DNA Replication: Seeing Double
... the Leading and Lagging strands two complete strands of DNA separate from one another. ...
... the Leading and Lagging strands two complete strands of DNA separate from one another. ...
Protein - DNA interaction in chromatin
... tRNA act as 'carriers' of amino acids during protein synthesis. They have a characteristic 'clover leaf' structure and they are relatively small, 73-93 nucleotides long. rRNa is a structual component of ribosomes. The molecules consist of single strands of RNA. The specific function of rRNA is not f ...
... tRNA act as 'carriers' of amino acids during protein synthesis. They have a characteristic 'clover leaf' structure and they are relatively small, 73-93 nucleotides long. rRNa is a structual component of ribosomes. The molecules consist of single strands of RNA. The specific function of rRNA is not f ...
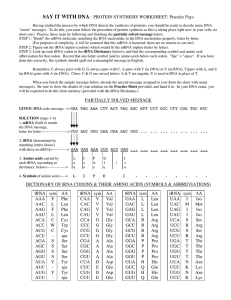
SAY IT WITH DNA: PROTEIN SYNTHESIS WORKSHEET: Practice
... SAY IT WITH DNA: PROTEIN SYNTHESIS WORKSHEET: Practice Pays Having studied the process by which DNA directs the synthesis of proteins, you should be ready to decode some DNA "secret" messages. To do this, you must follow the procedure of protein synthesis as this is taking place right now in your ce ...
... SAY IT WITH DNA: PROTEIN SYNTHESIS WORKSHEET: Practice Pays Having studied the process by which DNA directs the synthesis of proteins, you should be ready to decode some DNA "secret" messages. To do this, you must follow the procedure of protein synthesis as this is taking place right now in your ce ...
AP Exam 5 Study Guide
... Step 1- DNA is unwound with an enzyme called helicase. This causes a replication fork to form. The replication fork is stabilized with single-stranded binding proteins. There are multiple replication forks in a DNA molecule at one time. Step 2- New nucleotides are brought in to match up to the templ ...
... Step 1- DNA is unwound with an enzyme called helicase. This causes a replication fork to form. The replication fork is stabilized with single-stranded binding proteins. There are multiple replication forks in a DNA molecule at one time. Step 2- New nucleotides are brought in to match up to the templ ...
DNA 2 - Website of Neelay Gandhi
... 67% of ribosome is RNA 33% is protein Eukaryote 60S + 40S = 80S 60S = 28S + 5.8S + 5S + 50 proteins 40S = 18S + 30 proteins tRNA Codon is on mRNA Anticodon is on tRNA Base pairs with codon on mRNA corresponding to an amino acid that tRNA carries Different tRNA have different anticodons Codon – Antic ...
... 67% of ribosome is RNA 33% is protein Eukaryote 60S + 40S = 80S 60S = 28S + 5.8S + 5S + 50 proteins 40S = 18S + 30 proteins tRNA Codon is on mRNA Anticodon is on tRNA Base pairs with codon on mRNA corresponding to an amino acid that tRNA carries Different tRNA have different anticodons Codon – Antic ...
Protein Synthesis
... Mutations may be harmful and may be the cause of many genetic disorders and cancer. Source of genetic variability in a species (may be highly beneficial). ...
... Mutations may be harmful and may be the cause of many genetic disorders and cancer. Source of genetic variability in a species (may be highly beneficial). ...
Genetic Technology
... process of making changes in the DNA code of living organisms uses DNA technology to cure diseases, treat genetic disorders, improve food crops, etc. ...
... process of making changes in the DNA code of living organisms uses DNA technology to cure diseases, treat genetic disorders, improve food crops, etc. ...
Protein Synthesis Activity
... DNA and RNA, the two types of nucleic acids found in cells, determine which protein molecules a cell makes, or synthesizes. Protein molecules, formed by sequencing twenty different amino acids in various combinations, are important to living things because they control biological pathways, direct th ...
