NH 2
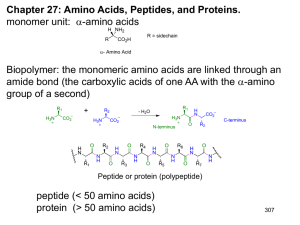
... - is formed when the carboxyl group of one aa molecule reacts with the amine group of the other aa molecule in front of it, thereby releasing a molecule of water (H2O). - this is a dehydration synthesis reaction or condensation reaction, - the resulting CO-NH bond is called a peptide bond, and the r ...
... - is formed when the carboxyl group of one aa molecule reacts with the amine group of the other aa molecule in front of it, thereby releasing a molecule of water (H2O). - this is a dehydration synthesis reaction or condensation reaction, - the resulting CO-NH bond is called a peptide bond, and the r ...
Quantitative analysis of complex amino acids and RGD peptides by
... Glycine has a single nitrogen atom in its structure (Figure 1) giving rise to a single photoemission signal at 401.4 eV for both the - and -polymorphic forms (Figure 2a, Table 1). This value is in the range for protonated nitrogen (NH3+),[20] in line with the zwitterionic nature of crystalline gly ...
... Glycine has a single nitrogen atom in its structure (Figure 1) giving rise to a single photoemission signal at 401.4 eV for both the - and -polymorphic forms (Figure 2a, Table 1). This value is in the range for protonated nitrogen (NH3+),[20] in line with the zwitterionic nature of crystalline gly ...
Nucleic Acids - Farmasi Unand
... the peptides and proteins required by the body. • The sequence of bases that act as the code for the production of one specific peptide or protein molecule is known as a gene. ...
... the peptides and proteins required by the body. • The sequence of bases that act as the code for the production of one specific peptide or protein molecule is known as a gene. ...
Genetics - davis.k12.ut.us
... Before you read, decide if you agree or disagree with each of these statements. As you read this chapter, see if you change your mind about any of the statements. 1 Like mixing paints, parents’ traits always blend in their offspring. 2 If you look more like your mother than you look like your father ...
... Before you read, decide if you agree or disagree with each of these statements. As you read this chapter, see if you change your mind about any of the statements. 1 Like mixing paints, parents’ traits always blend in their offspring. 2 If you look more like your mother than you look like your father ...
pdf
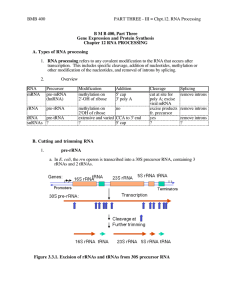
... 3. Small nuclear ribonucleoproteins (or snRNPs) form the functional splicesome on pre-mRNA and catalyze splicing. a. "U" RNAs and associated proteins Small nuclear RNAs (snRNAs) are about 100 to 300 nts long and can be as abundant as 105 to 106 molecules per cell. They are named U followed by an int ...
... 3. Small nuclear ribonucleoproteins (or snRNPs) form the functional splicesome on pre-mRNA and catalyze splicing. a. "U" RNAs and associated proteins Small nuclear RNAs (snRNAs) are about 100 to 300 nts long and can be as abundant as 105 to 106 molecules per cell. They are named U followed by an int ...
pdf
... challenges in the history of biochemistry. In eukaryotic cells, protein synthesis requires the participation of 80 different ribosomal proteins and 4 ribosomal RNA’s (rRNA); 40 or more different kinds of transfer RNA’s (tRNA); 20 or more enzymes to activate the amino acids by attaching them to their ...
... challenges in the history of biochemistry. In eukaryotic cells, protein synthesis requires the participation of 80 different ribosomal proteins and 4 ribosomal RNA’s (rRNA); 40 or more different kinds of transfer RNA’s (tRNA); 20 or more enzymes to activate the amino acids by attaching them to their ...
Beads on a string Bowater Biochem Soc Trans 2012
... around the transcription start site of genes, which was proposed to result from the physical properties and relative stiffness of the DNA in these regions. In a related study, but with contrasting conclusions, Philipp Korber [10] presented some striking data on the location of nucleosomes on DNA rec ...
