Name - EdWeb
... ______________________________________________________________________________ 2. What does DNA stand for? ________________________________________________________ 3. Why is DNA called a blueprint? _____________________________________________________ ________________________________________________ ...
... ______________________________________________________________________________ 2. What does DNA stand for? ________________________________________________________ 3. Why is DNA called a blueprint? _____________________________________________________ ________________________________________________ ...
Mutation
... - break in the glycosidic bond between the base and the deoxyribose sugar - results in the loss of an A or G base from the DNA -> called apurinic site - no base -> at replication, a template that is apurinic can not specify a base -> replication error -> mutation 2) Deamination - Fig 14-18(8th) 16-8 ...
... - break in the glycosidic bond between the base and the deoxyribose sugar - results in the loss of an A or G base from the DNA -> called apurinic site - no base -> at replication, a template that is apurinic can not specify a base -> replication error -> mutation 2) Deamination - Fig 14-18(8th) 16-8 ...
Genetics - StudyWise
... Pieces of DNA which have a sequence where the same base is repeated many times are called ‘slippery’. When ‘slippery’ DNA is copied during replications, errors may occur in copying. Individual bases may be copied more than once. This may give rise to differences in the protein which is produced by t ...
... Pieces of DNA which have a sequence where the same base is repeated many times are called ‘slippery’. When ‘slippery’ DNA is copied during replications, errors may occur in copying. Individual bases may be copied more than once. This may give rise to differences in the protein which is produced by t ...
DNA - Doctor Jade
... • carbon sugar-deoxyribose • nitrogenous base • 1-3 PO4 groups • contains 4 different nucleotides • each with different nitrogenous base • bases are found in 2 major groups • Purines – double ring structures – adenine (A) – guanine (G) • Pyrimidines – single ring structures – thymine (T) – cytosine ...
... • carbon sugar-deoxyribose • nitrogenous base • 1-3 PO4 groups • contains 4 different nucleotides • each with different nitrogenous base • bases are found in 2 major groups • Purines – double ring structures – adenine (A) – guanine (G) • Pyrimidines – single ring structures – thymine (T) – cytosine ...
DNA Replication Paper Lab
... alive, there must be a way to make sure every new cell gets these instructions. A new cell is made by already existing cells, therefore, there is a mechanism to copy these “life instructions” into new cells. DNA has the instructions for life coded by the order in which the nucleotides occur in a chr ...
... alive, there must be a way to make sure every new cell gets these instructions. A new cell is made by already existing cells, therefore, there is a mechanism to copy these “life instructions” into new cells. DNA has the instructions for life coded by the order in which the nucleotides occur in a chr ...
Document
... 1. What does DNA stand for? 2. What is this group of organic molecules called? 3. What is the name of the DNA structure (shape)? 4. What are the building blocks of DNA? 5. This building block consists of three components. What are they? 6. Name (not just letter) the four nitrogen bases and how the p ...
... 1. What does DNA stand for? 2. What is this group of organic molecules called? 3. What is the name of the DNA structure (shape)? 4. What are the building blocks of DNA? 5. This building block consists of three components. What are they? 6. Name (not just letter) the four nitrogen bases and how the p ...
Chapter 16 and 17 Review
... it add nucleotides 16. What is the name of the region where this enzyme binds with DNA? 17. When does transcription begin? What is the start codon? 18. What molecule is produced by prokaryotic transcription? 19. What molecule is produced by eukaryotic transcription? 20. How do the molecules produced ...
... it add nucleotides 16. What is the name of the region where this enzyme binds with DNA? 17. When does transcription begin? What is the start codon? 18. What molecule is produced by prokaryotic transcription? 19. What molecule is produced by eukaryotic transcription? 20. How do the molecules produced ...
