Maintaining Linkage: More examples
... Both HIFα and ARNT contain an N-terminal bHLH DNA binding domain and two adjacent PAS domains, referred to as PAS-A and PAS-B. PAS domains are structural modules found in proteins from all kingdoms of life that have significant structural homology despite little conservation of amino acid sequence. ...
... Both HIFα and ARNT contain an N-terminal bHLH DNA binding domain and two adjacent PAS domains, referred to as PAS-A and PAS-B. PAS domains are structural modules found in proteins from all kingdoms of life that have significant structural homology despite little conservation of amino acid sequence. ...
Organic Compounds Overview - Kenwood Academy High School
... – Primary (single chain) – Secondary (alpha helix or pleated sheet) – Tertiary (globular or fibrous) caused by hydrophobic/hydrophillic interactions or by disulfide bonds – Quaternary (2 or more polypeptides fit together) ...
... – Primary (single chain) – Secondary (alpha helix or pleated sheet) – Tertiary (globular or fibrous) caused by hydrophobic/hydrophillic interactions or by disulfide bonds – Quaternary (2 or more polypeptides fit together) ...
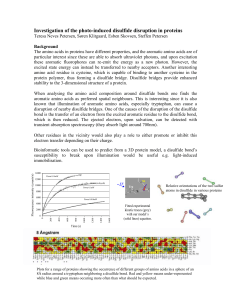
Investigation of the photo-induced disulfide disruption in
... particular interest since these are able to absorb ultraviolet photons, and upon excitation these aromatic fluorophores can re-emit the energy as a new photon. However, the excited state energy can instead be transferred to nearby acceptors. Another interesting amino acid residue is cysteine, which ...
... particular interest since these are able to absorb ultraviolet photons, and upon excitation these aromatic fluorophores can re-emit the energy as a new photon. However, the excited state energy can instead be transferred to nearby acceptors. Another interesting amino acid residue is cysteine, which ...
Transcrip_Translation
... 3. Send the copy out of the Nucleus to be read off of, so that proteins can be made ...
... 3. Send the copy out of the Nucleus to be read off of, so that proteins can be made ...
Protein Folding and Membrane Structure
... There are Multiple Levels at which Proteins Production is Controlled ...
... There are Multiple Levels at which Proteins Production is Controlled ...
BIOCHEMISTRY - Mexico Central School District
... Carbohydrates, Proteins, Lipids, Nucleic Acids ...
... Carbohydrates, Proteins, Lipids, Nucleic Acids ...
Protein misfolding associated to mild modifications of local cellular pH
... mutants: Gly26Arg (a substitution mutant with a gain in a positive charge), and Lys1070 (showing a deletion of a Lisine residue). Structural analysis shows that acidic pH induces a strong conformational shift, decreasing the cooperative denaturation pattern, and the hydrophobic cavities present in t ...
... mutants: Gly26Arg (a substitution mutant with a gain in a positive charge), and Lys1070 (showing a deletion of a Lisine residue). Structural analysis shows that acidic pH induces a strong conformational shift, decreasing the cooperative denaturation pattern, and the hydrophobic cavities present in t ...
Chapter 5 – The Proteins and Amino Acids
... intestine, where the resulting amino acids are absorbed and then released into the bloodstream. The body cells must have all the essential acids required in order to make a specific protein. If any are missing, the process halts and the amino acid strand is dismantled so that the amino acids can be ...
... intestine, where the resulting amino acids are absorbed and then released into the bloodstream. The body cells must have all the essential acids required in order to make a specific protein. If any are missing, the process halts and the amino acid strand is dismantled so that the amino acids can be ...
Lehninger Notes Chapter 2 Hydrogen bond
... assumed its three dimensional structure (native structure), it is ready to carry out its function. IS THERE ANY WAY WE CAN AFFECT THE PROTEIN STRUCTURE? There are a variety of ways that we can disrupt a protein’s three-dimensional structure. We will investigate some of them today. First, we could ad ...
... assumed its three dimensional structure (native structure), it is ready to carry out its function. IS THERE ANY WAY WE CAN AFFECT THE PROTEIN STRUCTURE? There are a variety of ways that we can disrupt a protein’s three-dimensional structure. We will investigate some of them today. First, we could ad ...
Chapter 3: The Chemistry of Organic Molecules
... • Waxes are long-chain fatty acid bonded to a long-chain alcohol. • Solid at room temp., hydrophobic, usually act as a protective coating in plants and animals. (ex.: ear wax in humans for trapping dirt and dust particles, preventing them from reaching the eardrum.) ...