... around the transcription start site of genes, which was proposed to result from the physical properties and relative stiffness of the DNA in these regions. In a related study, but with contrasting conclusions, Philipp Korber [10] presented some striking data on the location of nucleosomes on DNA rec ...
a Disulfide Bridge DataBase for the predictive analysis of cysteine
... [4] Neves Petersen Maria Teresa, Johnson Per Harald and Petersen Steffen B., Amino acid neighbours and detailed conformational analysis of cysteines in proteins, Protein Engineering, vol 12, no. 7, pp 535-548, 1999. [5] Hyunsoo Kim and Haesun Park, Protein secondary structure prediction based on an ...
... [4] Neves Petersen Maria Teresa, Johnson Per Harald and Petersen Steffen B., Amino acid neighbours and detailed conformational analysis of cysteines in proteins, Protein Engineering, vol 12, no. 7, pp 535-548, 1999. [5] Hyunsoo Kim and Haesun Park, Protein secondary structure prediction based on an ...
Chapter 7: Photosynthesis
... 15.What is the name of the bond that joins two amino acids? What kind of a bond is it? 16.What is meant by primary, secondary, tertiary, and quaternary protein structure? What types of bonds are involved in each level of structure? 17.Why is protein structure important? 18.Explain what it means when ...
... 15.What is the name of the bond that joins two amino acids? What kind of a bond is it? 16.What is meant by primary, secondary, tertiary, and quaternary protein structure? What types of bonds are involved in each level of structure? 17.Why is protein structure important? 18.Explain what it means when ...
Patenting DNA-Related I nventions in the European Union, United
... patent application discloses only nucleic acid molecular structure for a newly discovered gene, and no utility for the claimed isolated gene, the claimed invention is not patentable. But when the inventor also discloses how to use the purified gene isolated from its natural state, the application sa ...
... patent application discloses only nucleic acid molecular structure for a newly discovered gene, and no utility for the claimed isolated gene, the claimed invention is not patentable. But when the inventor also discloses how to use the purified gene isolated from its natural state, the application sa ...
Ch03Pt1.doc
... These are the structures at the equivalence points. Charges: 1 = +2. 2 = +1. 3 = 0. 4 = -1. c. Migration in an electric field: cathode has a – charge, and anode has a + charge. So structures 1 and 2 would migrate toward the cathode, 3 wouldn’t move, 4 would move toward the anode. ...
... These are the structures at the equivalence points. Charges: 1 = +2. 2 = +1. 3 = 0. 4 = -1. c. Migration in an electric field: cathode has a – charge, and anode has a + charge. So structures 1 and 2 would migrate toward the cathode, 3 wouldn’t move, 4 would move toward the anode. ...
The Structure and Function of Large Biological Molecules
... molecules that does not include true polymers Chitin, embedded in proteins, forms the exoskeleton of arthropods. ...
... molecules that does not include true polymers Chitin, embedded in proteins, forms the exoskeleton of arthropods. ...
Short Response Part 2 Answers
... The venom produced by each species is prey specific. It may contain two or more different types of neurotoxins, each composed of long chains of amino acids. ...
... The venom produced by each species is prey specific. It may contain two or more different types of neurotoxins, each composed of long chains of amino acids. ...
Phytanic acid omega-oxidation in human liver microsomes
... far greater than (ω-1)-hydroxyphytanic acid which is beneficial because the former product is a substrate for the next step in the pathway. CYP4F3A is the most active CYP450 but is not present in liver and therefore is not responsible for phytanic acid ωhydroxylation activity in liver. The other CYP ...
... far greater than (ω-1)-hydroxyphytanic acid which is beneficial because the former product is a substrate for the next step in the pathway. CYP4F3A is the most active CYP450 but is not present in liver and therefore is not responsible for phytanic acid ωhydroxylation activity in liver. The other CYP ...
