as an analytical tool for studying proteins in the laboratory, as well as industrially, for example in food processing and stain removal.