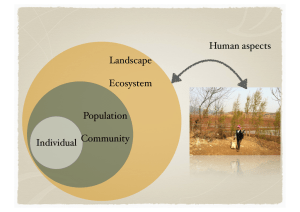
Individual Population Community Landscape Ecosystem Human
... Are these stochastic process? Higher temperature due to climate change increases disease risk and mortality? Higher temperature due to climate change select for genotypes with weak immunity? Higher temperature due to climate change changes life history to early reproduction? ...
... Are these stochastic process? Higher temperature due to climate change increases disease risk and mortality? Higher temperature due to climate change select for genotypes with weak immunity? Higher temperature due to climate change changes life history to early reproduction? ...
Models of Biological Interaction Among Species or Populations
... constituting (part of) that population‟s environment. The modeller would then give greater attention to modelling that environment – perhaps by treating it as being stochastic or uncertain in some way – but would not develop models of interaction between specific species or populations. But there ar ...
... constituting (part of) that population‟s environment. The modeller would then give greater attention to modelling that environment – perhaps by treating it as being stochastic or uncertain in some way – but would not develop models of interaction between specific species or populations. But there ar ...
Resolving Global Overpopulation - Bystroff Lab Home Page
... So every good hypothesis needs data to back it up. Jared Diamond is the author of Guns, Germs and Steel, the story of how geographical features can lead to historical outcomes. His latest book “Collapse” chronicles how populations have grown, outgrown their environments, and collapsed, sometimes dra ...
... So every good hypothesis needs data to back it up. Jared Diamond is the author of Guns, Germs and Steel, the story of how geographical features can lead to historical outcomes. His latest book “Collapse” chronicles how populations have grown, outgrown their environments, and collapsed, sometimes dra ...
Bio 5.2
... Competition can be within one’s own species. For example, many grazing species compete for territories in which to breed and raise offspring. Competition can also be between different species that attempt to use similar or overlapping resources. Different predators can compete over the same prey. Ei ...
... Competition can be within one’s own species. For example, many grazing species compete for territories in which to breed and raise offspring. Competition can also be between different species that attempt to use similar or overlapping resources. Different predators can compete over the same prey. Ei ...
Carrying Capacity
... 8. How many years did the population stay at the second carrying capacity? ...
... 8. How many years did the population stay at the second carrying capacity? ...
Things to know for the Test
... 49. How can some bugs survive after being sprayed by an insecticide? 50. List four abiotic factors of an ecosystem. 51. List three sources of carbon dioxide in the atmosphere. 52. Why are invasive species such a big problem in an ecosystem? 53. What is the carrying capacity? 54. An energy pyramid i ...
... 49. How can some bugs survive after being sprayed by an insecticide? 50. List four abiotic factors of an ecosystem. 51. List three sources of carbon dioxide in the atmosphere. 52. Why are invasive species such a big problem in an ecosystem? 53. What is the carrying capacity? 54. An energy pyramid i ...
APES Guided Reading * Chapter 2, 3, and 4
... 9. Why do ecologists assess the population size, population density, population distribution, sex ratio, age structure, birth and death rates of populations? 10. Why are S-curves more common than exponential growth curves? 11. Draw a graph of a population growing under ideal conditions (label your a ...
... 9. Why do ecologists assess the population size, population density, population distribution, sex ratio, age structure, birth and death rates of populations? 10. Why are S-curves more common than exponential growth curves? 11. Draw a graph of a population growing under ideal conditions (label your a ...
Appendix 1
... In the field station nursery at BRT, we carried out annual germination experiments from 2005 to 2008. In each of the four years, between 30-50 seeds of each ...
... In the field station nursery at BRT, we carried out annual germination experiments from 2005 to 2008. In each of the four years, between 30-50 seeds of each ...
Review sheet chapters 8, 9 and 10
... a very strong current. They would jump out of the water which made it seem like they were flying for a few seconds and then dove back down in the water. c- This biome has lots of grazing animals in a very open space. I was told to bring sunscreen because there are few trees around and it gets very h ...
... a very strong current. They would jump out of the water which made it seem like they were flying for a few seconds and then dove back down in the water. c- This biome has lots of grazing animals in a very open space. I was told to bring sunscreen because there are few trees around and it gets very h ...
4.5 Factors Controlling Population Size S. Preston 1 A2 Unit BY4
... Weather, predation, parasitism (disease), food supply, living space and competition may affect population growth. The effect of density dependent factors varies with the size of the population whereas the effect of density independent will be the same regardless of the population size. Be able to de ...
... Weather, predation, parasitism (disease), food supply, living space and competition may affect population growth. The effect of density dependent factors varies with the size of the population whereas the effect of density independent will be the same regardless of the population size. Be able to de ...
Ecosystems and Communitiesthird class
... and abiotic factors that affect it Niche: an organism’s habitat plus its role in an ecosystem ...
... and abiotic factors that affect it Niche: an organism’s habitat plus its role in an ecosystem ...
Jeopardy - School Without Walls Biology
... Why does a population, once it reaches its carrying capacity, fluctuate above and below that carrying capacity, rather than remaining steady? ...
... Why does a population, once it reaches its carrying capacity, fluctuate above and below that carrying capacity, rather than remaining steady? ...
A6.71 Bar-tailed Godwit Limosa lapponica
... be expected as a consequence of variation in weather and predation pressures on breeding areas. Overall, the biogeographic population has shown a general increase since at least the mid-1980s from 100,000 individuals (Lack 1986) to 115,000 individuals (Rose & Scott 1997). A decrease has been reporte ...
