Apparent competition with an invasive plant hastens the extinction of
... National Seashore, northern California, USA; Peromyscus maniculatus; population viability analysis; predispersal seed consumption; stochastic population model. ...
... National Seashore, northern California, USA; Peromyscus maniculatus; population viability analysis; predispersal seed consumption; stochastic population model. ...
AP BIOLOGY - Mrs. Loyd`s Biology
... Lecture: “boom-and-bust” cycles, r- and K-selection, human population growth, age structures, ecological footprint. ...
... Lecture: “boom-and-bust” cycles, r- and K-selection, human population growth, age structures, ecological footprint. ...
Food Chains and Food Webs
... your answer sheet, underline all of the characteristics of life that the organism shows. ...
... your answer sheet, underline all of the characteristics of life that the organism shows. ...
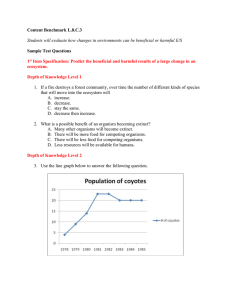
Content Benchmark L.8.C.3 Sample Test Questions
... and the spotted salamander. They are affected because they will have fewer options when looking for food. This could cause a reduction in these populations. If that occurs, then the water snake, the egret, the fish, and the shrew also would have fewer options and greater competition of the available ...
... and the spotted salamander. They are affected because they will have fewer options when looking for food. This could cause a reduction in these populations. If that occurs, then the water snake, the egret, the fish, and the shrew also would have fewer options and greater competition of the available ...
Adapt or disperse: understanding species persistence
... tivity of growth rate for herbivores compared with plants will increase grazing pressure on plants, potentially triggering outbreak population dynamics (Fig. 1). Another illustration of the strength of this approach is work on the causes of the widespread amphibian extinction over the last decades. ...
... tivity of growth rate for herbivores compared with plants will increase grazing pressure on plants, potentially triggering outbreak population dynamics (Fig. 1). Another illustration of the strength of this approach is work on the causes of the widespread amphibian extinction over the last decades. ...
2008-03 - International Mathematical Union
... complexity. Approximation theory. Applied and computational aspects of harmonic analysis. Numerical solution of algebraic, functional, differential, and integral equations. Grid generation and adaptivity. Connections with sections 8, 10, 11, 13, 15, 17, 18. 17. Control theory and optimization (6-7 l ...
... complexity. Approximation theory. Applied and computational aspects of harmonic analysis. Numerical solution of algebraic, functional, differential, and integral equations. Grid generation and adaptivity. Connections with sections 8, 10, 11, 13, 15, 17, 18. 17. Control theory and optimization (6-7 l ...
Adapt or disperse: understanding species persistence in a changing
... tivity of growth rate for herbivores compared with plants will increase grazing pressure on plants, potentially triggering outbreak population dynamics (Fig. 1). Another illustration of the strength of this approach is work on the causes of the widespread amphibian extinction over the last decades. ...
... tivity of growth rate for herbivores compared with plants will increase grazing pressure on plants, potentially triggering outbreak population dynamics (Fig. 1). Another illustration of the strength of this approach is work on the causes of the widespread amphibian extinction over the last decades. ...
Blackburn
... for any particular test may result in the acceptance of a pattern as the result of a biological process, when in fact it is no more than an artefact of a particular methodology, or would be expected in the absence of any biological mechanism. An example of the first problem is provided by the study ...
... for any particular test may result in the acceptance of a pattern as the result of a biological process, when in fact it is no more than an artefact of a particular methodology, or would be expected in the absence of any biological mechanism. An example of the first problem is provided by the study ...
Group A: Impacts of IS on organisms, communities, and landscapes
... from the experimental level to the landscape level and scale down the risk from the continental level to the local level. o Many studies that are done are small scale and difficult to figure out what emergent effects are if invasion occurs across the landscape o Temporal scaling: How well do we unde ...
