AN EXPERIMENTAL STUDY OF FORAGING AGGRESSION IN TWO
... one of the greatest convolutions of the world’s flora and fauna.” He was speaking of the humanmediated biological invasions which accompany the expansion of human civilization (Crosby 1986) and greatly alter patterns of global biodiversity (Vitousek et al. 1997). In fact, the impact of biological in ...
... one of the greatest convolutions of the world’s flora and fauna.” He was speaking of the humanmediated biological invasions which accompany the expansion of human civilization (Crosby 1986) and greatly alter patterns of global biodiversity (Vitousek et al. 1997). In fact, the impact of biological in ...
APPENDIX B-2A Duchess Paradise Project
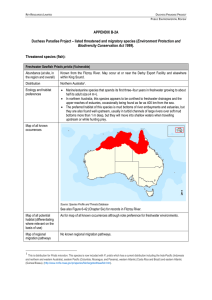
... Marine/estuarine species that spends its first three–four years in freshwater growing to about half its adult size (4 m+). In northern Australia, this species appears to be confined to freshwater drainages and the upper reaches of estuaries, occasionally being found as far as 400 km from the sea ...
... Marine/estuarine species that spends its first three–four years in freshwater growing to about half its adult size (4 m+). In northern Australia, this species appears to be confined to freshwater drainages and the upper reaches of estuaries, occasionally being found as far as 400 km from the sea ...
Perth 2015 - Australasian Wildlife Management Society
... Welcome to the 2015 AWMS conference. It is the 28th consecutive year that AWMS has met to discuss the issues and practice of wildlife management in Australia. As AWMS has grown and matured, so too has the praxis of wildlife management in our region and AWMS can be justifiably proud of the role it ha ...
... Welcome to the 2015 AWMS conference. It is the 28th consecutive year that AWMS has met to discuss the issues and practice of wildlife management in Australia. As AWMS has grown and matured, so too has the praxis of wildlife management in our region and AWMS can be justifiably proud of the role it ha ...
Nest Predation Processes and Farmland Birds
... It is generally expected that predators affect the breeding biology of prey species, but most studies have had a prey-biased view of the predator-prey relationship. Without studying the predator, one may draw erroneous conclusions of how predators and prey interact and conservation strategies for pr ...
... It is generally expected that predators affect the breeding biology of prey species, but most studies have had a prey-biased view of the predator-prey relationship. Without studying the predator, one may draw erroneous conclusions of how predators and prey interact and conservation strategies for pr ...
Neoscona crucifera N. adianta - Indian Journal of Life Sciences
... It was done on the basis of morphometric characters of various body parts. The help was mainly taken from the keys and catalogues provided by Biswas and Biswas (2003, 2004); Nentwig et al., (2003) and Plantik (2004), information and photographs available on internet and other relevant literature. St ...
... It was done on the basis of morphometric characters of various body parts. The help was mainly taken from the keys and catalogues provided by Biswas and Biswas (2003, 2004); Nentwig et al., (2003) and Plantik (2004), information and photographs available on internet and other relevant literature. St ...
The Feeding Ecology of Flatfish in the Northwest Atlantic
... et al., 1994; Gonzalez et al., MS 1998; Methven, 1999). However, none of these studies have examined flatfish diets across broad spatial or temporal scales, particularly after major perturbations to the ocean bottom from decades of fishing. Additionally, fisheries management and stock assessment sci ...
... et al., 1994; Gonzalez et al., MS 1998; Methven, 1999). However, none of these studies have examined flatfish diets across broad spatial or temporal scales, particularly after major perturbations to the ocean bottom from decades of fishing. Additionally, fisheries management and stock assessment sci ...
Sea Urchin Predation in Misali Island Marine Park
... however, the high abundance of sea urchins in some areas suggest that finfish fisheries, upon which the food security of Pemba depends, may be changing the structure and diversity of Misali reefs by removing key top level predators, such as triggerfish (Balistidae). Due to the lack of quantitative d ...
... however, the high abundance of sea urchins in some areas suggest that finfish fisheries, upon which the food security of Pemba depends, may be changing the structure and diversity of Misali reefs by removing key top level predators, such as triggerfish (Balistidae). Due to the lack of quantitative d ...
Ecology
... to study this “natural experiment.” They were able to document the sequence of biological changes that started soon after the eruption. Much of what has been learned has been unexpected, and has changed the way we view the recovery of communities and the persistence of life ...
... to study this “natural experiment.” They were able to document the sequence of biological changes that started soon after the eruption. Much of what has been learned has been unexpected, and has changed the way we view the recovery of communities and the persistence of life ...
