Diabetes Mellitus Overview and Treatments
... The bulk of the pancreas is an exocrine gland secreting pancreatic fluid into the duodenum after a meal. Inside the pancreas are millions of clusters of cells called islets of Langerhans. The islets are endocrine tissue containing four types of cells. In order of abundance, they are: beta cells, wh ...
... The bulk of the pancreas is an exocrine gland secreting pancreatic fluid into the duodenum after a meal. Inside the pancreas are millions of clusters of cells called islets of Langerhans. The islets are endocrine tissue containing four types of cells. In order of abundance, they are: beta cells, wh ...
Diabetes
... The bulk of the pancreas is an exocrine gland secreting pancreatic fluid into the duodenum after a meal. Inside the pancreas are millions of clusters of cells called islets of Langerhans. The islets are endocrine tissue containing four types of cells. In order of abundance, they are: beta cells, wh ...
... The bulk of the pancreas is an exocrine gland secreting pancreatic fluid into the duodenum after a meal. Inside the pancreas are millions of clusters of cells called islets of Langerhans. The islets are endocrine tissue containing four types of cells. In order of abundance, they are: beta cells, wh ...
Resource Guide
... Well fed calves can gain up to 1 kg a day without getting fat! Farmers should aim to have their calves gain 0.6 kg (small breeds) to 0.75 kg (large breeds) per day. Calves need to gain weight so they’re big enough to have a calf by the time they’re two years old. If it takes longer than that, the fa ...
... Well fed calves can gain up to 1 kg a day without getting fat! Farmers should aim to have their calves gain 0.6 kg (small breeds) to 0.75 kg (large breeds) per day. Calves need to gain weight so they’re big enough to have a calf by the time they’re two years old. If it takes longer than that, the fa ...
Gluconeogenesis, Glycogen Metabolism, and the Pentose
... The starting material oxaloacetate is generated in the mitochondria from amino acid catabolism or it is drawn out of the TCA cycle to slow the pathway. The oxaloacetate is converted to malate by the action of the mitochondrial isoenzyme of Malate Dehydrogenase, the TCA cycle enzyme running in the re ...
... The starting material oxaloacetate is generated in the mitochondria from amino acid catabolism or it is drawn out of the TCA cycle to slow the pathway. The oxaloacetate is converted to malate by the action of the mitochondrial isoenzyme of Malate Dehydrogenase, the TCA cycle enzyme running in the re ...
Preview Sample 2
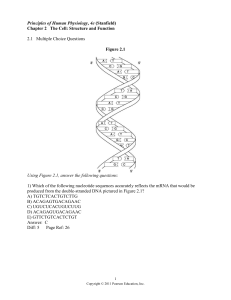
... B) The nuclear envelope is continuous with the membrane of the endoplasmic reticulum. C) The Golgi apparatus contains the enzyme catalase to break down the hydrogen peroxide it produces when degrading oxygen-derived wastes. D) Proteins to be secreted from the cell are synthesized in the mitochondria ...
... B) The nuclear envelope is continuous with the membrane of the endoplasmic reticulum. C) The Golgi apparatus contains the enzyme catalase to break down the hydrogen peroxide it produces when degrading oxygen-derived wastes. D) Proteins to be secreted from the cell are synthesized in the mitochondria ...
Collagen XV: Exploring Its Structure and Role within the Tumor
... The extracellular matrix (ECM) is a critical component of stroma-to-cell interactions that subsequently activate intracellular signaling cascades, many of which are associated with tumor invasion and metastasis. The ECM contains a wide range of proteins with multiple functions, including cytokines, ...
... The extracellular matrix (ECM) is a critical component of stroma-to-cell interactions that subsequently activate intracellular signaling cascades, many of which are associated with tumor invasion and metastasis. The ECM contains a wide range of proteins with multiple functions, including cytokines, ...
Energy 1
... What happens when not enough oxygen is supplied to the muscles? Hydrogens from glycolysis? Pyruvate to Lactate ...
