How hair can reveal a history
... folk-wisdom but singled out DNA as the one forensic science worthy of the name. Yet in recent years Hampikian and other geneticists have begun to question the technology. Thanks to a series of advances—including the polymerase chain reaction, which can multiply tiny amounts of DNA—it’s now possible ...
... folk-wisdom but singled out DNA as the one forensic science worthy of the name. Yet in recent years Hampikian and other geneticists have begun to question the technology. Thanks to a series of advances—including the polymerase chain reaction, which can multiply tiny amounts of DNA—it’s now possible ...
ppt - Faculty
... great deal of ATP energy. DNA replication in humans occurs at a rate of 50 nucleotides per second and ~500/second in prokaryotes. Nucleotides have to be assembled and available in the nucleus, along with energy to make bonds between nucleotides. DNA helicase enzymes unzip the DNA helix by breaking t ...
... great deal of ATP energy. DNA replication in humans occurs at a rate of 50 nucleotides per second and ~500/second in prokaryotes. Nucleotides have to be assembled and available in the nucleus, along with energy to make bonds between nucleotides. DNA helicase enzymes unzip the DNA helix by breaking t ...
Genetics Notes C Molecular Genetics Vocabulary • central dogma of
... DNA is the genetic material in your cells. It was passed on to you from your parents and determines your characteristics. The discovery that DNA is the genetic material was another important milestone in molecular biology. An important discovery about DNA was made in the mid-1900s by Erwin Chargaff. ...
... DNA is the genetic material in your cells. It was passed on to you from your parents and determines your characteristics. The discovery that DNA is the genetic material was another important milestone in molecular biology. An important discovery about DNA was made in the mid-1900s by Erwin Chargaff. ...
In meiosis, what is the difference between metaphase 1 and
... 17. What are the nucleic acids that are found in DNA? What about RNA? DNA= thymine (T), adenine (A), cytosine (C), guanine (G) RNA= uracil (U), adenine (A), cytosine (C), guanine (G) ...
... 17. What are the nucleic acids that are found in DNA? What about RNA? DNA= thymine (T), adenine (A), cytosine (C), guanine (G) RNA= uracil (U), adenine (A), cytosine (C), guanine (G) ...
Macromolecules - Haiku Learning
... life. Since these molecules are microscopic, it is easier to understand how they are built using models. In this part of the activity, your team will be modeling dehydration and hydrolysis reactions to obtain a better understanding of these processes. ...
... life. Since these molecules are microscopic, it is easier to understand how they are built using models. In this part of the activity, your team will be modeling dehydration and hydrolysis reactions to obtain a better understanding of these processes. ...
DNA Basics - Haiku Learning : Login
... use of Rosalind Franklin’s X-ray diffraction photograph, W&C determined double helix structure ...
... use of Rosalind Franklin’s X-ray diffraction photograph, W&C determined double helix structure ...
Molecular Biology Fourth Edition
... • In many cases, the 2′-hydroxyl group on ribose, a chemical feature that distinguishes RNA from DNA, seems to be directly or indirectly responsible for these unique structural properties. • The presence of the 2′ hydroxyl makes RNA vulnerable to hydrolysis, but it also allows for additional hydroge ...
... • In many cases, the 2′-hydroxyl group on ribose, a chemical feature that distinguishes RNA from DNA, seems to be directly or indirectly responsible for these unique structural properties. • The presence of the 2′ hydroxyl makes RNA vulnerable to hydrolysis, but it also allows for additional hydroge ...
Science 101 Pop Quiz - Dutchess Community College
... 5. CH3COOH is the molecular formula for a compound called acetic acid. This statement tells you that the dissociation products of acetic acid must be a) H3 and C2OOH d) H- and CH3COO+ b) H2 and C2OOH2 e) H+ and CH3COOc) H4 and C2O2 ...
... 5. CH3COOH is the molecular formula for a compound called acetic acid. This statement tells you that the dissociation products of acetic acid must be a) H3 and C2OOH d) H- and CH3COO+ b) H2 and C2OOH2 e) H+ and CH3COOc) H4 and C2O2 ...
Unit 1 – Human Cells Key Areas 1
... DNA molecule of 4000 bases, if 20% of the base molecules are cytosine? A. 400 B. 600 C. 800 D. 1200 7. Which of the following statements about DNA replication is correct? A. Polymerase adds nucleotides to the 3’ end of a DNA strand B. Polymerase adds nucleotides to the 5’ end of a DNA strand C. Liga ...
