View - BioOne
... respectively, relative to the control treatment. However, cell numbers in A. azollea and A. azotica were increased by 120 to 135% and 80 to 103% at 0.03 to 3 nmol L21, and reduced by 93 and 69% at 300 nmol L21, after 144 h, respectively, relative to the control treatment. Thus, the three algae had d ...
... respectively, relative to the control treatment. However, cell numbers in A. azollea and A. azotica were increased by 120 to 135% and 80 to 103% at 0.03 to 3 nmol L21, and reduced by 93 and 69% at 300 nmol L21, after 144 h, respectively, relative to the control treatment. Thus, the three algae had d ...
PDF - Biochemical Society Transactions
... can be trapped intramolecularly to produce fused ring systems (e.g. 21 -+ 22) (Armstrong et af., 1985)and imines of vinyl amino acid esters undergo cyclization via 1,5dipole formation (23 -+ 24) (Grigg & Gunaratne, ...
... can be trapped intramolecularly to produce fused ring systems (e.g. 21 -+ 22) (Armstrong et af., 1985)and imines of vinyl amino acid esters undergo cyclization via 1,5dipole formation (23 -+ 24) (Grigg & Gunaratne, ...
Chance and Necessity in Arthur Peacocke`s Scientific Work
... Peacocke’s work with DNA intercalating agents was being done at the time when Watson and Crick had just defined the crystal structure of the DNA molecule demonstrating that it was double-stranded and that the bases were located in the center in a protected region of the molecule. Nevertheless, very ...
... Peacocke’s work with DNA intercalating agents was being done at the time when Watson and Crick had just defined the crystal structure of the DNA molecule demonstrating that it was double-stranded and that the bases were located in the center in a protected region of the molecule. Nevertheless, very ...
Streptococcus faecium - International Journal of Systematic and
... Transfer of Streptococcus faecalis and Streptococcus faecium to the Genus Enterococcus norn. rev. as Enterococcus faecalis comb. nov. and Enterococcus faecium comb. nov. KARL H. SCHLEIFER* A N D RENATE KILPPER-BALZ Lehrstuhl fur Mikrobiologie, Technische Universitat Miinchen, D-8000 Miinchen 2, Fede ...
... Transfer of Streptococcus faecalis and Streptococcus faecium to the Genus Enterococcus norn. rev. as Enterococcus faecalis comb. nov. and Enterococcus faecium comb. nov. KARL H. SCHLEIFER* A N D RENATE KILPPER-BALZ Lehrstuhl fur Mikrobiologie, Technische Universitat Miinchen, D-8000 Miinchen 2, Fede ...
Lec6 Fatty acid oxid..
... Energy yield from β- oxidation: Each β- oxidation cycle yields : -acyl CoA with 2 carbon atoms less -one NADH+H+ (give 3 ATP via respiratory chain) -one FADH2 (which give 2 ATP via respiratory chain) - one acetyl CoA (oxidized through Kreb's cycle to yield 12 ATP). Remember that the last cycle prod ...
... Energy yield from β- oxidation: Each β- oxidation cycle yields : -acyl CoA with 2 carbon atoms less -one NADH+H+ (give 3 ATP via respiratory chain) -one FADH2 (which give 2 ATP via respiratory chain) - one acetyl CoA (oxidized through Kreb's cycle to yield 12 ATP). Remember that the last cycle prod ...
Structural elements defining elongation factor Tu mediated
... Asn-tRNAAsn and Gln-tRNAGln does not, however, lead to erroneous incorporation of Asp and Glu into proteins, since EF-Tu discriminates the misacylated tRNAs from the correctly charged ones. This property contrasts with the canonical function of EF-Tu, which is to non-specifically bind the homologous ...
... Asn-tRNAAsn and Gln-tRNAGln does not, however, lead to erroneous incorporation of Asp and Glu into proteins, since EF-Tu discriminates the misacylated tRNAs from the correctly charged ones. This property contrasts with the canonical function of EF-Tu, which is to non-specifically bind the homologous ...
DNA Genetics
... b. anticodon on the mRNA only. c. anticodon on the tRNA to which the amino acid is attached only. d. codon on the mRNA and the anticodon on the tRNA to which the amino acid is attached. ____ 23. Genes contain instructions for assembling a. purines. b. nucleosomes. ...
... b. anticodon on the mRNA only. c. anticodon on the tRNA to which the amino acid is attached only. d. codon on the mRNA and the anticodon on the tRNA to which the amino acid is attached. ____ 23. Genes contain instructions for assembling a. purines. b. nucleosomes. ...
