gene to protein 1
... e. class III mutants have nonfunctional enzymes for all three steps. 5. The anticodon of a particular tRNA molecule is a. complementary to the corresponding mRNA codon. b. complementary to the corresponding triplet in rRNA. c. the part of tRNA that bonds to a specific amino acid. d. changeable, depe ...
... e. class III mutants have nonfunctional enzymes for all three steps. 5. The anticodon of a particular tRNA molecule is a. complementary to the corresponding mRNA codon. b. complementary to the corresponding triplet in rRNA. c. the part of tRNA that bonds to a specific amino acid. d. changeable, depe ...
Chapter 3 Review Questions
... 18. __Amino_____ and ______carboxyl__ functional groups are contained within an amino acid. 19. The carbonyl functional group when located on the end of the compound is called ___carbonyl end (Aldehyde)____________. ...
... 18. __Amino_____ and ______carboxyl__ functional groups are contained within an amino acid. 19. The carbonyl functional group when located on the end of the compound is called ___carbonyl end (Aldehyde)____________. ...
File
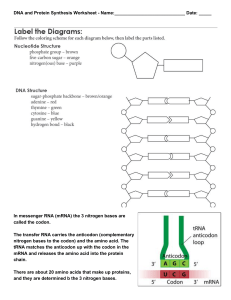
... In messenger RNA (mRNA) the 3 nitrogen bases are called the codon. The transfer RNA carries the anticodon (complementary nitrogen bases to the codon) and the amino acid. The tRNA matches the anticodon up with the codon in the mRNA and releases the amino acid into the protein chain. There are about 2 ...
... In messenger RNA (mRNA) the 3 nitrogen bases are called the codon. The transfer RNA carries the anticodon (complementary nitrogen bases to the codon) and the amino acid. The tRNA matches the anticodon up with the codon in the mRNA and releases the amino acid into the protein chain. There are about 2 ...
Clicker Review-DNAProtein Syn Mutation
... discovery of the structure of DNA? 1. Rosalind Franklin 2. Francis Crick 3. James Watson 4. Gregor Mendel 5. Both 2 and 3 ...
... discovery of the structure of DNA? 1. Rosalind Franklin 2. Francis Crick 3. James Watson 4. Gregor Mendel 5. Both 2 and 3 ...
Ch 9-11 Review - HensonsBiologyPage
... term best describes this process? A. adaptation B. mutation C. natural selection D. genetic engineering ...
... term best describes this process? A. adaptation B. mutation C. natural selection D. genetic engineering ...
Chromosomes, Alleles, Genes, Mutations
... One of the main reasons for karyotyping is to find out whether a fetus has Down Syndrome or other chromosomal abnormalities. ...
... One of the main reasons for karyotyping is to find out whether a fetus has Down Syndrome or other chromosomal abnormalities. ...
Carbon Compounds
... most things to ‘happen’ in a cell! • Without proteins the most basic functions of life could not be carried out. • Respiration, for example, requires muscle contractions, and muscle contractions require proteins. ...
... most things to ‘happen’ in a cell! • Without proteins the most basic functions of life could not be carried out. • Respiration, for example, requires muscle contractions, and muscle contractions require proteins. ...
HIV-1 Reverse Transcriptase
... The dsDNA bound to the RT (2HMI) has a hybrid structure. The five base-pairs near the polymerase active site have a conformation similar to A-form DNA, while the nine basepairs towards the RNase active site have a conformation similar to B-form DNA. There is a significant bend involving the four ba ...
... The dsDNA bound to the RT (2HMI) has a hybrid structure. The five base-pairs near the polymerase active site have a conformation similar to A-form DNA, while the nine basepairs towards the RNase active site have a conformation similar to B-form DNA. There is a significant bend involving the four ba ...
Ch .15 - Crestwood Local Schools
... Could produce 38,000 different polypeptides Many of these polypeptides have been found ...
... Could produce 38,000 different polypeptides Many of these polypeptides have been found ...
mutations
... Somatic mutations: mutations that take place in the body cells DNA , but do not affect their offspring. FYI- albinism can be the result of a somatic or germ-line mutation ...
... Somatic mutations: mutations that take place in the body cells DNA , but do not affect their offspring. FYI- albinism can be the result of a somatic or germ-line mutation ...
DNA and RNA
... • Before a cell divides, it copies its DNA in a process called replication. During DNA replication, – The DNA molecule separates into two strands. Each new strand of the DNA molecule serves as a model for the new strand. – Following the rules of basic pairing, new bases are added to each strand. For ...
... • Before a cell divides, it copies its DNA in a process called replication. During DNA replication, – The DNA molecule separates into two strands. Each new strand of the DNA molecule serves as a model for the new strand. – Following the rules of basic pairing, new bases are added to each strand. For ...