... DNA molecule of 4000 bases, if 20% of the base molecules are cytosine? A. 400 B. 600 C. 800 D. 1200 7. Which of the following statements about DNA replication is correct? A. Polymerase adds nucleotides to the 3’ end of a DNA strand B. Polymerase adds nucleotides to the 5’ end of a DNA strand C. Liga ...
Core Topic 2: Molecular biology 21 hours Essential idea: Living
... Nature of science: Looking for patterns, trends and discrepancies—most but not all organisms assemble proteins from the same amino acids. (3.1) Understandings: Amino acids are linked together by condensation to form polypeptides. There are 20 different amino acids in polypeptides synthesized on ...
... Nature of science: Looking for patterns, trends and discrepancies—most but not all organisms assemble proteins from the same amino acids. (3.1) Understandings: Amino acids are linked together by condensation to form polypeptides. There are 20 different amino acids in polypeptides synthesized on ...
Introduction to
... a. They are acellular, that is, they contain no cytoplasm or cellular organelles. b. No metabolic enzymes but must replicate using the host cell's metabolic machinery. In other words, viruses don't grow and divide. Instead, new viral components are synthesized and assembled within the infected host ...
... a. They are acellular, that is, they contain no cytoplasm or cellular organelles. b. No metabolic enzymes but must replicate using the host cell's metabolic machinery. In other words, viruses don't grow and divide. Instead, new viral components are synthesized and assembled within the infected host ...
Basic organic chemistry of important macromolecules (Lecture 11-12)
... 2) serve in the several cellular structures that choose, and then link into the correct order the amino acids of a protein chain (RNA). The structures of nucleotides and polynucleotides (a) Nucleotides, the monomers of nucleic acids, are themselves composed of three ...
... 2) serve in the several cellular structures that choose, and then link into the correct order the amino acids of a protein chain (RNA). The structures of nucleotides and polynucleotides (a) Nucleotides, the monomers of nucleic acids, are themselves composed of three ...
Chapter 9 Genetics Chromosome Genes • DNA RNA Protein Flow of
... for the assembly of amino acids into proteins tRNA – select amino acids and transfer the amino acids to the growing chain of a ...
... for the assembly of amino acids into proteins tRNA – select amino acids and transfer the amino acids to the growing chain of a ...
Questions - Vanier College
... 14. Which of the following represents the correct ordering of the molecules that are activated by a single molecule of epinephrine, from highest number of molecules to lowest number of molecules? a. cAMP, protein kinase A, phosphorylase kinase, glycogen phosphorylase b. Glycogen phosphorylase, phosp ...
... 14. Which of the following represents the correct ordering of the molecules that are activated by a single molecule of epinephrine, from highest number of molecules to lowest number of molecules? a. cAMP, protein kinase A, phosphorylase kinase, glycogen phosphorylase b. Glycogen phosphorylase, phosp ...
FREE Sample Here
... nucleic acids are called nucleotides, and consist of a phosphate group, a sugar (deoxyribose in DNA, ribose in RNA), and one of five possible carbon-nitrogen rings called purine or pyrimidine bases. Nucleotides are linked together by covalent bonds between the sugar and phosphate groups of adjacent ...
... nucleic acids are called nucleotides, and consist of a phosphate group, a sugar (deoxyribose in DNA, ribose in RNA), and one of five possible carbon-nitrogen rings called purine or pyrimidine bases. Nucleotides are linked together by covalent bonds between the sugar and phosphate groups of adjacent ...
36. ______ layers of ______ make up the cell membrane.
... 25. __________ bonds form when water is removed to hold _________ acids together. Lipids are large, nonpolar (won't dissolve in water) molecules. Phospholipids make up cell membranes. Lipids also serve as waxy coverings (cuticle) on plants, pigments (chlorophyll), and steroids. Lipids have more carb ...
... 25. __________ bonds form when water is removed to hold _________ acids together. Lipids are large, nonpolar (won't dissolve in water) molecules. Phospholipids make up cell membranes. Lipids also serve as waxy coverings (cuticle) on plants, pigments (chlorophyll), and steroids. Lipids have more carb ...
