
The Molecules of Life Outline
... ‐ Unfavorable temperature and pH changes can cause a protein to unravel, lose its shape and its function. ...
... ‐ Unfavorable temperature and pH changes can cause a protein to unravel, lose its shape and its function. ...
File
... Building blocks of proteins are the amino acids, each of which has a _________ group, an ________ group and a _____ chain called the R group. Proteins have complex shapes held together by _________________ bonds. Protein shapes, which determine how proteins function, can be altered by pH, temperatur ...
... Building blocks of proteins are the amino acids, each of which has a _________ group, an ________ group and a _____ chain called the R group. Proteins have complex shapes held together by _________________ bonds. Protein shapes, which determine how proteins function, can be altered by pH, temperatur ...
Ch 25 and 26 Phylogeny and The History of Life on Earth
... • Morphological- comparing body forms of current and extinct organisms • Molecular- comparing DNA; the closer the sequence the more related – Some analogous structures (wings in insect compared to a bat) may have very different molecular origins. The result of convergent evolution. ...
... • Morphological- comparing body forms of current and extinct organisms • Molecular- comparing DNA; the closer the sequence the more related – Some analogous structures (wings in insect compared to a bat) may have very different molecular origins. The result of convergent evolution. ...
Mutations - Choteau Schools
... At times, the problem is so severe that the organism does not survive. ...
... At times, the problem is so severe that the organism does not survive. ...
Reading GuideBacterialGenetics(CH8)
... on a GSA plate generating all of the necessary growth factors from glucose. If this organism (the wild-type) is mutated and the results are an organism that lacks the ability to produce the amino acid histidine, then this is now considered to be an auxotroph lacking the ability to produce histidine. ...
... on a GSA plate generating all of the necessary growth factors from glucose. If this organism (the wild-type) is mutated and the results are an organism that lacks the ability to produce the amino acid histidine, then this is now considered to be an auxotroph lacking the ability to produce histidine. ...
Gene Expression and DNA Replication
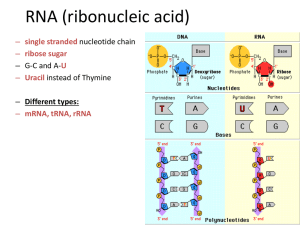
... • Two general types of nitrogenous bases Purines (two rings) Pyrimidines (one ring): Adenine (A) Cytosine (C) Guanine (G) Thymine (T) Uracil (U) – only RNA ...
... • Two general types of nitrogenous bases Purines (two rings) Pyrimidines (one ring): Adenine (A) Cytosine (C) Guanine (G) Thymine (T) Uracil (U) – only RNA ...
Central Dogma PPT
... parts transcription and translation. 1. Transcription: Process in which DNA serves as a template to produce complementary mRNA 2. Translation: Process in which mRNA is used to link amino acids together to synthesize proteins. DNA ...
... parts transcription and translation. 1. Transcription: Process in which DNA serves as a template to produce complementary mRNA 2. Translation: Process in which mRNA is used to link amino acids together to synthesize proteins. DNA ...
Sources of DNA
... Eukaryotic DNA Eukaryotic cells have several chromosomes that are long linear strands, ...
... Eukaryotic DNA Eukaryotic cells have several chromosomes that are long linear strands, ...
Transcription and Translation
... DNA •DNA double helix unwinds •DNA now single-stranded •New DNA strand forms using complementary base pairing (A-T, C-G) •Used to prepare DNA for cell division ...
... DNA •DNA double helix unwinds •DNA now single-stranded •New DNA strand forms using complementary base pairing (A-T, C-G) •Used to prepare DNA for cell division ...
國立嘉義大學九十二學年度
... (1) Nucleophilic attack of a 3' hydroxyl toward a nucleoside triphosphate, releasing PPi. (2) Nucleophilic attack of a 5' hydroxyl toward a nucleoside triphosphate, releasing PPi. (3) Nucleophilic attack of a 3' hydroxyl toward a nucleoside triphosphate, releasing Pi. (4) Nucleophilic attack of a 5' ...
... (1) Nucleophilic attack of a 3' hydroxyl toward a nucleoside triphosphate, releasing PPi. (2) Nucleophilic attack of a 5' hydroxyl toward a nucleoside triphosphate, releasing PPi. (3) Nucleophilic attack of a 3' hydroxyl toward a nucleoside triphosphate, releasing Pi. (4) Nucleophilic attack of a 5' ...
Slide 1
... deletion or insertion occurs, the more altered the protein produced is. Figure 8.17a, d ...
... deletion or insertion occurs, the more altered the protein produced is. Figure 8.17a, d ...
