Answers chapter 9
... enzymes MutS, MutL, and MutH. MutS first scans the DNA, looking specifically for distortions in the DNA backbone that are characteristic of mismatched base pairs. Once MutS localizes a mismatch, it binds to the site and recruits the MutL protein. MutL then induces the MutH enzyme to make an incision ...
... enzymes MutS, MutL, and MutH. MutS first scans the DNA, looking specifically for distortions in the DNA backbone that are characteristic of mismatched base pairs. Once MutS localizes a mismatch, it binds to the site and recruits the MutL protein. MutL then induces the MutH enzyme to make an incision ...
Protein Synthesis Powerpoint
... A tRNA molecule is a small piece of RNA that has a specific amino acid attached to it. ...
... A tRNA molecule is a small piece of RNA that has a specific amino acid attached to it. ...
交通大學特色研究計畫邀請 - 國立交通大學生物資訊研究所
... Both prokaryotic and eukaryotic chromosomes are organized into many independent topological domains. These topological domains may be formed through constraining each DNA end from rotating by interacting with nuclear proteins, i.e., DNA-binding proteins. However, so far, evidence to support this hyp ...
... Both prokaryotic and eukaryotic chromosomes are organized into many independent topological domains. These topological domains may be formed through constraining each DNA end from rotating by interacting with nuclear proteins, i.e., DNA-binding proteins. However, so far, evidence to support this hyp ...
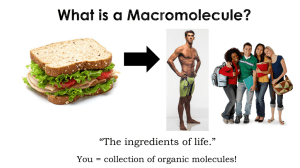
The ingredients of life. - Waterford Public Schools
... Organic compounds all contain… carbon! Carbon is special. It’s atomic properties cause it to easily bond with lots of other atoms and molecules. Carbon atoms love to form strong bonds to other carbon atoms, creating chains and rings. ...
... Organic compounds all contain… carbon! Carbon is special. It’s atomic properties cause it to easily bond with lots of other atoms and molecules. Carbon atoms love to form strong bonds to other carbon atoms, creating chains and rings. ...
Chemistry Option B: Human Biochemistry
... the nucleotides condense/form a phosphodiester bond; between the C3 of the sugar and a neighbouring phosphate group; bases form a part of nucleotide in DNA by bases are covalently bonded to deoxyribose/pentose sugar; bond via a condensation reaction with the sugar / N from the thymine bonds ...
... the nucleotides condense/form a phosphodiester bond; between the C3 of the sugar and a neighbouring phosphate group; bases form a part of nucleotide in DNA by bases are covalently bonded to deoxyribose/pentose sugar; bond via a condensation reaction with the sugar / N from the thymine bonds ...
Theory of PCR and its Applications
... The idea for PCR is credited to Kary Mullis who was a research scientist in the 1980s at a California biotechnology company called Cetus (bought out by Chiron). Mullis, and five other researchers in the Human Genetics Department at Cetus, demonstrated that oligonucleotide primers could be used to sp ...
... The idea for PCR is credited to Kary Mullis who was a research scientist in the 1980s at a California biotechnology company called Cetus (bought out by Chiron). Mullis, and five other researchers in the Human Genetics Department at Cetus, demonstrated that oligonucleotide primers could be used to sp ...
biochemistry - Bioscience High School
... shape changes. An incorrect shape can not bond with other molecules correctly and the enzyme does not function. Denaturalization occurs by ...
... shape changes. An incorrect shape can not bond with other molecules correctly and the enzyme does not function. Denaturalization occurs by ...
MUTATIONS, MUTAGENESIS, AND CARCINOGENESIS
... •Somatic vs. germline mutations Is a mutation inherited? •Loss of function vs. gain of function Is a new “allele” dominant/recessive/co-dominant? •How do new mutations spread (or decline) in a ...
... •Somatic vs. germline mutations Is a mutation inherited? •Loss of function vs. gain of function Is a new “allele” dominant/recessive/co-dominant? •How do new mutations spread (or decline) in a ...
Nomenclature for incompletely specified bases in nucleic acid
... 'NNNNNCNNGNTNN'with'-----C--G-T--, for example. Note that the use of the lower-case letter n may avoid the necessity for an additional symbol, as in 'nnnnnCnnGnTnn'. In addition, the use of the oblique or slash / may present advantages in the definition of the precise cleavage sites of restriction e ...
... 'NNNNNCNNGNTNN'with'-----C--G-T--, for example. Note that the use of the lower-case letter n may avoid the necessity for an additional symbol, as in 'nnnnnCnnGnTnn'. In addition, the use of the oblique or slash / may present advantages in the definition of the precise cleavage sites of restriction e ...
File
... b. Change of less than three caused reading c. Concluded code was simple , not punctuated 4. Determination of words of code a. Added artificial RNA to cell-free RNA and protein b. Poly-U resulted in synthesis of polyphenylalanine c. Concluded UUU coded for phenylalanine d. Repeated for all other tri ...
... b. Change of less than three caused reading c. Concluded code was simple , not punctuated 4. Determination of words of code a. Added artificial RNA to cell-free RNA and protein b. Poly-U resulted in synthesis of polyphenylalanine c. Concluded UUU coded for phenylalanine d. Repeated for all other tri ...