Habitat Features Determine the Basking Distribution of
... space and experiences heavy traffic from people and their pets but also supports relatively large numbers of turtles. The majority of the turtle population in the Arboretum waterway consists of E. marmorata and the nonnative redeared slider, T. s. elegans. Whereas competition for basking sites is on ...
... space and experiences heavy traffic from people and their pets but also supports relatively large numbers of turtles. The majority of the turtle population in the Arboretum waterway consists of E. marmorata and the nonnative redeared slider, T. s. elegans. Whereas competition for basking sites is on ...
Importance of fragmentation-tolerant species as seed
... and Duber (2001) found that a loss of seed predators and dispersers in fragmented or poached forests increased seedling density of Attalea palms, but principally under the parent trees where long-term survival may have been compromised. Chapman and Chapman (2003) found lower seedling densities and r ...
... and Duber (2001) found that a loss of seed predators and dispersers in fragmented or poached forests increased seedling density of Attalea palms, but principally under the parent trees where long-term survival may have been compromised. Chapman and Chapman (2003) found lower seedling densities and r ...
The interplay of physical and biotic factors in
... Vermeij (1977, 1987, 1994) argued that evolutionary changes in the effectiveness of shellpenetrating predators drove a change in the structure of marine communities, and in the range of morphologies present in bivalves, gastropods and other marine prey. The biotic interactions engendered by this ‘Me ...
... Vermeij (1977, 1987, 1994) argued that evolutionary changes in the effectiveness of shellpenetrating predators drove a change in the structure of marine communities, and in the range of morphologies present in bivalves, gastropods and other marine prey. The biotic interactions engendered by this ‘Me ...
methods of the mathematical morphology of landscape
... where v is the trial plot area, t is time, λ is the average number of sites appearing within a unit area per unit time. The research shows that the mathematical models of landscape patterns are characterized with an amazing feature. It is invariant (Victorov, 1998, 2006). This feature means that the ...
... where v is the trial plot area, t is time, λ is the average number of sites appearing within a unit area per unit time. The research shows that the mathematical models of landscape patterns are characterized with an amazing feature. It is invariant (Victorov, 1998, 2006). This feature means that the ...
Competition between apex predators? Brown bears decrease wolf
... about how competition between apex predators affects predation, the mechanism driving top-down forcing in ecosystems. We used long-term datasets from Scandinavia (Europe) and Yellowstone National Park (North America) to evaluate how grey wolf (Canis lupus) kill rate was affected by a sympatric apex ...
... about how competition between apex predators affects predation, the mechanism driving top-down forcing in ecosystems. We used long-term datasets from Scandinavia (Europe) and Yellowstone National Park (North America) to evaluate how grey wolf (Canis lupus) kill rate was affected by a sympatric apex ...
- Wiley Online Library
... types, traits consistently covary in what have been described as ‘economics spectra’ that broadly summarize trade-offs between slow-growing and fast-growing plants (Wright et al. 2004; Chave et al. 2009). Two studies have more recently integrated leaf and stem traits together in large data sets of tr ...
... types, traits consistently covary in what have been described as ‘economics spectra’ that broadly summarize trade-offs between slow-growing and fast-growing plants (Wright et al. 2004; Chave et al. 2009). Two studies have more recently integrated leaf and stem traits together in large data sets of tr ...
Leaf, stem and root tissue strategies across 758
... types, traits consistently covary in what have been described as ‘economics spectra’ that broadly summarize trade-offs between slow-growing and fast-growing plants (Wright et al. 2004; Chave et al. 2009). Two studies have more recently integrated leaf and stem traits together in large data sets of tr ...
... types, traits consistently covary in what have been described as ‘economics spectra’ that broadly summarize trade-offs between slow-growing and fast-growing plants (Wright et al. 2004; Chave et al. 2009). Two studies have more recently integrated leaf and stem traits together in large data sets of tr ...
Antipredatory Defensive Roles of Natural Products from Marine
... Marine chemical ecology is a young discipline, having emerged from the collaboration of natural products chemists and ecologists in the 1980s with the goal of examining the ecological functions of the unusual secondary metabolites that were being isolated from the tissues of marine organisms. The re ...
... Marine chemical ecology is a young discipline, having emerged from the collaboration of natural products chemists and ecologists in the 1980s with the goal of examining the ecological functions of the unusual secondary metabolites that were being isolated from the tissues of marine organisms. The re ...
View - OhioLINK Electronic Theses and Dissertations Center
... forms…[but] it would be cheaper and easier in the short term to say there was not scientific consensus and we should delay regulation” (Simberloff, 2005). He goes on to explain that such reasoning not only fails to provide sound justification for non-action, but that it is both incorrect and dangero ...
