03. Metabolism of lipids
... • Lipids are water-insoluble organic biomolecules that can be extracted from cells and tissues by nonpolar solvents, e.g., chloroform, ether, or benzene. ...
... • Lipids are water-insoluble organic biomolecules that can be extracted from cells and tissues by nonpolar solvents, e.g., chloroform, ether, or benzene. ...
22: Peptides, Proteins, and
... chains (the R groups) with each other and with the medium surrounding the protein. These interactions involve electrostatic forces, hydrogen bonding, hydrophobic bonding, and disulfide bonds. [graphic 22.33] We will see below that the same forces also bind together the multiple peptide chains of a p ...
... chains (the R groups) with each other and with the medium surrounding the protein. These interactions involve electrostatic forces, hydrogen bonding, hydrophobic bonding, and disulfide bonds. [graphic 22.33] We will see below that the same forces also bind together the multiple peptide chains of a p ...
Alu Background Information
... First, the inserted Alu is transcribed into messenger RNA by the cellular RNA polymerase. Then, the mRNA is converted to a double-stranded DNA molecule by reverse transcriptase. Finally, the DNA copy of Alu is integrated into a new chromosomal locus at the site of a single- or double-stranded break. ...
... First, the inserted Alu is transcribed into messenger RNA by the cellular RNA polymerase. Then, the mRNA is converted to a double-stranded DNA molecule by reverse transcriptase. Finally, the DNA copy of Alu is integrated into a new chromosomal locus at the site of a single- or double-stranded break. ...
Organic Molecules chapt03
... Some proteins contain more than one polypeptide chain. Each of these polypeptides has its own unique tertiary structure. ...
... Some proteins contain more than one polypeptide chain. Each of these polypeptides has its own unique tertiary structure. ...
VOLATILE COMPOUNDS AND AMINO ACIDS IN CHEESE
... product γ-aminobutyric acid (GABA), which has been shown to contribute to sour and umami as well as astringent sensations. The taste characteristic and taste threshold of α-aminobutyric acid (AABA) has not been well established, but due to its structural resemblance with glutamic acid it may also be ...
... product γ-aminobutyric acid (GABA), which has been shown to contribute to sour and umami as well as astringent sensations. The taste characteristic and taste threshold of α-aminobutyric acid (AABA) has not been well established, but due to its structural resemblance with glutamic acid it may also be ...
Demarcation of coding and non-coding regions of DNA using linear
... Deoxyribonucleic Acid (DNA) strand carries genetic information in the cell. A strand of DNA consists of nitrogenous molecules called nucleotides. Nucleotides triplets, or the codons, code for amino acids. There are two distinct regions in DNA, the gene and the intergenic DNA, or the junk DNA. Two re ...
... Deoxyribonucleic Acid (DNA) strand carries genetic information in the cell. A strand of DNA consists of nitrogenous molecules called nucleotides. Nucleotides triplets, or the codons, code for amino acids. There are two distinct regions in DNA, the gene and the intergenic DNA, or the junk DNA. Two re ...
ThermalAce™ DNA Polymerase
... Limited Use Label License No. 82: ThermalAce™ Enzyme Life Technologies has an exclusive license under US Patent No. 5,948,666, pending US patent applications and corresponding foreign patents and patent applications owned and licensed by Verenium Corporation to sell the ThermalAce™ enzyme to scienti ...
... Limited Use Label License No. 82: ThermalAce™ Enzyme Life Technologies has an exclusive license under US Patent No. 5,948,666, pending US patent applications and corresponding foreign patents and patent applications owned and licensed by Verenium Corporation to sell the ThermalAce™ enzyme to scienti ...
handout
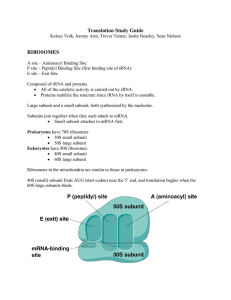
... AUG start codon. 2. Next, the tRNA and small sub-unit complex bind to translation initiation factors and attach to the 5’ cap of the mature mRNA. 3. Next, the entire complex scans in the 3’ direction until it finds the AUG start codon of the mRNA 4. Lastly, the 60S large sub-unit binds to the comple ...