Ch. 2 A&P
... • ATP is a RNA nucleotide containing adenine with two additional phosphate groups attached. • When bonds (high energy bonds) between phosphate groups are broken, energy is released. • When phosphate group is lost, resulting molecule is ...
... • ATP is a RNA nucleotide containing adenine with two additional phosphate groups attached. • When bonds (high energy bonds) between phosphate groups are broken, energy is released. • When phosphate group is lost, resulting molecule is ...
Chapter 3 Test Review
... Carbon Hydrogen Oxygen Ratio is 1 Carbon : 2 Hydrogen : 1 Oxygen The large molecules can be broken down into smaller that are exactly alike. ...
... Carbon Hydrogen Oxygen Ratio is 1 Carbon : 2 Hydrogen : 1 Oxygen The large molecules can be broken down into smaller that are exactly alike. ...
Solutions - Vanier College
... 14. Which of the following represents the correct ordering of the molecules that are activated by a single molecule of epinephrine, from highest number of molecules to lowest number of molecules? a. cAMP, protein kinase A, phosphorylase kinase, glycogen phosphorylase b. Glycogen phosphorylase, phosp ...
... 14. Which of the following represents the correct ordering of the molecules that are activated by a single molecule of epinephrine, from highest number of molecules to lowest number of molecules? a. cAMP, protein kinase A, phosphorylase kinase, glycogen phosphorylase b. Glycogen phosphorylase, phosp ...
Reagents - NutriTech
... institution that has made the SOP available. Please use a form of words such as: We used the NuGO Standard Operating Procedure (SOP) number 52 produced by the University of Copenhagen. Details of the SOP are available via the web link: http://www.nugo.org/frames.asp?actionID=38662&action=loginFromPP ...
... institution that has made the SOP available. Please use a form of words such as: We used the NuGO Standard Operating Procedure (SOP) number 52 produced by the University of Copenhagen. Details of the SOP are available via the web link: http://www.nugo.org/frames.asp?actionID=38662&action=loginFromPP ...
103 Lecture Ch22b
... • However, the cell has mechanisms to protect against mutation - during replication, the new DNA is proofread, and most mistakes are corrected - mutations that remain after proofreading may be corrected by other DNA repair mechanisms - mutated DNA that can not be repaired is usually recognized, and ...
... • However, the cell has mechanisms to protect against mutation - during replication, the new DNA is proofread, and most mistakes are corrected - mutations that remain after proofreading may be corrected by other DNA repair mechanisms - mutated DNA that can not be repaired is usually recognized, and ...
Chapter 19
... chromosomes—since you get “sticky ends” These were first discovered in bacteria, bac. used them to cut up foreign DNA from viruses or other bacteria. ...
... chromosomes—since you get “sticky ends” These were first discovered in bacteria, bac. used them to cut up foreign DNA from viruses or other bacteria. ...
omproteinsandnucleicacids
... enzyme is free to act on another substrate until it is metabolized (chemically destroyed). 2. If during protein synthesis amino acids are not placed in the proper order then the enzyme will have the wrong shape which means the substrate won’t fit into the active site. *Cause of many recessive traits ...
... enzyme is free to act on another substrate until it is metabolized (chemically destroyed). 2. If during protein synthesis amino acids are not placed in the proper order then the enzyme will have the wrong shape which means the substrate won’t fit into the active site. *Cause of many recessive traits ...
5 POINT QUESTIONS 1. A. Give the anticodon sequences (with 5` 3
... The F DNA must undergo homologous recombination with a complementary sequence (IS element or transposon) in the chromosome so that the 2 DNA molecules fuse. ...
... The F DNA must undergo homologous recombination with a complementary sequence (IS element or transposon) in the chromosome so that the 2 DNA molecules fuse. ...
Brooker Chapter 11
... • cis-acting elements • DNA sequences that exert their effect only on nearby genes • Example: TATA box, enhancers and silencers ...
... • cis-acting elements • DNA sequences that exert their effect only on nearby genes • Example: TATA box, enhancers and silencers ...
Nucleic acid analogue
Nucleic acid analogues are compounds which are analogous (structurally similar) to naturally occurring RNA and DNA, used in medicine and in molecular biology research.Nucleic acids are chains of nucleotides, which are composed of three parts: a phosphate backbone, a pucker-shaped pentose sugar, either ribose or deoxyribose, and one of four nucleobases.An analogue may have any of these altered. Typically the analogue nucleobases confer, among other things, different base pairing and base stacking properties. Examples include universal bases, which can pair with all four canonical bases, and phosphate-sugar backbone analogues such as PNA, which affect the properties of the chain (PNA can even form a triple helix).Nucleic acid analogues are also called Xeno Nucleic Acid and represent one of the main pillars of xenobiology, the design of new-to-nature forms of life based on alternative biochemistries.Artificial nucleic acids include peptide nucleic acid (PNA), Morpholino and locked nucleic acid (LNA), as well as glycol nucleic acid (GNA) and threose nucleic acid (TNA). Each of these is distinguished from naturally occurring DNA or RNA by changes to the backbone of the molecule.In May 2014, researchers announced that they had successfully introduced two new artificial nucleotides into bacterial DNA, and by including individual artificial nucleotides in the culture media, were able to passage the bacteria 24 times; they did not create mRNA or proteins able to use the artificial nucleotides. The artificial nucleotides featured 2 fused aromatic rings.