... What happens when not enough oxygen is supplied to the muscles? Hydrogens from glycolysis? Pyruvate to Lactate ...
NAD (H) Linked Enzyme Catalyzed Reactions using Coupled
... of binding of enzymes to alumina nanoparticles while it worked for zirconium nanoparticles. No detectable activity was observed in either the supernatant or in the particles by adsorption method when enzymes were added to alumina. This suggests that direct contact with the surface of the alumina par ...
... of binding of enzymes to alumina nanoparticles while it worked for zirconium nanoparticles. No detectable activity was observed in either the supernatant or in the particles by adsorption method when enzymes were added to alumina. This suggests that direct contact with the surface of the alumina par ...
Raw Glycerol as Substrate for the Production of Yeast Biomass
... oil and Jatropha curcas oil are the raw materials most frequently used for the production of biodiesel, and glycerol is an inherent byproduct of this reaction [1]. Conversion of the crude product into pure glycerol requires several purification steps, all being energy-consuming and costly processes. ...
... oil and Jatropha curcas oil are the raw materials most frequently used for the production of biodiesel, and glycerol is an inherent byproduct of this reaction [1]. Conversion of the crude product into pure glycerol requires several purification steps, all being energy-consuming and costly processes. ...
biosynthesis of fatty acids - Academic Research Collections
... lipids and nucleic acids, grouped under a category called macromolecules, form the basic components that make life possible. In addition to these molecules there are micromolecules like hormones, vitamins and minerals that also play a vital role in the process of life. Among the macromolecules, prot ...
... lipids and nucleic acids, grouped under a category called macromolecules, form the basic components that make life possible. In addition to these molecules there are micromolecules like hormones, vitamins and minerals that also play a vital role in the process of life. Among the macromolecules, prot ...
Effect of salinity on growth of green alga Botryococcus braunii and
... 1990). Hydrocarbons extracted from the alga can be converted into fuel such as gasoline and diesel by catalytic ...
... 1990). Hydrocarbons extracted from the alga can be converted into fuel such as gasoline and diesel by catalytic ...
(ATP). - WordPress.com
... begins in the small intestine, where bile salts break fat globules into smaller particles called micelles requires enzymes from pancreas to hydrolyze triacylglycerols to yield monoacylglycerols and fatty acids absorbed by intestinal lining ...
... begins in the small intestine, where bile salts break fat globules into smaller particles called micelles requires enzymes from pancreas to hydrolyze triacylglycerols to yield monoacylglycerols and fatty acids absorbed by intestinal lining ...
Early bioenergetic evolution
... of what kind of organic products? Shock and co-workers have studied the question of organic synthesis at hydrothermal vents from the thermodynamic standpoint, and what they find is encouraging from an origin-of-life perspective (reviewed in [14]). They find that CO2 reduction and organic synthesis i ...
... of what kind of organic products? Shock and co-workers have studied the question of organic synthesis at hydrothermal vents from the thermodynamic standpoint, and what they find is encouraging from an origin-of-life perspective (reviewed in [14]). They find that CO2 reduction and organic synthesis i ...
New Reactions in the Crotonase Superfamily: Structure of
... ongoing studies of members of the enolase superfamily (19). In the enolase superfamily, the active sites are found at the interfaces between two domains: the catalytic groups are located in conserved positions at the ends of the β-strands in an (R/β)8-barrel motif, while the specificity determinants ...
... ongoing studies of members of the enolase superfamily (19). In the enolase superfamily, the active sites are found at the interfaces between two domains: the catalytic groups are located in conserved positions at the ends of the β-strands in an (R/β)8-barrel motif, while the specificity determinants ...
Identification of a Cytoplasm to Vacuole Targeting Determinant in
... secretory pathway has been carefully documented for a number of vacuolar hydrolases (reviewed in Klionsky et al., 1990). These proteins translocate across the ER membrane via an NH2-terminal cleavable signal sequence or noncleaved internal hydrophobic domain. The signal sequence serves no further pu ...