... AUG start codon. 2. Next, the tRNA and small sub-unit complex bind to translation initiation factors and attach to the 5’ cap of the mature mRNA. 3. Next, the entire complex scans in the 3’ direction until it finds the AUG start codon of the mRNA 4. Lastly, the 60S large sub-unit binds to the comple ...
Lesson 1 – Introduction to Biotechnology
... This lab allows the students to practice their copying and replication of DNA. They need a basic understanding of what is all involved in biotechnology before moving on to future lessons. In order for students to understand how DNA replicates they need to understand how to copy DNA. Before class, cr ...
... This lab allows the students to practice their copying and replication of DNA. They need a basic understanding of what is all involved in biotechnology before moving on to future lessons. In order for students to understand how DNA replicates they need to understand how to copy DNA. Before class, cr ...
fatty acids: straight-chain saturated
... not listed the more obscure of these (a comprehensive list is available on the AOCS web site (see our Links page). However, this advice is perhaps too pedantic for the most common of them. Long-chain saturated fatty acids (12:0 upwards) have relatively high melting points. Animal fats and seed oils ...
... not listed the more obscure of these (a comprehensive list is available on the AOCS web site (see our Links page). However, this advice is perhaps too pedantic for the most common of them. Long-chain saturated fatty acids (12:0 upwards) have relatively high melting points. Animal fats and seed oils ...
Level of endogenous free amino acids during various stages of
... The present study was designed to evaluate the endogenous levels of different amino acids associated with a particular state of in vitro development, i.e. embryogenic or regenerating tissue and regenerated shoots of Vigna mungo (L.) Hepper, one of the most important pulse crops of India. Plant regen ...
... The present study was designed to evaluate the endogenous levels of different amino acids associated with a particular state of in vitro development, i.e. embryogenic or regenerating tissue and regenerated shoots of Vigna mungo (L.) Hepper, one of the most important pulse crops of India. Plant regen ...
A fatty acid
... carboxly -COOH group at the head. • Saturated - no double bonds; saturated with H • Unsaturated - one or more H replaced by double bond - stays liquid – Carboxyl groups on fatty acid link to -OH group on a 3-carbon alcohol (glycerol) ...
... carboxly -COOH group at the head. • Saturated - no double bonds; saturated with H • Unsaturated - one or more H replaced by double bond - stays liquid – Carboxyl groups on fatty acid link to -OH group on a 3-carbon alcohol (glycerol) ...
CB3 - Homework
... backbones or ‘spines’ joined together by ‘rungs’. Each rung is made of substances called ‘bases’. Each rung contains two bases, which are joined together. We describe this as a ‘base pair’. You will need a copy of the second page of this sheet on a separate piece of paper. A The base pairs are shown ...
... backbones or ‘spines’ joined together by ‘rungs’. Each rung is made of substances called ‘bases’. Each rung contains two bases, which are joined together. We describe this as a ‘base pair’. You will need a copy of the second page of this sheet on a separate piece of paper. A The base pairs are shown ...
Ch 18 - Bob Bruner`s Chemistry and Molecular Biology Resources
... tool in genome analysis -- to predict highly expressed genes. [There are other reasons, not relating to tRNA availability, why a change between synonymous codons might not be as neutral as expected from just reading the code. A base change may affect the mRNA 2° structure, and this may affect transl ...
... tool in genome analysis -- to predict highly expressed genes. [There are other reasons, not relating to tRNA availability, why a change between synonymous codons might not be as neutral as expected from just reading the code. A base change may affect the mRNA 2° structure, and this may affect transl ...
WHAT ARE NEURAL TUBE DEFECTS (NTDs)?
... Essential for creating heme, the iron containing substance in haemoglobin [1] Proper formation of the brain, spinal cord, and nerve cells in the embryo. Closure of the neural tube in the fetus cannot be completed without it (Northrup H, 2000). Essential for synthesis of serine, methionine, ATP, GTP, ...