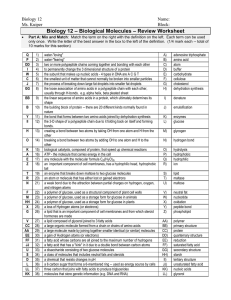
Biology 12 - Biologically Important Molecules – Review Worksheet
... a lipid composed of glycerol joined to 3 fatty acids a large organic molecule formed from a chain or chains of amino acids a large molecule made by joining together smaller identical (or similar) molecules a gain of Hydrogen atoms (or electrons) a fatty acid whose carbons are all joined to the maxim ...
... a lipid composed of glycerol joined to 3 fatty acids a large organic molecule formed from a chain or chains of amino acids a large molecule made by joining together smaller identical (or similar) molecules a gain of Hydrogen atoms (or electrons) a fatty acid whose carbons are all joined to the maxim ...
Lecture 20
... for all the amino acid. In the triplet code three consecutive متتالىbases specify تحددan amino acid. The genetic instructions for a polypeptide chain are written in DNA as a series of three-nucleotidewords (triplets). During transcription, one DNA strand (the template strand) provides an RNA t ...
... for all the amino acid. In the triplet code three consecutive متتالىbases specify تحددan amino acid. The genetic instructions for a polypeptide chain are written in DNA as a series of three-nucleotidewords (triplets). During transcription, one DNA strand (the template strand) provides an RNA t ...
Wanganui High School
... meiosis: this is a genetically inexact division of cell reducing the number of chromosomes to a half the normal number. This is what happens in the testis and ovary; meiosis produces gametes mitosis: this is a genetically exact division of a cell monohybrid cross: a straight forward cross involving ...
... meiosis: this is a genetically inexact division of cell reducing the number of chromosomes to a half the normal number. This is what happens in the testis and ovary; meiosis produces gametes mitosis: this is a genetically exact division of a cell monohybrid cross: a straight forward cross involving ...
Biology 4974/5974, Evolution
... To code for 20 amino acids + stop code, at least 1,070 possibilities using 64 codons. Why this code? Proposed explanations (hypotheses): 1. Stereochemical affinity between either a codon or an anticodon and an amino acid: no evidence. 2. Amino acid-codon association arose by chance and perhaps sever ...
... To code for 20 amino acids + stop code, at least 1,070 possibilities using 64 codons. Why this code? Proposed explanations (hypotheses): 1. Stereochemical affinity between either a codon or an anticodon and an amino acid: no evidence. 2. Amino acid-codon association arose by chance and perhaps sever ...
Chapter 3
... Complementary base pairing makes the copying of RNA and DNA possible, because one strand provides the template for forming a new strand. Base-pairing rules in DNA mean that a guanine in the template strand will cause a cytosine to be placed in the new strand, and a thymine in the template strand wil ...
... Complementary base pairing makes the copying of RNA and DNA possible, because one strand provides the template for forming a new strand. Base-pairing rules in DNA mean that a guanine in the template strand will cause a cytosine to be placed in the new strand, and a thymine in the template strand wil ...
Nucleic acid analogue
Nucleic acid analogues are compounds which are analogous (structurally similar) to naturally occurring RNA and DNA, used in medicine and in molecular biology research.Nucleic acids are chains of nucleotides, which are composed of three parts: a phosphate backbone, a pucker-shaped pentose sugar, either ribose or deoxyribose, and one of four nucleobases.An analogue may have any of these altered. Typically the analogue nucleobases confer, among other things, different base pairing and base stacking properties. Examples include universal bases, which can pair with all four canonical bases, and phosphate-sugar backbone analogues such as PNA, which affect the properties of the chain (PNA can even form a triple helix).Nucleic acid analogues are also called Xeno Nucleic Acid and represent one of the main pillars of xenobiology, the design of new-to-nature forms of life based on alternative biochemistries.Artificial nucleic acids include peptide nucleic acid (PNA), Morpholino and locked nucleic acid (LNA), as well as glycol nucleic acid (GNA) and threose nucleic acid (TNA). Each of these is distinguished from naturally occurring DNA or RNA by changes to the backbone of the molecule.In May 2014, researchers announced that they had successfully introduced two new artificial nucleotides into bacterial DNA, and by including individual artificial nucleotides in the culture media, were able to passage the bacteria 24 times; they did not create mRNA or proteins able to use the artificial nucleotides. The artificial nucleotides featured 2 fused aromatic rings.