... from the experimental level to the landscape level and scale down the risk from the continental level to the local level. o Many studies that are done are small scale and difficult to figure out what emergent effects are if invasion occurs across the landscape o Temporal scaling: How well do we unde ...
Adaptation, density dependence and the responses of trophic level
... The responses of abundances to the extrinsic per capita mortality rates are obtained by differentiating the equilibrium conditions for equations (1a–d) with respect to each of the di. The resulting formulae can be simplified somewhat by assuming that the equilibrium of the system is locally stable. ...
... The responses of abundances to the extrinsic per capita mortality rates are obtained by differentiating the equilibrium conditions for equations (1a–d) with respect to each of the di. The resulting formulae can be simplified somewhat by assuming that the equilibrium of the system is locally stable. ...
A-level Environmental Science Mark scheme Unit 3 - The
... understands and applies it in the same correct way. As preparation for the standardisation meeting each examiner analyses a number of candidates’ scripts: alternative answers not already covered by the mark scheme are discussed at the meeting and legislated for. If, after this meeting, examiners enc ...
... understands and applies it in the same correct way. As preparation for the standardisation meeting each examiner analyses a number of candidates’ scripts: alternative answers not already covered by the mark scheme are discussed at the meeting and legislated for. If, after this meeting, examiners enc ...
Version 3 - Science Writing Resources
... (BC) has many negative effects on these habitats. For [?????], cheatgrass reduces biodiversity, leads to more frequent wildfires, and causes health problems for cattle that eat it. [?????], negative effects on ecosystems are also financially costly; it costs a lot of money to restore a habitat after ...
... (BC) has many negative effects on these habitats. For [?????], cheatgrass reduces biodiversity, leads to more frequent wildfires, and causes health problems for cattle that eat it. [?????], negative effects on ecosystems are also financially costly; it costs a lot of money to restore a habitat after ...
Pachycoris torridus - ICB - Universidade Federal de Minas Gerais
... color patterns and this phenotypic variation can yield important consequences on their evolutionary ecology since different phenotypes can differ in their adaptive value. Paleari (1992, 1994) detected different diapause length, parasite preference, offspring production, and even survival among the d ...
... color patterns and this phenotypic variation can yield important consequences on their evolutionary ecology since different phenotypes can differ in their adaptive value. Paleari (1992, 1994) detected different diapause length, parasite preference, offspring production, and even survival among the d ...
Small River Communities - North Carolina Wildlife Resources
... Tables 2 through 7 at the end of this report identify the species of conservation concern and priority species that use habitats in this ecosystem. Piedmont riverine aquatic communities provide a number of important habitats, life cycle, or prey components to a vast assemblage of terrestrial, semi-a ...
... Tables 2 through 7 at the end of this report identify the species of conservation concern and priority species that use habitats in this ecosystem. Piedmont riverine aquatic communities provide a number of important habitats, life cycle, or prey components to a vast assemblage of terrestrial, semi-a ...
FOOD NICHE OVERLAP IN CO-EXISTING BARN OWL TYTO ALBA
... KEY WORDS: diet, Tyto alba, Bubo virginianus, intensively used farmland, food niche, Oregon One of the central concept in ecology is the competitive exclusion principle, which explain species coexistence. In general this concept forbids the coexistence of two species with identical or similar food n ...
... KEY WORDS: diet, Tyto alba, Bubo virginianus, intensively used farmland, food niche, Oregon One of the central concept in ecology is the competitive exclusion principle, which explain species coexistence. In general this concept forbids the coexistence of two species with identical or similar food n ...
North American Lakes and Pond Ecosystems Introductions to the
... If This Were to Continue What Would Happen to This Ecosystem? Scientists, from all different backgrounds all have different perspectives have different beliefs on the whole idea of global warming and what the effects will be. Some believe that it’s a sign that we are just ending the Ice Age, or tha ...
... If This Were to Continue What Would Happen to This Ecosystem? Scientists, from all different backgrounds all have different perspectives have different beliefs on the whole idea of global warming and what the effects will be. Some believe that it’s a sign that we are just ending the Ice Age, or tha ...