... DNA and RNA, the two types of nucleic acids found in cells, determine which protein molecules a cell makes, or synthesizes. Protein molecules, formed by sequencing twenty different amino acids in various combinations, are important to living things because they control biological pathways, direct th ...
DNA Review Questions (answers) no applications
... 2. What are Chargaff’s rules? How did they help in determining the structure of DNA? That in any sample of DNA, the concentration of A = concentration of T and C = G. This helped Watson and Crick confirm their idea that A would bind (via hydrogen bonds) to T and C would bind to G base pairing rule ...
... 2. What are Chargaff’s rules? How did they help in determining the structure of DNA? That in any sample of DNA, the concentration of A = concentration of T and C = G. This helped Watson and Crick confirm their idea that A would bind (via hydrogen bonds) to T and C would bind to G base pairing rule ...
Biomolecules - Kendriya Vidyalaya, Bailey Road, Patna
... deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) and ribonucleic acid(RNA). nucleic acids are long chain polymers of nucleotides, so they are also called polynucleotides. DNA contains four bases viz. adenine (A), guanine (G), cytosine (C) and thymine (T). RNA also contains four bases, the first three bases are s ...
... deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) and ribonucleic acid(RNA). nucleic acids are long chain polymers of nucleotides, so they are also called polynucleotides. DNA contains four bases viz. adenine (A), guanine (G), cytosine (C) and thymine (T). RNA also contains four bases, the first three bases are s ...
DNA Detectives What is Your DNA Alias? The central dogma of
... We use four letters to code all the information contained in DNA: A, T, C and G. The letters are used in groups of three. A group is called a codon. DNA contains the information that is needed by your body to make proteins. The different proteins have specific functions, such as making our hearts, h ...
... We use four letters to code all the information contained in DNA: A, T, C and G. The letters are used in groups of three. A group is called a codon. DNA contains the information that is needed by your body to make proteins. The different proteins have specific functions, such as making our hearts, h ...
180-183
... factor from heat-killed bacteria of one strain could change the inherited characteristics of another strain. He called the process transformation because one type of bacteria (a harmless form) had been changed permanently into another (a disease-carrying form). Because the ability to cause disease w ...
... factor from heat-killed bacteria of one strain could change the inherited characteristics of another strain. He called the process transformation because one type of bacteria (a harmless form) had been changed permanently into another (a disease-carrying form). Because the ability to cause disease w ...
Week 5
... Because DNA polymerase will bind only to double-stranded nucleic acid it is necessary to produce a hybrid DNA-RNA strand on the single-stranded template strand of DNA before replication of that sequence can begin. The RNA is referred to as primer RNA Procaryotes: ...
... Because DNA polymerase will bind only to double-stranded nucleic acid it is necessary to produce a hybrid DNA-RNA strand on the single-stranded template strand of DNA before replication of that sequence can begin. The RNA is referred to as primer RNA Procaryotes: ...
Chapter 2 Review PPT
... Kind of chemical reaction used by cells to join molecules together by removing an H and OH to make a water molecule ...
... Kind of chemical reaction used by cells to join molecules together by removing an H and OH to make a water molecule ...
DNA upgrade supplement WITH PICS
... membered rings attached to pyrimidine type of rings. The two DNA pyrimidines are named cytosine and thymine, and the two purines are adenine and guanine. These bases are commonly abbreviated as C, T, A, and G. Also, it helps to remember which nitrogenous bases are pyrimidines if you note that thymin ...
... membered rings attached to pyrimidine type of rings. The two DNA pyrimidines are named cytosine and thymine, and the two purines are adenine and guanine. These bases are commonly abbreviated as C, T, A, and G. Also, it helps to remember which nitrogenous bases are pyrimidines if you note that thymin ...
DNA Packaging - kyoussef-mci
... repeating sequences can be of any length usually 2 – 6 NTs sequence repeated a different amount of times ...