... be expected as a consequence of variation in weather and predation pressures on breeding areas. Overall, the biogeographic population has shown a general increase since at least the mid-1980s from 100,000 individuals (Lack 1986) to 115,000 individuals (Rose & Scott 1997). A decrease has been reporte ...
Woodland Hills - Science 8 - Lesson 15 Guided Notes Answer Key
... Usually population size will change depending on the number of births and the number of deaths. -With more births than deaths, the population size will increase. -With more deaths than births, the population size will decrease. -Most populations reach a stable point where births equal deaths. -This ...
... Usually population size will change depending on the number of births and the number of deaths. -With more births than deaths, the population size will increase. -With more deaths than births, the population size will decrease. -Most populations reach a stable point where births equal deaths. -This ...
File - Pedersen Science
... density-independent factors as they relates to their effect on populations? What are examples of each category of factor? How can an ecological footprint be useful? ...
... density-independent factors as they relates to their effect on populations? What are examples of each category of factor? How can an ecological footprint be useful? ...
ECOLOGY Study Guide
... density-independent factors as they relates to their effect on populations? What are examples of each category of factor? How can an ecological footprint be useful? ...
... density-independent factors as they relates to their effect on populations? What are examples of each category of factor? How can an ecological footprint be useful? ...
Empirical and Other Stock Assessment Approaches
... (where M is natural mortality, K is the growth rate, tm is the age at maturity and Lm is the length at maturity as a proportion of the asymptotic length L∞, see Chapter 11). FAO Fish. Tech. Paper 487; Section 4.2, Chapter 11 ...
... (where M is natural mortality, K is the growth rate, tm is the age at maturity and Lm is the length at maturity as a proportion of the asymptotic length L∞, see Chapter 11). FAO Fish. Tech. Paper 487; Section 4.2, Chapter 11 ...
Interdependent Relationships In Ecosystems
... many resources or reached its carrying capacity. This is known as logistic growth. Resources that were once plentiful are now in demand, and competition for food, shelter, mates, and other resources will increase as the population continues to grow. The limited resources and increasing competition c ...
... many resources or reached its carrying capacity. This is known as logistic growth. Resources that were once plentiful are now in demand, and competition for food, shelter, mates, and other resources will increase as the population continues to grow. The limited resources and increasing competition c ...
1 - Scioly.org
... Asexual reproduction such as parthenogenesis takes greatest advantage of unlimited space and resources in a stable environment. This mode of reproduction facilitates rapid population growth. Although species diversity created through sexual reproduction is sacrificed, it is not necessary in a noncom ...
... Asexual reproduction such as parthenogenesis takes greatest advantage of unlimited space and resources in a stable environment. This mode of reproduction facilitates rapid population growth. Although species diversity created through sexual reproduction is sacrificed, it is not necessary in a noncom ...
ECOLOGY EVENT EXAM Science Olympiad
... 32. A pigeon finds its way home using landmarks such as mountain ranges and buildings. These landmarks are a) external stimuli. c) internal stimuli. b) known as body language. D) known as estivation. 33. The largest number of individuals of one species that an ecosystem can support over time. a) car ...
... 32. A pigeon finds its way home using landmarks such as mountain ranges and buildings. These landmarks are a) external stimuli. c) internal stimuli. b) known as body language. D) known as estivation. 33. The largest number of individuals of one species that an ecosystem can support over time. a) car ...
Ecology Review Game
... observing the relationships that woodpeckers have with other species in their environment studying the internal organs of a seal to learn how it survives in its environment ...
... observing the relationships that woodpeckers have with other species in their environment studying the internal organs of a seal to learn how it survives in its environment ...
Ch. 18-20 Ecology Unit
... Red alder disperses easily and is capable of rapid growth on the nutrientpoor, volcanic deposits. A red-legged frog –one of the creatures living in one of the dozens of ponds created after the eruption. 70 species of birds, including ...
... Red alder disperses easily and is capable of rapid growth on the nutrientpoor, volcanic deposits. A red-legged frog –one of the creatures living in one of the dozens of ponds created after the eruption. 70 species of birds, including ...
Ecology
... • Ramet - an ecological unit; ecologically considered an individual unit because it is mostly autonomous with regard to utilization of resources, even though it is physically connected to one or more individuals of the exact same species and identical genetic ...
... • Ramet - an ecological unit; ecologically considered an individual unit because it is mostly autonomous with regard to utilization of resources, even though it is physically connected to one or more individuals of the exact same species and identical genetic ...
Gene Flow - manorlakesscience
... Allele frequencies of large populations = more stable because greater reservoir of variability less affected by changes involving only a few individuals. Small populations have fewer alleles to begin with and - severity and speed of changes in allele frequencies are greater. Endangered species ...
... Allele frequencies of large populations = more stable because greater reservoir of variability less affected by changes involving only a few individuals. Small populations have fewer alleles to begin with and - severity and speed of changes in allele frequencies are greater. Endangered species ...
Biological Populations
... All organisms, including humans are organized into populations, which are themselves grouped into communities and form ecosystems. In sociology and biology, a population is the collection people or organisms of a particular species, living in a given geographic area (or space), at a given time. Thes ...
... All organisms, including humans are organized into populations, which are themselves grouped into communities and form ecosystems. In sociology and biology, a population is the collection people or organisms of a particular species, living in a given geographic area (or space), at a given time. Thes ...