Local and Global Stability of Host-Vector Disease Models
... (resp. Sv and Iv ). We consider a compartmental model that is to say that every population is divided into classes, and that one individual of a population passes from one class to another with a suitable rate. We use the SIS (Susceptible-Infectious-Susceptible) model for the host population and a S ...
... (resp. Sv and Iv ). We consider a compartmental model that is to say that every population is divided into classes, and that one individual of a population passes from one class to another with a suitable rate. We use the SIS (Susceptible-Infectious-Susceptible) model for the host population and a S ...
Closure as a scientific concept and its application to
... with two reservoirs, a source and a sink, so that the steady state involves a flow of matter or energy. The simplest example of such a system is one in contact with two thermal reservoirs of temperatures T1 and T2 through diathermal walls. Suppose the system contains gaseous neon. When the steady sta ...
... with two reservoirs, a source and a sink, so that the steady state involves a flow of matter or energy. The simplest example of such a system is one in contact with two thermal reservoirs of temperatures T1 and T2 through diathermal walls. Suppose the system contains gaseous neon. When the steady sta ...
Relationships Among Living Things A. Organizing Ecosystems
... then the frog population might not have enough food. This would limit the size of the frog population. ...
... then the frog population might not have enough food. This would limit the size of the frog population. ...
msc_botnay_final_pap6_bl1 - Madhya Pradesh Bhoj Open
... Reference ___________________________________________________________________ ...
... Reference ___________________________________________________________________ ...
WORDS BY ALAN WATSON FEATHERSTONE, FOUNDER OF
... by people does play a role in limiting the population, it does not replicate the other functions of predators. Another serious impediment to rewilding is the proliferation of large-scale wind farms. Financed by massive subsidies, these ...
... by people does play a role in limiting the population, it does not replicate the other functions of predators. Another serious impediment to rewilding is the proliferation of large-scale wind farms. Financed by massive subsidies, these ...
BEFORE THE PUBLIC SERVICE COMMISSION OF MARYLAND IN
... nests are currently inactive. A third nest is located near the southwest property boundary, within the floodplain of Stanley Run. This nest is considered active and the construction and operation of the existing Chalk Point facility has produced no adverse effects upon nesting bald eagles. In additi ...
... nests are currently inactive. A third nest is located near the southwest property boundary, within the floodplain of Stanley Run. This nest is considered active and the construction and operation of the existing Chalk Point facility has produced no adverse effects upon nesting bald eagles. In additi ...
Theoretical ecology

Theoretical ecology is the scientific discipline devoted to the study of ecological systems using theoretical methods such as simple conceptual models, mathematical models, computational simulations, and advanced data analysis. Effective models improve understanding of the natural world by revealing how the dynamics of species populations are often based on fundamental biological conditions and processes. Further, the field aims to unify a diverse range of empirical observations by assuming that common, mechanistic processes generate observable phenomena across species and ecological environments. Based on biologically realistic assumptions, theoretical ecologists are able to uncover novel, non-intuitive insights about natural processes. Theoretical results are often verified by empirical and observational studies, revealing the power of theoretical methods in both predicting and understanding the noisy, diverse biological world.The field is broad and includes foundations in applied mathematics, computer science, biology, statistical physics, genetics, chemistry, evolution, and conservation biology. Theoretical ecology aims to explain a diverse range of phenomena in the life sciences, such as population growth and dynamics, fisheries, competition, evolutionary theory, epidemiology, animal behavior and group dynamics, food webs, ecosystems, spatial ecology, and the effects of climate change.Theoretical ecology has further benefited from the advent of fast computing power, allowing the analysis and visualization of large-scale computational simulations of ecological phenomena. Importantly, these modern tools provide quantitative predictions about the effects of human induced environmental change on a diverse variety of ecological phenomena, such as: species invasions, climate change, the effect of fishing and hunting on food network stability, and the global carbon cycle.