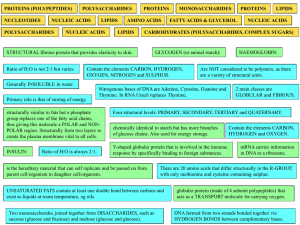
biol 3 biomolecules table activity
... chemically identical to starch but has more branches of glucose chains. Also used for energy storage. Y-shaped globular protein that is involved in the immune response by specifically binding to foreign substances. ...
... chemically identical to starch but has more branches of glucose chains. Also used for energy storage. Y-shaped globular protein that is involved in the immune response by specifically binding to foreign substances. ...
Glossary of Genetic Terms
... Translation -- the formation of a polypeptide chain in the specific amino acid sequence directed by the genetic information carried by mRNA. UNESCO -- United National Educational, Scientific, and Cultural Organization. ...
... Translation -- the formation of a polypeptide chain in the specific amino acid sequence directed by the genetic information carried by mRNA. UNESCO -- United National Educational, Scientific, and Cultural Organization. ...
Biochemistry and the Genomic Revolution
... van der Waals interactions • Based upon changing electronic charge distribution around atoms • Asymmetry of charge of one atom induces complementary asymmetry in neighboring atoms ...
... van der Waals interactions • Based upon changing electronic charge distribution around atoms • Asymmetry of charge of one atom induces complementary asymmetry in neighboring atoms ...
Biomolecules - Good Earth School
... solution and towards the anode in basic solution. Hence, at a particular pH of the solution, the amino acid molecule should not migrate to either electrode and should exist as a neutral dipolar ion. This pH is known as Isoelectric point. Denaturation of proteins: Proteins are very sensitive to the a ...
... solution and towards the anode in basic solution. Hence, at a particular pH of the solution, the amino acid molecule should not migrate to either electrode and should exist as a neutral dipolar ion. This pH is known as Isoelectric point. Denaturation of proteins: Proteins are very sensitive to the a ...
C13 Genetic Engineering
... with our gene in it. Animals also being used, like the cow that makes milk with a human protein. Plants are important transgenic organisms. In the year 2000, 52% of soybeans, and 25% of corn grown in the US were transgenic (or genetically modified). Most were modified for pesticide resistance. ...
... with our gene in it. Animals also being used, like the cow that makes milk with a human protein. Plants are important transgenic organisms. In the year 2000, 52% of soybeans, and 25% of corn grown in the US were transgenic (or genetically modified). Most were modified for pesticide resistance. ...
RNA polymerase
... (transfer RNA) - transports specific amino acids to ribosome during protein synthesis (translation). Anticodon - specific sequence of 3 nucleotides; complementary to an mRNA codon. ...
... (transfer RNA) - transports specific amino acids to ribosome during protein synthesis (translation). Anticodon - specific sequence of 3 nucleotides; complementary to an mRNA codon. ...
Gene Expression
... Though most of the genome is non-coding, the coding regions (“genes”) are what primarily determine the traits of organisms. Triplet codes found in a gene code for amino acids. The genetic code is considered to be universal. Structural and functional differences exist between DNA and the three types ...
... Though most of the genome is non-coding, the coding regions (“genes”) are what primarily determine the traits of organisms. Triplet codes found in a gene code for amino acids. The genetic code is considered to be universal. Structural and functional differences exist between DNA and the three types ...
2-centrioles & fibers disappear
... DNA, and replaced with 40. Thymine is in ______ Uracil on the _____ RNA strand. (p. 297-299 & 302) ...
... DNA, and replaced with 40. Thymine is in ______ Uracil on the _____ RNA strand. (p. 297-299 & 302) ...
You should be able to find the information necessary to answer
... You should be able to find the information necessary to answer these questions in Tortora, Funke, and Case, or in lecture. However, for a fuller understanding of the concept, or to add more detail to your answer you are encouraged to use other sources (see on-line resources by chapter) 1. Use exampl ...
... You should be able to find the information necessary to answer these questions in Tortora, Funke, and Case, or in lecture. However, for a fuller understanding of the concept, or to add more detail to your answer you are encouraged to use other sources (see on-line resources by chapter) 1. Use exampl ...