12-4 Mutations - Lincoln Park High School
... insertion or deletion a)The addition or deletion of a nucleotide causes a shift in the grouping of codons b)Can change every amino acid that follows the point of the mutation c) can change a protein so much that it does not work normally ...
... insertion or deletion a)The addition or deletion of a nucleotide causes a shift in the grouping of codons b)Can change every amino acid that follows the point of the mutation c) can change a protein so much that it does not work normally ...
transcription - Geneticskippnyc
... made in the nucleus and sent out to a ribosome. The ribosome reads the mRNA message and makes a protein containing 120 amino acids. The mRNA consisted of at least how many codons? ...
... made in the nucleus and sent out to a ribosome. The ribosome reads the mRNA message and makes a protein containing 120 amino acids. The mRNA consisted of at least how many codons? ...
Document
... system, which involves a series of proteins that can carry out the energy transfer reactions. Note the role of atmospheric oxygen in this! ...
... system, which involves a series of proteins that can carry out the energy transfer reactions. Note the role of atmospheric oxygen in this! ...
October 3, 2016 Worksheet
... Do we use introns or exons? Draw a strand of DNA that contains silencer, repressor, basal transcription factors, TATA box, (transcription factors): https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=ysxtZJUeTCE Why does these processes need to happen? ...
... Do we use introns or exons? Draw a strand of DNA that contains silencer, repressor, basal transcription factors, TATA box, (transcription factors): https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=ysxtZJUeTCE Why does these processes need to happen? ...
Seventh Grade 2nd Quarter CRT Review
... 2. **What happens before mitosis begins? The cell grows and copies its DNA. 3. Why are chromosomes even numbers? So that they may divide in half because one comes from mom and one from dad. 4. A change in ocean current causes the climate on an island to become drier. As a result, the grasses that co ...
... 2. **What happens before mitosis begins? The cell grows and copies its DNA. 3. Why are chromosomes even numbers? So that they may divide in half because one comes from mom and one from dad. 4. A change in ocean current causes the climate on an island to become drier. As a result, the grasses that co ...
DNA
... Erwin Chargaff studied the DNA of organisms within a single species. Chargaff discovered that the amount of adenine is about equal to the amount of thymine. Which of these explains why the ratio of adenine to thymine is nearly 1:1? A Adenine and thymine pair with each other. B Adenine binds with pho ...
... Erwin Chargaff studied the DNA of organisms within a single species. Chargaff discovered that the amount of adenine is about equal to the amount of thymine. Which of these explains why the ratio of adenine to thymine is nearly 1:1? A Adenine and thymine pair with each other. B Adenine binds with pho ...
Lesson Plan
... how information for specifying a trait of an organism is carried in the DNA. 6B(S): SWBAT recognize that components that make up the genetic code are common to all organisms. 6C (S) Explain the purpose and ...
... how information for specifying a trait of an organism is carried in the DNA. 6B(S): SWBAT recognize that components that make up the genetic code are common to all organisms. 6C (S) Explain the purpose and ...
Virus -Consists or a nucleic acid surrounded by a protein coat
... -Viruses have a limited host range. This means that they can infect only a very limited variety of hosts. Ex: Human cold virus infects only cells of the upper respiratory tract -Viral reproduction occurs only in the host cells; Two variations have been studied in viruses: --Lytic Cycle --Lysogenic C ...
... -Viruses have a limited host range. This means that they can infect only a very limited variety of hosts. Ex: Human cold virus infects only cells of the upper respiratory tract -Viral reproduction occurs only in the host cells; Two variations have been studied in viruses: --Lytic Cycle --Lysogenic C ...
Nucleic acid analogue
Nucleic acid analogues are compounds which are analogous (structurally similar) to naturally occurring RNA and DNA, used in medicine and in molecular biology research.Nucleic acids are chains of nucleotides, which are composed of three parts: a phosphate backbone, a pucker-shaped pentose sugar, either ribose or deoxyribose, and one of four nucleobases.An analogue may have any of these altered. Typically the analogue nucleobases confer, among other things, different base pairing and base stacking properties. Examples include universal bases, which can pair with all four canonical bases, and phosphate-sugar backbone analogues such as PNA, which affect the properties of the chain (PNA can even form a triple helix).Nucleic acid analogues are also called Xeno Nucleic Acid and represent one of the main pillars of xenobiology, the design of new-to-nature forms of life based on alternative biochemistries.Artificial nucleic acids include peptide nucleic acid (PNA), Morpholino and locked nucleic acid (LNA), as well as glycol nucleic acid (GNA) and threose nucleic acid (TNA). Each of these is distinguished from naturally occurring DNA or RNA by changes to the backbone of the molecule.In May 2014, researchers announced that they had successfully introduced two new artificial nucleotides into bacterial DNA, and by including individual artificial nucleotides in the culture media, were able to passage the bacteria 24 times; they did not create mRNA or proteins able to use the artificial nucleotides. The artificial nucleotides featured 2 fused aromatic rings.