B 262, S 2009
... 4. Researchers∗ examined the effect of burning on species diversity of the low-growing mosses, liverworts and lichens (photosynthetic organisms that grow along the ground underneath grasses and forbs). They examined twenty 5m x 5m grassland plots (New South Wales, Australia) in each of many areas t ...
... 4. Researchers∗ examined the effect of burning on species diversity of the low-growing mosses, liverworts and lichens (photosynthetic organisms that grow along the ground underneath grasses and forbs). They examined twenty 5m x 5m grassland plots (New South Wales, Australia) in each of many areas t ...
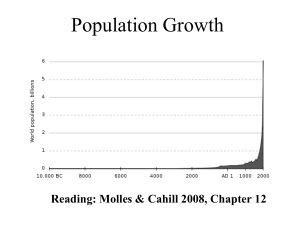
Population Growth
... Predator release is common where humans hunt, trap, or otherwise reduce predator populations, allowing the prey population to increase. Elimination of wolves and panthers have led to increase in their natural prey: deer. There are more deer estimated in the United States than there were when Europea ...
... Predator release is common where humans hunt, trap, or otherwise reduce predator populations, allowing the prey population to increase. Elimination of wolves and panthers have led to increase in their natural prey: deer. There are more deer estimated in the United States than there were when Europea ...
Limits to Growth and Human Carrying Capacity
... 1. Water and soil are valuable resources, which must be used more carefully as the human population grows. 2. Much of the current agricultural practices result in soil degradation and water pollution. Thus our food supply is unsustainable. 3. Nonrenewable energy resources will be consumed at some po ...
... 1. Water and soil are valuable resources, which must be used more carefully as the human population grows. 2. Much of the current agricultural practices result in soil degradation and water pollution. Thus our food supply is unsustainable. 3. Nonrenewable energy resources will be consumed at some po ...
Impact of maximum sustainable yield on competitive community
... conditions on the existence of the maximal value of Yt are external, they do not necessarily imply Nni 40, i¼1,2 nor the stability of the equilibrium. When r1 ¼r2, K1 ¼K2 and a ¼ b, the TMSY exists and it is the global maximum (Fig. 1a and b). As the competition coefficients increase, the area of spe ...
... conditions on the existence of the maximal value of Yt are external, they do not necessarily imply Nni 40, i¼1,2 nor the stability of the equilibrium. When r1 ¼r2, K1 ¼K2 and a ¼ b, the TMSY exists and it is the global maximum (Fig. 1a and b). As the competition coefficients increase, the area of spe ...
Intro. To Environmental Science 120
... * extinct/extirpated/endangered/threatened/special concern/ data deficient/not at risk ...
... * extinct/extirpated/endangered/threatened/special concern/ data deficient/not at risk ...
Name______________________________________
... 3. ____________________ the largest population that an area can support 4. ____________________ number of deaths in a population in a certain amount of time 5. ____________________ leaving a population 6. ____________________ number of births in a population in a certain amount of time 7. __________ ...
... 3. ____________________ the largest population that an area can support 4. ____________________ number of deaths in a population in a certain amount of time 5. ____________________ leaving a population 6. ____________________ number of births in a population in a certain amount of time 7. __________ ...
Population Growth
... Note that Ro (net reproductive rate) can also be called λ (geometric rate of increase) Fig. 11.12, Molles & Cahill, 2008 ...
... Note that Ro (net reproductive rate) can also be called λ (geometric rate of increase) Fig. 11.12, Molles & Cahill, 2008 ...
Bell Work Questions
... Exponential growth model: If a population of organisms has no limiting factors, it grows exponentially until some environmental factor begins to limit it. Is called a J curve. Logistic Population Growth: this is the growth pattern associated with most populations. The curve of growth associate ...
... Exponential growth model: If a population of organisms has no limiting factors, it grows exponentially until some environmental factor begins to limit it. Is called a J curve. Logistic Population Growth: this is the growth pattern associated with most populations. The curve of growth associate ...
Population Dynamics and Regulation
... By the second half of the twentieth century, the concept of K- and r-selected species was used extensively and successfully to study populations. The concept relates not only reproductive strategies, but also to a species' habitat and behavior, especially in the way that they obtain resources and ca ...
... By the second half of the twentieth century, the concept of K- and r-selected species was used extensively and successfully to study populations. The concept relates not only reproductive strategies, but also to a species' habitat and behavior, especially in the way that they obtain resources and ca ...
Population Growth
... the population grows by 10 percent per year, there will be 1100 individuals in the population next year (1000 + 100). The year after that, there will be 1210 (1100 + 110), and then 1331 (1210 + 121) the next year. Notice that even though the growth rate (10%) remains the same, each increase in popul ...
... the population grows by 10 percent per year, there will be 1100 individuals in the population next year (1000 + 100). The year after that, there will be 1210 (1100 + 110), and then 1331 (1210 + 121) the next year. Notice that even though the growth rate (10%) remains the same, each increase in popul ...
a population. - kimscience.com
... sustained only when there are no constraints from the environment. ...
... sustained only when there are no constraints from the environment. ...
Sustainability of Ecosystems
... • Interspecific competition: between different species • Population density: refers to the population of a species that can survive in a certain area. This is closely linked with the carrying capacity for an area. • Density-dependant factors: those factors that increase stress as the population incr ...
... • Interspecific competition: between different species • Population density: refers to the population of a species that can survive in a certain area. This is closely linked with the carrying capacity for an area. • Density-dependant factors: those factors that increase stress as the population incr ...