... forms…[but] it would be cheaper and easier in the short term to say there was not scientific consensus and we should delay regulation” (Simberloff, 2005). He goes on to explain that such reasoning not only fails to provide sound justification for non-action, but that it is both incorrect and dangero ...
Bog Bird.s-foot Trefoil (Lotus pinnatus)
... source (Kirkbride 1999). In Homer’s Odyssey, the hero Ulysses almost lost his crew when they became intoxicated by the honey-sweet fruit of Zizyphus lotus L. in the land of the Lotus-Eaters. Camarario (1588) was the first to apply the Latin name ‘lotus’ to a trefoil in his “Hortus Medicus”. Consider ...
... source (Kirkbride 1999). In Homer’s Odyssey, the hero Ulysses almost lost his crew when they became intoxicated by the honey-sweet fruit of Zizyphus lotus L. in the land of the Lotus-Eaters. Camarario (1588) was the first to apply the Latin name ‘lotus’ to a trefoil in his “Hortus Medicus”. Consider ...
Pacific oyster, Crassostrea gigas
... They grow best in water with salinity between 24 and 28 ppt, but can tolerate low salinities (down to 5 ppt) for short periods (Shatkin et al. 1997). These wide tolerances enable C. gigas to grow in a variety of environments that are unsuitable for native oyster species. This broad environmental tol ...
... They grow best in water with salinity between 24 and 28 ppt, but can tolerate low salinities (down to 5 ppt) for short periods (Shatkin et al. 1997). These wide tolerances enable C. gigas to grow in a variety of environments that are unsuitable for native oyster species. This broad environmental tol ...
Interspecific Interactions in Phytophagous Insects: Competition
... tioning (e.g. 108, 143, 147, 179, 184). The rationale for such studies stemmed from classical competition theory, which predicted that two species could not occupy the same niche and coexist, and that coexistence could be achieved only through divergence in resource use (reviewed in 152). Thus, many ...
... tioning (e.g. 108, 143, 147, 179, 184). The rationale for such studies stemmed from classical competition theory, which predicted that two species could not occupy the same niche and coexist, and that coexistence could be achieved only through divergence in resource use (reviewed in 152). Thus, many ...
Standard PDF - Wiley Online Library
... of the spatial variation component of our data. We evaluated the complete set of models with four or less parameters (in order to guarantee at least 10 observations per parameter) that includes these three explanatory variables. We used Poisson error distributions and log link functions. Model selec ...
... of the spatial variation component of our data. We evaluated the complete set of models with four or less parameters (in order to guarantee at least 10 observations per parameter) that includes these three explanatory variables. We used Poisson error distributions and log link functions. Model selec ...
Nauplius
... The majority of collected shells (with gastropod and empty) had small size (SAW < 10.8 mm), representing 95% of the total sample. However, available shells of small size that were collected empty represented 12% of the total. Thus, despite of their abundance, small sized shells represent a limiting ...
... The majority of collected shells (with gastropod and empty) had small size (SAW < 10.8 mm), representing 95% of the total sample. However, available shells of small size that were collected empty represented 12% of the total. Thus, despite of their abundance, small sized shells represent a limiting ...
Theoretical ecology

Theoretical ecology is the scientific discipline devoted to the study of ecological systems using theoretical methods such as simple conceptual models, mathematical models, computational simulations, and advanced data analysis. Effective models improve understanding of the natural world by revealing how the dynamics of species populations are often based on fundamental biological conditions and processes. Further, the field aims to unify a diverse range of empirical observations by assuming that common, mechanistic processes generate observable phenomena across species and ecological environments. Based on biologically realistic assumptions, theoretical ecologists are able to uncover novel, non-intuitive insights about natural processes. Theoretical results are often verified by empirical and observational studies, revealing the power of theoretical methods in both predicting and understanding the noisy, diverse biological world.The field is broad and includes foundations in applied mathematics, computer science, biology, statistical physics, genetics, chemistry, evolution, and conservation biology. Theoretical ecology aims to explain a diverse range of phenomena in the life sciences, such as population growth and dynamics, fisheries, competition, evolutionary theory, epidemiology, animal behavior and group dynamics, food webs, ecosystems, spatial ecology, and the effects of climate change.Theoretical ecology has further benefited from the advent of fast computing power, allowing the analysis and visualization of large-scale computational simulations of ecological phenomena. Importantly, these modern tools provide quantitative predictions about the effects of human induced environmental change on a diverse variety of ecological phenomena, such as: species invasions, climate change, the effect of fishing and hunting on food network stability, and the global carbon cycle.