... Essential for creating heme, the iron containing substance in haemoglobin [1] Proper formation of the brain, spinal cord, and nerve cells in the embryo. Closure of the neural tube in the fetus cannot be completed without it (Northrup H, 2000). Essential for synthesis of serine, methionine, ATP, GTP, ...
Lecture 5 PP
... The selection of the correct amino acid must be highly accurate or the polypeptides may be nonfunctional Error rate is less than one in every 100,000 Sequences throughout the tRNA including but not limited to the anticodon are used as recognition sites ...
... The selection of the correct amino acid must be highly accurate or the polypeptides may be nonfunctional Error rate is less than one in every 100,000 Sequences throughout the tRNA including but not limited to the anticodon are used as recognition sites ...
Spider Silk - Consortium for Mathematics and its Applications
... The information in DNA is encoded using four different nucleotides: adenine (A), guanine (G), cytosine (C), and thymine (T). These nucleotides are connected together sequentially along a phosphate-sugar backbone. The order of these nucleotides in this sequence determines the information that can be ...
... The information in DNA is encoded using four different nucleotides: adenine (A), guanine (G), cytosine (C), and thymine (T). These nucleotides are connected together sequentially along a phosphate-sugar backbone. The order of these nucleotides in this sequence determines the information that can be ...
tryptophan operon - Biology Notes Help
... The mRNA transcript of the leader region includes a sequence that can be translated to produce a short polypeptide. Just before the stop codon of the transcript, two adjacent codon for tryptophan present that play an important role in attenuation. There are four regions of the leader peptide mRNA th ...
... The mRNA transcript of the leader region includes a sequence that can be translated to produce a short polypeptide. Just before the stop codon of the transcript, two adjacent codon for tryptophan present that play an important role in attenuation. There are four regions of the leader peptide mRNA th ...
Action
... Antimetabolites are usually closely related to the structure of metabolite. They are derivatives of the building blocks of DNA itself, such as the nucleoside based inhibitors, or analogs of critical cofactors such as the antifolates. ...
... Antimetabolites are usually closely related to the structure of metabolite. They are derivatives of the building blocks of DNA itself, such as the nucleoside based inhibitors, or analogs of critical cofactors such as the antifolates. ...
Structure of Porphobilinogen Synthase from Pseudomonas
... of two molecules of aminolevulinic acid (ALA). Crystal structures of PBGS from various sources confirm the presence of two distinct binding sites for each ALA molecule, termed A and P. We have solved the structure of the active-site variant D139N of the Mg2þ-dependent PBGS from Pseudomonas aeruginos ...
... of two molecules of aminolevulinic acid (ALA). Crystal structures of PBGS from various sources confirm the presence of two distinct binding sites for each ALA molecule, termed A and P. We have solved the structure of the active-site variant D139N of the Mg2þ-dependent PBGS from Pseudomonas aeruginos ...
Nucleic acid analogue
Nucleic acid analogues are compounds which are analogous (structurally similar) to naturally occurring RNA and DNA, used in medicine and in molecular biology research.Nucleic acids are chains of nucleotides, which are composed of three parts: a phosphate backbone, a pucker-shaped pentose sugar, either ribose or deoxyribose, and one of four nucleobases.An analogue may have any of these altered. Typically the analogue nucleobases confer, among other things, different base pairing and base stacking properties. Examples include universal bases, which can pair with all four canonical bases, and phosphate-sugar backbone analogues such as PNA, which affect the properties of the chain (PNA can even form a triple helix).Nucleic acid analogues are also called Xeno Nucleic Acid and represent one of the main pillars of xenobiology, the design of new-to-nature forms of life based on alternative biochemistries.Artificial nucleic acids include peptide nucleic acid (PNA), Morpholino and locked nucleic acid (LNA), as well as glycol nucleic acid (GNA) and threose nucleic acid (TNA). Each of these is distinguished from naturally occurring DNA or RNA by changes to the backbone of the molecule.In May 2014, researchers announced that they had successfully introduced two new artificial nucleotides into bacterial DNA, and by including individual artificial nucleotides in the culture media, were able to passage the bacteria 24 times; they did not create mRNA or proteins able to use the artificial nucleotides. The artificial nucleotides featured 2 fused aromatic rings.