Populations and Ecosystems Limiting Factors
... removal of individuals as they are eaten. Diseases limit populations in the same way. Even though we don’t usually think of a large animal or plant being attacked by a microscopic bacterium, the result can be the same. A mountain lion capturing a deer, or a hawk taking a squirrel, removes an indivi ...
... removal of individuals as they are eaten. Diseases limit populations in the same way. Even though we don’t usually think of a large animal or plant being attacked by a microscopic bacterium, the result can be the same. A mountain lion capturing a deer, or a hawk taking a squirrel, removes an indivi ...
Populations Notes
... These populations are found in stable environments who live close to the carrying capacity (K) of the environment. - populations become crowded, causing intraspecific competition - members are usually large in size and produce young that are slow-growing and require parental care - low reproduction ...
... These populations are found in stable environments who live close to the carrying capacity (K) of the environment. - populations become crowded, causing intraspecific competition - members are usually large in size and produce young that are slow-growing and require parental care - low reproduction ...
SB4a LEQ1 Relationships Fall 2008
... reproductive strategy of a species. – Diagram showing the number of surviving members over time from a measured set of births. ...
... reproductive strategy of a species. – Diagram showing the number of surviving members over time from a measured set of births. ...
population dynamics - general considerations
... the length of the track accumulated while searching through the parasite's lifetime. Fluctuates with parasite density due to "interference". Abbreviated "a". Biotic mortality factors: Living environmental factors that bring about premature death of plants and animals. Carrying capacity: The density ...
... the length of the track accumulated while searching through the parasite's lifetime. Fluctuates with parasite density due to "interference". Abbreviated "a". Biotic mortality factors: Living environmental factors that bring about premature death of plants and animals. Carrying capacity: The density ...
Original Population
... 5. You are a new introduced predator to the habitat. In your search for food, you find that the green variety of S. colorus are the easiest to capture. As a result, you eat all but one of them. 6. Place the new data on the second data table and recalculate the color frequencies as you did above. ...
... 5. You are a new introduced predator to the habitat. In your search for food, you find that the green variety of S. colorus are the easiest to capture. As a result, you eat all but one of them. 6. Place the new data on the second data table and recalculate the color frequencies as you did above. ...
Unit Test: Ecology/Weather
... 27. Biodiversity is the term that is used to describe differences that exist in the: a) abiotic factors b) variety of organisms c) sizes of populations d) rates of reproduction 28. A biotic or an abiotic resource in the environment that prevents a population size from increasing is called a: a) carr ...
... 27. Biodiversity is the term that is used to describe differences that exist in the: a) abiotic factors b) variety of organisms c) sizes of populations d) rates of reproduction 28. A biotic or an abiotic resource in the environment that prevents a population size from increasing is called a: a) carr ...
Population Ecology and Ecosystems Ecology Human Population
... • Americans have a disproportionately large effect on the world’s resources • Per capita, Americans consume more resources and create more pollution than citizens of less developed nations ...
... • Americans have a disproportionately large effect on the world’s resources • Per capita, Americans consume more resources and create more pollution than citizens of less developed nations ...
Les populations et les communautés
... True. Both populations benefit from this interaction. d) Competition has a positive impact on population density. False. On the contrary, competition reduces population density. e) Parasitism and predation refer to exactly the same phenomenon. False. In parasitism, the parasite lives inside its host ...
... True. Both populations benefit from this interaction. d) Competition has a positive impact on population density. False. On the contrary, competition reduces population density. e) Parasitism and predation refer to exactly the same phenomenon. False. In parasitism, the parasite lives inside its host ...
Population dynamics of small game
... Predation – especially during vole population low Diseases Parasites A combination of these (and unknown) factors (In addition, population age structure is playing (at least some) role in cyclic fluctuations) ...
... Predation – especially during vole population low Diseases Parasites A combination of these (and unknown) factors (In addition, population age structure is playing (at least some) role in cyclic fluctuations) ...
PreTest Keys - drrossymathandscience
... A. The mark-recapture method was used to estimate the size of the groundhog population in a field. According to this estimate, the population was 50. a) Subsequent studies of groundhog behaviour revealed that these animals can recognize a trap more easily if they have already been captured. In light ...
... A. The mark-recapture method was used to estimate the size of the groundhog population in a field. According to this estimate, the population was 50. a) Subsequent studies of groundhog behaviour revealed that these animals can recognize a trap more easily if they have already been captured. In light ...
Lesson 5: Population structure and plant
... ideas of Malthus regarding the limitation of resources Through the animal and vegetable kingdoms, nature has scattered the seeds of life abroad with the most profuse and liberal hand. She has been comparatively sparing in the room and nourishment necessary to rear them. Their germs of existence cont ...
... ideas of Malthus regarding the limitation of resources Through the animal and vegetable kingdoms, nature has scattered the seeds of life abroad with the most profuse and liberal hand. She has been comparatively sparing in the room and nourishment necessary to rear them. Their germs of existence cont ...
NCEAS WORKING GROUP REPORT
... Most previous examination of age structures using matrix models has assumed that the population is at the stable age structure. For ungulate populations this is rarely the case. However, the age structure may be an important component of population dynamics, because individuals in different age cate ...
... Most previous examination of age structures using matrix models has assumed that the population is at the stable age structure. For ungulate populations this is rarely the case. However, the age structure may be an important component of population dynamics, because individuals in different age cate ...