... secretory pathway has been carefully documented for a number of vacuolar hydrolases (reviewed in Klionsky et al., 1990). These proteins translocate across the ER membrane via an NH2-terminal cleavable signal sequence or noncleaved internal hydrophobic domain. The signal sequence serves no further pu ...
Virology Journal
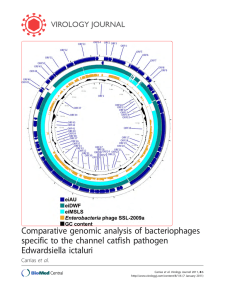
... the cell membrane [21]. These two proteins work in conjunction to destroy the cell wall of bacteria and subsequently lyse the cell [24]. These components of a host lysis cassette are each present in the genome of phages eiAU, eiDWF, and eiMSLS including a putative Rz lysis accessory protein encoded ...
... the cell membrane [21]. These two proteins work in conjunction to destroy the cell wall of bacteria and subsequently lyse the cell [24]. These components of a host lysis cassette are each present in the genome of phages eiAU, eiDWF, and eiMSLS including a putative Rz lysis accessory protein encoded ...
ppt - Chair of Computational Biology
... - important goal: annotation of structural and functional properties assumption: sequence, structure, and function are inter-related. ...
... - important goal: annotation of structural and functional properties assumption: sequence, structure, and function are inter-related. ...
Resistance training, insulin sensitivity and muscle
... effect on the GS (glycogen synthase) enzyme. Thus, an increase in Akt may ultimately lead to a stimulation of GS and glycogen formation. Another robust finding is the training induced increase in GS activity [7]. As glucose enters the cytoplasm of the muscle cell, it is rapidly phosphorylated into gl ...
... effect on the GS (glycogen synthase) enzyme. Thus, an increase in Akt may ultimately lead to a stimulation of GS and glycogen formation. Another robust finding is the training induced increase in GS activity [7]. As glucose enters the cytoplasm of the muscle cell, it is rapidly phosphorylated into gl ...
Isoenzymes in Clinical Diagnosis
... based on enzymes. In one respect, however, the wide distribution of some enzymes is illusory: the enzyme activity is widespread, but the specific protein catalyst may vary from tissue to tissue. This was recognized early in the case of phosphatases.3 Bone, prostate, and red cells are rich in protein ...
... based on enzymes. In one respect, however, the wide distribution of some enzymes is illusory: the enzyme activity is widespread, but the specific protein catalyst may vary from tissue to tissue. This was recognized early in the case of phosphatases.3 Bone, prostate, and red cells are rich in protein ...
Comparative Analysis of ,Multiple Protein
... homologous (ancestrally related) features,while the identity) it is very difficultto deduce which residues of other attempts to align functionally or spatially equiv- a pr0tei.nare necessary for function or structure, on the alent features of protein a family. Whilethere is consid- basis of multiple ...
... homologous (ancestrally related) features,while the identity) it is very difficultto deduce which residues of other attempts to align functionally or spatially equiv- a pr0tei.nare necessary for function or structure, on the alent features of protein a family. Whilethere is consid- basis of multiple ...
Proteolysis
Proteolysis is the breakdown of proteins into smaller polypeptides or amino acids. Uncatalysed, the hydrolysis of peptide bonds is extremely slow, taking hundreds of years. Proteolysis is typically catalysed by cellular enzymes called proteases, but may also occur by intra-molecular digestion. Low pH or high temperatures can also cause proteolysis non-enzymatically.Proteolysis in organisms serves many purposes; for example, digestive enzymes break down proteins in food to provide amino acids for the organism, while proteolytic processing of a polypeptide chain after its synthesis may be necessary for the production of an active protein. It is also important in the regulation of some physiological and cellular processes, as well as preventing the accumulation of unwanted or abnormal proteins in cells. Consequently, dis-regulation of proteolysis can cause diseases, and is used in some venoms to damage their prey.Proteolysis is important as an analytical tool for studying proteins in the laboratory, as well as industrially, for example in food processing and stain removal.