WO 2012/149481 Al
... have synthesized peptides that interrupt the 5-HT 2cR:PTEN complex to result in enhanced 5HT2C R function. An assay has been established and can be used to screen disrupters of the 5HT2cR:PTEN complex. ...
... have synthesized peptides that interrupt the 5-HT 2cR:PTEN complex to result in enhanced 5HT2C R function. An assay has been established and can be used to screen disrupters of the 5HT2cR:PTEN complex. ...
Investigation of asparagine deamidation in a SOD1
... order structures) factors. The influence of protein sequence and structure on Asn deamidation is significant. An increased conversion of Asn to Asp/isoAsp derivatives was observed for those proteins in which Asn was followed by small, flexible or hydrophilic residues. In particular, glycine was foun ...
... order structures) factors. The influence of protein sequence and structure on Asn deamidation is significant. An increased conversion of Asn to Asp/isoAsp derivatives was observed for those proteins in which Asn was followed by small, flexible or hydrophilic residues. In particular, glycine was foun ...
MusselsAlive Report
... and, therefore, the contribution in fat is very low. The recommended adequate intake (AI) for ω3 ...
... and, therefore, the contribution in fat is very low. The recommended adequate intake (AI) for ω3 ...
Plant Microbial and mineral contributions to amino acid and protein
... dominated by the concept of intrinsic molecular resistance as one of the major controllers of soil C turnover and storage. Accordingly, the molecular structure and lability of organic material has long been thought to determine long-term decomposition rates. However, recent observations have shown t ...
... dominated by the concept of intrinsic molecular resistance as one of the major controllers of soil C turnover and storage. Accordingly, the molecular structure and lability of organic material has long been thought to determine long-term decomposition rates. However, recent observations have shown t ...
Alu Human Polymorphism
... Alu elements • Alu elements are only found in the primate branch • Each Alu insertion is a unique event and is inherited from each parent – Most occurred millions of years ago and are often on both pairs of chromosomes – There are Alu elements that have occurred since humans branched from other pri ...
... Alu elements • Alu elements are only found in the primate branch • Each Alu insertion is a unique event and is inherited from each parent – Most occurred millions of years ago and are often on both pairs of chromosomes – There are Alu elements that have occurred since humans branched from other pri ...
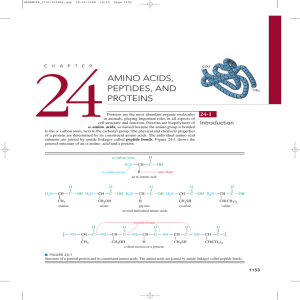
Amino Acids, Peptides, and Proteins
... The side chains of aspartic acid and glutamic acid contain acidic carboxyl groups. These amino acids have acidic isoelectric points around pH 3. An acidic solution is needed to prevent deprotonation of the second carboxylic acid group and to keep the amino acid in its neutral isoelectric state. Basi ...
... The side chains of aspartic acid and glutamic acid contain acidic carboxyl groups. These amino acids have acidic isoelectric points around pH 3. An acidic solution is needed to prevent deprotonation of the second carboxylic acid group and to keep the amino acid in its neutral isoelectric state. Basi ...
Carbohydrate-Based Mimetics in Drug Design: Sugar Amino Acids
... molecular recognition. In order to perform these functions, the correct folding of the biopolymers creating the active site is crucial, since any kind of interaction is observed only if the reactive groups are positioned in the correct spatial orientation to each other. Thus, the development of smal ...
... molecular recognition. In order to perform these functions, the correct folding of the biopolymers creating the active site is crucial, since any kind of interaction is observed only if the reactive groups are positioned in the correct spatial orientation to each other. Thus, the development of smal ...
View PDF - e-Science Central
... different media [2-15]. The kinetics and mechanism of antitumor activity of platinum (IV) compounds can be understood by investigating the reactivity of these compounds toward their reduction by bio-reductants such as amino acids [5-15]. Amino acids act as the building blocks in the synthesis of pro ...
... different media [2-15]. The kinetics and mechanism of antitumor activity of platinum (IV) compounds can be understood by investigating the reactivity of these compounds toward their reduction by bio-reductants such as amino acids [5-15]. Amino acids act as the building blocks in the synthesis of pro ...
Disposition of Glutathione Conjugates in Rats by a Novel Glutamic
... comparisons with synthetic standards. This pathway (addition of glutamic acids) led to larger peptides, in contrast to the mercapturic acid pathway, in which the glutathione adducts are broken down to smaller molecules. The enzyme responsible for the addition of glutamic acid to the different elemen ...
... comparisons with synthetic standards. This pathway (addition of glutamic acids) led to larger peptides, in contrast to the mercapturic acid pathway, in which the glutathione adducts are broken down to smaller molecules. The enzyme responsible for the addition of glutamic acid to the different elemen ...
