Exp 4 Lecture - Seattle Central College
... • This transformation procedure involves three main steps. These steps are intended to introduce the plasmid DNA into the E. coli cells and provide an environment for the cells to express their newly acquired genes. • To move the plasmid DNA, pGLO, through the cell membrane you will: 1. Use a transf ...
... • This transformation procedure involves three main steps. These steps are intended to introduce the plasmid DNA into the E. coli cells and provide an environment for the cells to express their newly acquired genes. • To move the plasmid DNA, pGLO, through the cell membrane you will: 1. Use a transf ...
Abstract-Template-2016
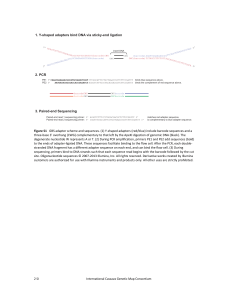
... During analysis of the promoter region of the human MEST gene, we noted apparent nonMendelian behaviour of three closely linked single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) 1. MEST plays a role in mammalian development and maternal behaviour. It is genomically imprinted, with the maternally inherited alle ...
... During analysis of the promoter region of the human MEST gene, we noted apparent nonMendelian behaviour of three closely linked single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) 1. MEST plays a role in mammalian development and maternal behaviour. It is genomically imprinted, with the maternally inherited alle ...
Abstract-Template-2017 - Queenstown Research Week
... During analysis of the promoter region of the human MEST gene, we noted apparent nonMendelian behaviour of three closely linked single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) 1. MEST plays a role in mammalian development and maternal behaviour. It is genomically imprinted, with the maternally inherited alle ...
... During analysis of the promoter region of the human MEST gene, we noted apparent nonMendelian behaviour of three closely linked single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) 1. MEST plays a role in mammalian development and maternal behaviour. It is genomically imprinted, with the maternally inherited alle ...
Chemical reaction
... May be used many times. • May fail to work if environment is changed. Temperature or pH can cause a change in the shape of the enzyme or substrate. ...
... May be used many times. • May fail to work if environment is changed. Temperature or pH can cause a change in the shape of the enzyme or substrate. ...
Ch 13 Genetic Engineering
... scientist can create new plants with double or even triple the amount of chromosomes • Plants tolerate being polyploidy better than animals ...
... scientist can create new plants with double or even triple the amount of chromosomes • Plants tolerate being polyploidy better than animals ...
Section 8.4: DNA Transcription
... • Transcription makes several types of RNA, the three that concern us are: – Messenger RNA (mRNA) carries the message that will be translated to form a protein (made by transcription of DNA). – Ribosomal RNA (rRNA) forms part of ribosomes where proteins are made. – Transfer RNA (tRNA) brings amino a ...
... • Transcription makes several types of RNA, the three that concern us are: – Messenger RNA (mRNA) carries the message that will be translated to form a protein (made by transcription of DNA). – Ribosomal RNA (rRNA) forms part of ribosomes where proteins are made. – Transfer RNA (tRNA) brings amino a ...
Recombinant DNA - Westwind Alternate School
... 1. use restriction enzymes to cut the DNA of both organisms to isolate the gene(s) you want 2. place cut pieces of DNA together with DNA ligase, allow recombination 3. Have(hope) the cells take up the DNA 4. use a selection technique to determine if the DNA has recombined the way you want it to in a ...
... 1. use restriction enzymes to cut the DNA of both organisms to isolate the gene(s) you want 2. place cut pieces of DNA together with DNA ligase, allow recombination 3. Have(hope) the cells take up the DNA 4. use a selection technique to determine if the DNA has recombined the way you want it to in a ...
Controls - Warren`s Science Page
... Enhancers: binding sites where such proteins increase transcription rates Methylation and Acetylation: are the names for the addition of such groups to DNA or any other molecule Cell Differentiation: nearly all of your body cells became specialized in composition, structure, and function ...
... Enhancers: binding sites where such proteins increase transcription rates Methylation and Acetylation: are the names for the addition of such groups to DNA or any other molecule Cell Differentiation: nearly all of your body cells became specialized in composition, structure, and function ...
Please pass last week`s warm up to the aisle. HW # 63: Read and
... Discovery of the Double Helix • By 1900:components of DNA were known – sugar, phosphate and bases ...
... Discovery of the Double Helix • By 1900:components of DNA were known – sugar, phosphate and bases ...
Ch 12 Gen Eng QA PP Ques 1
... genetically modified organisms and food, transplantation of genes, cloning) Biotechnology uses GE to use organisms and their components to make useful products ...
... genetically modified organisms and food, transplantation of genes, cloning) Biotechnology uses GE to use organisms and their components to make useful products ...
Micro Lab Unit 1 Flashcards
... What color will it change to in the presence of amino acids? What are the building blocks for carbohydrates? What are the building blocks for proteins? What are the building blocks for nucleic acids? ...
... What color will it change to in the presence of amino acids? What are the building blocks for carbohydrates? What are the building blocks for proteins? What are the building blocks for nucleic acids? ...
The Organic Macromolecules of Life
... carbohydrates and uses the energy in their chemical bonds to fuel the activities of life. Carbohydrates are a group of chemicals that include sugars, starches, and cellulose. Carbohydrates provide energy for organisms and they also provide structure for some organisms. For example, the cell walls of ...
... carbohydrates and uses the energy in their chemical bonds to fuel the activities of life. Carbohydrates are a group of chemicals that include sugars, starches, and cellulose. Carbohydrates provide energy for organisms and they also provide structure for some organisms. For example, the cell walls of ...