... repeating sequences can be of any length usually 2 – 6 NTs sequence repeated a different amount of times ...
Chapter 2 - SCHOOLinSITES
... • Very hydrophobic: hate water • Examples: fats and oils, triglycerides and phospholipids • Functions: stored energy (triglycerides), components of cell structures like the cell membrane (phosopholipids and cholesterol) ...
... • Very hydrophobic: hate water • Examples: fats and oils, triglycerides and phospholipids • Functions: stored energy (triglycerides), components of cell structures like the cell membrane (phosopholipids and cholesterol) ...
GENE MUTATION = POINT MUTATION at the DNA level: at the level
... Spontaneous mutations: a mutation that occurs in the absence of known mutagens • uncorrected errors* that occur during DNA replication, repair or recombination • spontaneous lesions that occur to the DNA molecule under normal physiological conditions and that are not repaired by the cell’s DNA exci ...
... Spontaneous mutations: a mutation that occurs in the absence of known mutagens • uncorrected errors* that occur during DNA replication, repair or recombination • spontaneous lesions that occur to the DNA molecule under normal physiological conditions and that are not repaired by the cell’s DNA exci ...
Key to Protein Synthesis Vocabulary
... a mutation occurring when the number of nucleotides inserted or deleted is not a multiple of three. This results in the improper grouping of the following nucleotides into codons a mutation involving the addition of one or more nucleotide pairs to a gene ...
... a mutation occurring when the number of nucleotides inserted or deleted is not a multiple of three. This results in the improper grouping of the following nucleotides into codons a mutation involving the addition of one or more nucleotide pairs to a gene ...
biol-1406_ch3notes.ppt
... 3.5. What Are Proteins? • Proteins are formed from chains of ______ ______ (monomers; _____ different) • The _______________________ of amino acids in a protein dictates its function ...
... 3.5. What Are Proteins? • Proteins are formed from chains of ______ ______ (monomers; _____ different) • The _______________________ of amino acids in a protein dictates its function ...
biol-1406_ch3notes.pdf
... 3.1. Why Is Carbon So Important in Biological Molecules? • Each carbon can form up to ______ bonds (single(2 electrons), double, or triple) and rings • Carbon makes bonds mostly with ________ ________________ in living systems • Biomolecules are large and contain _______ _____________ attached to th ...
... 3.1. Why Is Carbon So Important in Biological Molecules? • Each carbon can form up to ______ bonds (single(2 electrons), double, or triple) and rings • Carbon makes bonds mostly with ________ ________________ in living systems • Biomolecules are large and contain _______ _____________ attached to th ...
Nucleic acid analogue
Nucleic acid analogues are compounds which are analogous (structurally similar) to naturally occurring RNA and DNA, used in medicine and in molecular biology research.Nucleic acids are chains of nucleotides, which are composed of three parts: a phosphate backbone, a pucker-shaped pentose sugar, either ribose or deoxyribose, and one of four nucleobases.An analogue may have any of these altered. Typically the analogue nucleobases confer, among other things, different base pairing and base stacking properties. Examples include universal bases, which can pair with all four canonical bases, and phosphate-sugar backbone analogues such as PNA, which affect the properties of the chain (PNA can even form a triple helix).Nucleic acid analogues are also called Xeno Nucleic Acid and represent one of the main pillars of xenobiology, the design of new-to-nature forms of life based on alternative biochemistries.Artificial nucleic acids include peptide nucleic acid (PNA), Morpholino and locked nucleic acid (LNA), as well as glycol nucleic acid (GNA) and threose nucleic acid (TNA). Each of these is distinguished from naturally occurring DNA or RNA by changes to the backbone of the molecule.In May 2014, researchers announced that they had successfully introduced two new artificial nucleotides into bacterial DNA, and by including individual artificial nucleotides in the culture media, were able to passage the bacteria 24 times; they did not create mRNA or proteins able to use the artificial nucleotides. The artificial nucleotides featured 2 fused aromatic rings.