Deciphering the molecular basis of the specificity of protein
... determine their amino acid preferences. Two datasets have been examined. Firstly, one composed of non-covalently bound carbohydrates ligands. The results of this analysis is compared to the second dataset, obtained from the study of the spatial vicinity of the monosaccharides that form the common st ...
... determine their amino acid preferences. Two datasets have been examined. Firstly, one composed of non-covalently bound carbohydrates ligands. The results of this analysis is compared to the second dataset, obtained from the study of the spatial vicinity of the monosaccharides that form the common st ...
APPLICATION OF LACTIC ACID BACTERIA TO CONTROL
... producer, but the quality of cocoa beans produced have not been uniform and not in accordance with international standard, resulting in low international price of cocoa market. One of the opportunities to improve the quality of cocoa is through development on fermentation and preservation technology ...
... producer, but the quality of cocoa beans produced have not been uniform and not in accordance with international standard, resulting in low international price of cocoa market. One of the opportunities to improve the quality of cocoa is through development on fermentation and preservation technology ...
The Photoassimilation of Organic Compounds by
... grow photosynthetically and, unlike the photosynthetic bacteria, produce oxygen. Apart from studies on their photosynthetic activities and, with certain species, also on their nitrogen-fixing activities, surprisingly few biochemical investigations have been made on this important group of organisms. ...
... grow photosynthetically and, unlike the photosynthetic bacteria, produce oxygen. Apart from studies on their photosynthetic activities and, with certain species, also on their nitrogen-fixing activities, surprisingly few biochemical investigations have been made on this important group of organisms. ...
The Photoassimilation of Organic Compounds by Autotrophic Blue
... grow photosynthetically and, unlike the photosynthetic bacteria, produce oxygen. Apart from studies on their photosynthetic activities and, with certain species, also on their nitrogen-fixing activities, surprisingly few biochemical investigations have been made on this important group of organisms. ...
... grow photosynthetically and, unlike the photosynthetic bacteria, produce oxygen. Apart from studies on their photosynthetic activities and, with certain species, also on their nitrogen-fixing activities, surprisingly few biochemical investigations have been made on this important group of organisms. ...
Fatty acid oxidation and the P-oxidation complex in
... aseptically : octanoate, myristate, palmitate (all 2 TBq mol-I), 10000 Bq; decanoate (1.92 Bq) 9620 Bq; laurate (2.15 TBq mol-I), 10730 Bq; stearate, oleate (both at 2-07 TBq mol-I), 10360 Bq; lignocerate (1.0 TBq mol-l), 8510 TBq mol-I; arachidonate (2.15 TBq mol-I), 5500 Bq plus 2.4 nmol unlabelle ...
... aseptically : octanoate, myristate, palmitate (all 2 TBq mol-I), 10000 Bq; decanoate (1.92 Bq) 9620 Bq; laurate (2.15 TBq mol-I), 10730 Bq; stearate, oleate (both at 2-07 TBq mol-I), 10360 Bq; lignocerate (1.0 TBq mol-l), 8510 TBq mol-I; arachidonate (2.15 TBq mol-I), 5500 Bq plus 2.4 nmol unlabelle ...
Nucleic acid analogue
Nucleic acid analogues are compounds which are analogous (structurally similar) to naturally occurring RNA and DNA, used in medicine and in molecular biology research.Nucleic acids are chains of nucleotides, which are composed of three parts: a phosphate backbone, a pucker-shaped pentose sugar, either ribose or deoxyribose, and one of four nucleobases.An analogue may have any of these altered. Typically the analogue nucleobases confer, among other things, different base pairing and base stacking properties. Examples include universal bases, which can pair with all four canonical bases, and phosphate-sugar backbone analogues such as PNA, which affect the properties of the chain (PNA can even form a triple helix).Nucleic acid analogues are also called Xeno Nucleic Acid and represent one of the main pillars of xenobiology, the design of new-to-nature forms of life based on alternative biochemistries.Artificial nucleic acids include peptide nucleic acid (PNA), Morpholino and locked nucleic acid (LNA), as well as glycol nucleic acid (GNA) and threose nucleic acid (TNA). Each of these is distinguished from naturally occurring DNA or RNA by changes to the backbone of the molecule.In May 2014, researchers announced that they had successfully introduced two new artificial nucleotides into bacterial DNA, and by including individual artificial nucleotides in the culture media, were able to passage the bacteria 24 times; they did not create mRNA or proteins able to use the artificial nucleotides. The artificial nucleotides featured 2 fused aromatic rings.