AA G
... asisDNA to “RNA gene. processing”. While average enzyme, human the mRNA key molecule molecule for has the about manufacture ...
... asisDNA to “RNA gene. processing”. While average enzyme, human the mRNA key molecule molecule for has the about manufacture ...
Topic 3 The Chemistry of Life
... Explain the process of DNA replication in prokaryotes, including the role of enzymes (helicase, DNA polymerase, RNA primase and DNA ligase), Okazaki fragments and deoxynucleoside triphosphates. o The explanation of Okazaki fragments in relation to the direction of DNA polymerase III action is requir ...
... Explain the process of DNA replication in prokaryotes, including the role of enzymes (helicase, DNA polymerase, RNA primase and DNA ligase), Okazaki fragments and deoxynucleoside triphosphates. o The explanation of Okazaki fragments in relation to the direction of DNA polymerase III action is requir ...
103 Lecture Ch22a
... Nucleosides and Nucleotides • A nucleoside consists of a nitrogen base linked by a glycosidic bond to C1’ of a ribose or deoxyribose • Nucleosides are named by changing the the nitrogen base ending to -osine for purines and –idine for pyrimidines • A nucleotide is a nucleoside that forms a phosphat ...
... Nucleosides and Nucleotides • A nucleoside consists of a nitrogen base linked by a glycosidic bond to C1’ of a ribose or deoxyribose • Nucleosides are named by changing the the nitrogen base ending to -osine for purines and –idine for pyrimidines • A nucleotide is a nucleoside that forms a phosphat ...
Biomolecule
... Carbon can share electrons with as many as four other atoms Consequently, it can form several different shapes ...
... Carbon can share electrons with as many as four other atoms Consequently, it can form several different shapes ...
Activities for Bioengineering
... • How many pieces of DNA does the child have in common with the mother? 4 • Who is the father, C or D? D, notice the DNA section not common with the mother have to be common with the father. • What is the name of this technique? ...
... • How many pieces of DNA does the child have in common with the mother? 4 • Who is the father, C or D? D, notice the DNA section not common with the mother have to be common with the father. • What is the name of this technique? ...
Which Organic Molecules Are Important For Life? 1. List the 4 major
... 1. List the 4 major groups of organic molecules that are important for life and give the main function(s) of each; for molecules that are composed of monomers, name the general type of monomer. ...
... 1. List the 4 major groups of organic molecules that are important for life and give the main function(s) of each; for molecules that are composed of monomers, name the general type of monomer. ...
Nucleic acid analogue
Nucleic acid analogues are compounds which are analogous (structurally similar) to naturally occurring RNA and DNA, used in medicine and in molecular biology research.Nucleic acids are chains of nucleotides, which are composed of three parts: a phosphate backbone, a pucker-shaped pentose sugar, either ribose or deoxyribose, and one of four nucleobases.An analogue may have any of these altered. Typically the analogue nucleobases confer, among other things, different base pairing and base stacking properties. Examples include universal bases, which can pair with all four canonical bases, and phosphate-sugar backbone analogues such as PNA, which affect the properties of the chain (PNA can even form a triple helix).Nucleic acid analogues are also called Xeno Nucleic Acid and represent one of the main pillars of xenobiology, the design of new-to-nature forms of life based on alternative biochemistries.Artificial nucleic acids include peptide nucleic acid (PNA), Morpholino and locked nucleic acid (LNA), as well as glycol nucleic acid (GNA) and threose nucleic acid (TNA). Each of these is distinguished from naturally occurring DNA or RNA by changes to the backbone of the molecule.In May 2014, researchers announced that they had successfully introduced two new artificial nucleotides into bacterial DNA, and by including individual artificial nucleotides in the culture media, were able to passage the bacteria 24 times; they did not create mRNA or proteins able to use the artificial nucleotides. The artificial nucleotides featured 2 fused aromatic rings.