Organic Molecules Worksheet
... small, others are large, and others form chains and rings. The sequence and shapes of the “R” groups control the shape and function of the protein. 26. How many different amino acids are there? ___________________________________________ 27. What part of the amino acid varies from one amino acid to ...
... small, others are large, and others form chains and rings. The sequence and shapes of the “R” groups control the shape and function of the protein. 26. How many different amino acids are there? ___________________________________________ 27. What part of the amino acid varies from one amino acid to ...
File
... replication (nucleus) transcription (nucleus) translation (cytoplasm) Contains the sugar ribose Has the bases A, C, G, and T Typically single-stranded RNA polymerase A large transcription complex, including RNA polymerase and other proteins, assembles at the start of a gene and begins to unwind the ...
... replication (nucleus) transcription (nucleus) translation (cytoplasm) Contains the sugar ribose Has the bases A, C, G, and T Typically single-stranded RNA polymerase A large transcription complex, including RNA polymerase and other proteins, assembles at the start of a gene and begins to unwind the ...
Molecular Genetics
... The portions of DNA molecules that actually code for the production of proteins are called exons. parts of the mRNA that are kept and expressed ...
... The portions of DNA molecules that actually code for the production of proteins are called exons. parts of the mRNA that are kept and expressed ...
Glossary for Ancient DNA and Human Evolution
... CpG site: Locus where a cytosine nucleotide is followed by a guanine nucleotide in the linear sequence of bases. Cytosines in CpG dinucleotides can be methylated to form 5-methyl cytosine, a common epigentic mark. Enhancer: Short region of DNA that can be bound by proteins to alter transcription of ...
... CpG site: Locus where a cytosine nucleotide is followed by a guanine nucleotide in the linear sequence of bases. Cytosines in CpG dinucleotides can be methylated to form 5-methyl cytosine, a common epigentic mark. Enhancer: Short region of DNA that can be bound by proteins to alter transcription of ...
CB098-008.22_Biochemistry
... Organic Compound – A chemical compound containing the element carbon and usually synthesized by cells. The below macromolecules are examples of organic ...
... Organic Compound – A chemical compound containing the element carbon and usually synthesized by cells. The below macromolecules are examples of organic ...
Airgas template
... The __________________ square can be used to describe possible combinations that can occur with transmission of single-gene dominant and recessive traits. ...
... The __________________ square can be used to describe possible combinations that can occur with transmission of single-gene dominant and recessive traits. ...
DNA structure in the Cell
... DNA – Material of Heredity Bacteria carry their genetic material as a single circular chromosome, without it being enclosed by a nuclear membrane (prokaryotes) 1923 – Frederick Griffith performed studies with Streptococcus pneumoniae Two forms - S-Strain which is wild-type and highly pathogenic - R ...
... DNA – Material of Heredity Bacteria carry their genetic material as a single circular chromosome, without it being enclosed by a nuclear membrane (prokaryotes) 1923 – Frederick Griffith performed studies with Streptococcus pneumoniae Two forms - S-Strain which is wild-type and highly pathogenic - R ...
Carbohydrates
... Proteins: Polymers of amino acids Nucleic acids (DNA, RNA): Polymers of nucleotides Carbohydrates: Polymers of sugars Lipids: Polymers of fatty acids and glycerol ...
... Proteins: Polymers of amino acids Nucleic acids (DNA, RNA): Polymers of nucleotides Carbohydrates: Polymers of sugars Lipids: Polymers of fatty acids and glycerol ...
Principios de Biología Molecular
... • Transcription is highly regulated. Most DNA is in a dense form where it cannot be transcribed. • To begin transcription requires a promoter, a small specific sequence of DNA to which polymerase can bind (~40 base pairs “upstream” of gene) • Finding these promoter regions is a partially solved prob ...
... • Transcription is highly regulated. Most DNA is in a dense form where it cannot be transcribed. • To begin transcription requires a promoter, a small specific sequence of DNA to which polymerase can bind (~40 base pairs “upstream” of gene) • Finding these promoter regions is a partially solved prob ...
Nucleic acid analogue
Nucleic acid analogues are compounds which are analogous (structurally similar) to naturally occurring RNA and DNA, used in medicine and in molecular biology research.Nucleic acids are chains of nucleotides, which are composed of three parts: a phosphate backbone, a pucker-shaped pentose sugar, either ribose or deoxyribose, and one of four nucleobases.An analogue may have any of these altered. Typically the analogue nucleobases confer, among other things, different base pairing and base stacking properties. Examples include universal bases, which can pair with all four canonical bases, and phosphate-sugar backbone analogues such as PNA, which affect the properties of the chain (PNA can even form a triple helix).Nucleic acid analogues are also called Xeno Nucleic Acid and represent one of the main pillars of xenobiology, the design of new-to-nature forms of life based on alternative biochemistries.Artificial nucleic acids include peptide nucleic acid (PNA), Morpholino and locked nucleic acid (LNA), as well as glycol nucleic acid (GNA) and threose nucleic acid (TNA). Each of these is distinguished from naturally occurring DNA or RNA by changes to the backbone of the molecule.In May 2014, researchers announced that they had successfully introduced two new artificial nucleotides into bacterial DNA, and by including individual artificial nucleotides in the culture media, were able to passage the bacteria 24 times; they did not create mRNA or proteins able to use the artificial nucleotides. The artificial nucleotides featured 2 fused aromatic rings.