... • Waxes are long-chain fatty acid bonded to a long-chain alcohol. • Solid at room temp., hydrophobic, usually act as a protective coating in plants and animals. (ex.: ear wax in humans for trapping dirt and dust particles, preventing them from reaching the eardrum.) ...
handout 1
... Specialized centers for technology development leading to high throughput structure determination of difficult proteins Specialized centers for protein structures relevant to disease (other NIH Institutes and Centers) Included in NIH Structural Biology Roadmap plans NIGMS Protein Structure Initi ...
... Specialized centers for technology development leading to high throughput structure determination of difficult proteins Specialized centers for protein structures relevant to disease (other NIH Institutes and Centers) Included in NIH Structural Biology Roadmap plans NIGMS Protein Structure Initi ...
Protein
... The key elements of amino acids are Carbon, Hydrogen, Oxygen and Nitrogen. The most common amino acid is shown above, with a carbon atom attached to the carboxyl group, called an alpha amino acid. ...
... The key elements of amino acids are Carbon, Hydrogen, Oxygen and Nitrogen. The most common amino acid is shown above, with a carbon atom attached to the carboxyl group, called an alpha amino acid. ...
Molecules of Life! - Highline Public Schools
... • All organic molecules are made out of chains of elements. • Each molecule contains CARBON. (organic means they contain carbon) • Carbon is able to form 4 strong bonds, and is able to bond with HYDROGEN, NITROGEN,OXYGEN, PHOSPHOROUS, and SULFUR ...
... • All organic molecules are made out of chains of elements. • Each molecule contains CARBON. (organic means they contain carbon) • Carbon is able to form 4 strong bonds, and is able to bond with HYDROGEN, NITROGEN,OXYGEN, PHOSPHOROUS, and SULFUR ...
... function was fitted to the data of feed intake, body weight, feather-free body protein weight and feather protein weight of four strains of laying hens in the growth phase. The rates of consumption and daily protein deposition (PD) were calculated. The amino acid deposition was obtained by multiplyi ...
Leah Cooper
... for total nitrogen is the primary determinant of total protein requirement, which includes a need for both EAA and NEAA. There is a dietary nitrogen requirement for the de novo synthesis of the NEAA. It has been suggested that some NEAA might be metabolically very important and may have a dietary re ...
... for total nitrogen is the primary determinant of total protein requirement, which includes a need for both EAA and NEAA. There is a dietary nitrogen requirement for the de novo synthesis of the NEAA. It has been suggested that some NEAA might be metabolically very important and may have a dietary re ...
lecture10_12
... Builds a protein structure model based on its alignment to one or more related protein structures in the database ...
... Builds a protein structure model based on its alignment to one or more related protein structures in the database ...
Homework 3 - Haixu Tang`s Homepage
... Membrane proteins compromise a large fraction of eukaryotic proteins, and carry out many important protein functions as ion transporter, signal transduction and cell-cell recognition. Membrane proteins consist of transmembrane domains that can attach to the cellular membranes. The protein sequences ...
... Membrane proteins compromise a large fraction of eukaryotic proteins, and carry out many important protein functions as ion transporter, signal transduction and cell-cell recognition. Membrane proteins consist of transmembrane domains that can attach to the cellular membranes. The protein sequences ...
Unit 3: Chemistry of Life
... • Peptide Bond – covalent bond between the amino (NH2) group of one amino acid and the carboxylic group (COOH) of another >Dipeptide – two amino acids bonded together >Polypeptide – 3+ amino acids bonded together ...
... • Peptide Bond – covalent bond between the amino (NH2) group of one amino acid and the carboxylic group (COOH) of another >Dipeptide – two amino acids bonded together >Polypeptide – 3+ amino acids bonded together ...
Protein structure prediction

Protein structure prediction is the prediction of the three-dimensional structure of a protein from its amino acid sequence — that is, the prediction of its folding and its secondary, tertiary, and quaternary structure from its primary structure. Structure prediction is fundamentally different from the inverse problem of protein design. Protein structure prediction is one of the most important goals pursued by bioinformatics and theoretical chemistry; it is highly important in medicine (for example, in drug design) and biotechnology (for example, in the design of novel enzymes). Every two years, the performance of current methods is assessed in the CASP experiment (Critical Assessment of Techniques for Protein Structure Prediction). A continuous evaluation of protein structure prediction web servers is performed by the community project CAMEO3D.