Bruce Wallace Biotechnology Lab Program Student Guide 5th
... Beta lactamase, then, enables bacteria to reproduce in the presence of ampicillin. In addition, pARA carries a gene for the AraC protein, a protein that helps the bacterium make proteins encoded by genes inserted into this plasmid. A gene, even a foreign one, can be expressed (produced) if it is ins ...
... Beta lactamase, then, enables bacteria to reproduce in the presence of ampicillin. In addition, pARA carries a gene for the AraC protein, a protein that helps the bacterium make proteins encoded by genes inserted into this plasmid. A gene, even a foreign one, can be expressed (produced) if it is ins ...
Mutations: The Effect On Phenotype
... something, a receptor on the tongue bindsi a specific chemical in food. When the chemical binds to the receptor, a signal is sent to the brain where it is interpreted as a particular taste—sour, bitter, sweet, salty or umami. Recently, the gene that codes for the receptor that binds PTC was identifi ...
... something, a receptor on the tongue bindsi a specific chemical in food. When the chemical binds to the receptor, a signal is sent to the brain where it is interpreted as a particular taste—sour, bitter, sweet, salty or umami. Recently, the gene that codes for the receptor that binds PTC was identifi ...
Octadecabacter jejudonensis sp. nov., isolated from the junction
... arcticus DSM 13978T in that one additional major polar lipid (L4) is absent. The DNA G+C content of strain SSK2-1T was 60.1 mol%, a value slightly higher than those reported for species of the genus Octadecabacter (Table 1). From the results obtained from the chemotaxonomic analysis and the phylogen ...
... arcticus DSM 13978T in that one additional major polar lipid (L4) is absent. The DNA G+C content of strain SSK2-1T was 60.1 mol%, a value slightly higher than those reported for species of the genus Octadecabacter (Table 1). From the results obtained from the chemotaxonomic analysis and the phylogen ...
Biological-Anthropology-2nd-Edition-Stanford-Test-Bank
... forensic sciences. It would be interesting to share several murder cases with students that were solved with these techniques or to show how these techniques have cleared many convicted felons of their supposed crimes. ...
... forensic sciences. It would be interesting to share several murder cases with students that were solved with these techniques or to show how these techniques have cleared many convicted felons of their supposed crimes. ...
as a PDF
... of such fresh vegetables can have deleterious effects on their acceptability as a food source. To our knowledge, no information is available on the levels of sugars, fatty acids, proteins (free amino acids) and minerals in kale leaf. For leaf nutrient content, it is important to analyze the seed oil ...
... of such fresh vegetables can have deleterious effects on their acceptability as a food source. To our knowledge, no information is available on the levels of sugars, fatty acids, proteins (free amino acids) and minerals in kale leaf. For leaf nutrient content, it is important to analyze the seed oil ...
Nucleic acid analogue
Nucleic acid analogues are compounds which are analogous (structurally similar) to naturally occurring RNA and DNA, used in medicine and in molecular biology research.Nucleic acids are chains of nucleotides, which are composed of three parts: a phosphate backbone, a pucker-shaped pentose sugar, either ribose or deoxyribose, and one of four nucleobases.An analogue may have any of these altered. Typically the analogue nucleobases confer, among other things, different base pairing and base stacking properties. Examples include universal bases, which can pair with all four canonical bases, and phosphate-sugar backbone analogues such as PNA, which affect the properties of the chain (PNA can even form a triple helix).Nucleic acid analogues are also called Xeno Nucleic Acid and represent one of the main pillars of xenobiology, the design of new-to-nature forms of life based on alternative biochemistries.Artificial nucleic acids include peptide nucleic acid (PNA), Morpholino and locked nucleic acid (LNA), as well as glycol nucleic acid (GNA) and threose nucleic acid (TNA). Each of these is distinguished from naturally occurring DNA or RNA by changes to the backbone of the molecule.In May 2014, researchers announced that they had successfully introduced two new artificial nucleotides into bacterial DNA, and by including individual artificial nucleotides in the culture media, were able to passage the bacteria 24 times; they did not create mRNA or proteins able to use the artificial nucleotides. The artificial nucleotides featured 2 fused aromatic rings.