DNA Replication - The Biology Corner
... 2. DNA polymerase adds the complementary nucleotides and binds the sugars and phosphates. DNA polymerase travels from the 3' to the 5' end. The DNA is called the template strand. 3. DNA polymerase adds complementary nucleotides on the other side of the ladder. Traveling in the opposite direction. 4. ...
... 2. DNA polymerase adds the complementary nucleotides and binds the sugars and phosphates. DNA polymerase travels from the 3' to the 5' end. The DNA is called the template strand. 3. DNA polymerase adds complementary nucleotides on the other side of the ladder. Traveling in the opposite direction. 4. ...
Biology 30 Unit C 1 Mr. R. Peebles Biology 30
... a. Silent mutation – a change in base pairs that does not result in a change in an amino acid ie. Cysteine UGU to UGC b. Missense mutation – a change in base sequence which results in altering the codon leading to a different amino acid i.e. sickle cell anemia c. Nonsense mutation – a change in base ...
... a. Silent mutation – a change in base pairs that does not result in a change in an amino acid ie. Cysteine UGU to UGC b. Missense mutation – a change in base sequence which results in altering the codon leading to a different amino acid i.e. sickle cell anemia c. Nonsense mutation – a change in base ...
Macromolecules and Enzymes
... Effect of temperature and pH • The temperature and pH must be in check for an enzyme to be used • Sometimes that can be too high • Sometimes that can be too low • When the circumstances are too high or too low, nothing happens • When the circumstances are just right, enzymes go to work and the subs ...
... Effect of temperature and pH • The temperature and pH must be in check for an enzyme to be used • Sometimes that can be too high • Sometimes that can be too low • When the circumstances are too high or too low, nothing happens • When the circumstances are just right, enzymes go to work and the subs ...
DNA Notesheet
... DNA and Protein Synthesis Notes Directions: Use the accompanying PowerPoint (www.uhstitans.com/avid-biology) to complete this sheet. This sheet will be due the day of the test. 1. DNA is 2. It is kept in the ...
... DNA and Protein Synthesis Notes Directions: Use the accompanying PowerPoint (www.uhstitans.com/avid-biology) to complete this sheet. This sheet will be due the day of the test. 1. DNA is 2. It is kept in the ...
Biology 241 Placement Examination General
... What are nucleic acids? What do the initials stand for? Where in the cell are they found? What kinds of bonding are found in nucleotides, nucleoside, and nucleic acids? Make sure you know the differences between RNA and DNA. If I showed you a nucleotide you need to tell me if it is from DNA or RNA. ...
... What are nucleic acids? What do the initials stand for? Where in the cell are they found? What kinds of bonding are found in nucleotides, nucleoside, and nucleic acids? Make sure you know the differences between RNA and DNA. If I showed you a nucleotide you need to tell me if it is from DNA or RNA. ...
Chapter 3
... – Nitrogenous bases include • Purines: adenine and guanine • Pyrimidines: thymine, cytosine, uracil ...
... – Nitrogenous bases include • Purines: adenine and guanine • Pyrimidines: thymine, cytosine, uracil ...
Nucleic acid analogue
Nucleic acid analogues are compounds which are analogous (structurally similar) to naturally occurring RNA and DNA, used in medicine and in molecular biology research.Nucleic acids are chains of nucleotides, which are composed of three parts: a phosphate backbone, a pucker-shaped pentose sugar, either ribose or deoxyribose, and one of four nucleobases.An analogue may have any of these altered. Typically the analogue nucleobases confer, among other things, different base pairing and base stacking properties. Examples include universal bases, which can pair with all four canonical bases, and phosphate-sugar backbone analogues such as PNA, which affect the properties of the chain (PNA can even form a triple helix).Nucleic acid analogues are also called Xeno Nucleic Acid and represent one of the main pillars of xenobiology, the design of new-to-nature forms of life based on alternative biochemistries.Artificial nucleic acids include peptide nucleic acid (PNA), Morpholino and locked nucleic acid (LNA), as well as glycol nucleic acid (GNA) and threose nucleic acid (TNA). Each of these is distinguished from naturally occurring DNA or RNA by changes to the backbone of the molecule.In May 2014, researchers announced that they had successfully introduced two new artificial nucleotides into bacterial DNA, and by including individual artificial nucleotides in the culture media, were able to passage the bacteria 24 times; they did not create mRNA or proteins able to use the artificial nucleotides. The artificial nucleotides featured 2 fused aromatic rings.







![528 MISCELLANEOUS METHODS [32] [32] An Agarose Gel](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/022443032_1-e3381ebef96c7285b7f08982fb9c5a10-300x300.png)













