Species Interact in Five Major Ways Most Species Compete with
... Deer Population in the U.S. • 1900: deer habitat destruction and uncontrolled hunting • 1920s–1930s: laws to protect the deer • Current population explosion for deer ...
... Deer Population in the U.S. • 1900: deer habitat destruction and uncontrolled hunting • 1920s–1930s: laws to protect the deer • Current population explosion for deer ...
ppt
... • A logistic equation can describe the self-limiting growth of a biological population. • where r is the maximum growth rate of the population (N), and K is the carrying capacity of its local environmental setting, d stands for derivative, and t for time. ...
... • A logistic equation can describe the self-limiting growth of a biological population. • where r is the maximum growth rate of the population (N), and K is the carrying capacity of its local environmental setting, d stands for derivative, and t for time. ...
9.1 Mechanisms of Evolution
... better suited to survive and reproduce. Population has a wide variety of phenotypes and genotypes, and some individuals produce more offspring than the environment can support (carrying capacity). Selective forces, such as; predation and competition, will lead to selecting individuals with traits be ...
... better suited to survive and reproduce. Population has a wide variety of phenotypes and genotypes, and some individuals produce more offspring than the environment can support (carrying capacity). Selective forces, such as; predation and competition, will lead to selecting individuals with traits be ...
File - Mr. Shanks` Class
... Population growth models a. ______________ growth for populations with ____________ breeding times eg. one breeding cycle per year ...
... Population growth models a. ______________ growth for populations with ____________ breeding times eg. one breeding cycle per year ...
Introduction to Ecology
... If a population is growing, r is positive. If a population is declining, r is negative. Zero population growth occurs when r = 0 Exponential growth – maximum population growth rate • Intrinsic rate of increase is the maximum population growth rate, rmax • Exponential growth is: • dN/dt = rmax N ...
... If a population is growing, r is positive. If a population is declining, r is negative. Zero population growth occurs when r = 0 Exponential growth – maximum population growth rate • Intrinsic rate of increase is the maximum population growth rate, rmax • Exponential growth is: • dN/dt = rmax N ...
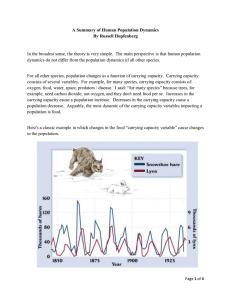
a Summary of Human Population Dynamics
... carrying capacity, the lynx population then decreases. Look at the Y-axis labels on the left and right. There are thousands of lynx and tens of thousands of hare. These fluctuations are part of the natural course of food and feeder population dynamics throughout the biological community. You might s ...
... carrying capacity, the lynx population then decreases. Look at the Y-axis labels on the left and right. There are thousands of lynx and tens of thousands of hare. These fluctuations are part of the natural course of food and feeder population dynamics throughout the biological community. You might s ...
Ecology I
... patterns. I can differentiate between exponential growth and logistic growth. I can define and identify density-dependent and density-independent limiting factors. ...
... patterns. I can differentiate between exponential growth and logistic growth. I can define and identify density-dependent and density-independent limiting factors. ...
Fundamentals Science and the environment
... • Coal; compressed peat, converts to coal under pressure and heat as layers accumulate on top • Oil; animal tissue, incomplete decomposition under high heat and pressure • Natural gas: methane, byproduct to oil production ...
... • Coal; compressed peat, converts to coal under pressure and heat as layers accumulate on top • Oil; animal tissue, incomplete decomposition under high heat and pressure • Natural gas: methane, byproduct to oil production ...
Symbiosis Resource Mutualism Parasitism
... Most animals have a built-in need for a certain amount of _________ and end up _________ among themselves if they become overcrowded. ...
... Most animals have a built-in need for a certain amount of _________ and end up _________ among themselves if they become overcrowded. ...
SUCCESSION AND LIMITING FACTORS
... melted where there is NOT soil. Secondary succession is where an ecosystem has been restored from a ecological disturbance.) B. Distinguish between pioneer species and climax community? (Pioneer species first to populate an area during primary succession. Climax community stable community of the dom ...
... melted where there is NOT soil. Secondary succession is where an ecosystem has been restored from a ecological disturbance.) B. Distinguish between pioneer species and climax community? (Pioneer species first to populate an area during primary succession. Climax community stable community of the dom ...
Ecology - Greeley Schools
... Populations have several properties that can describe them population range is the area throughout which a population occurs population distribution is the pattern of spacing of individuals within that range population size is the number of individuals in the population population density is ...
... Populations have several properties that can describe them population range is the area throughout which a population occurs population distribution is the pattern of spacing of individuals within that range population size is the number of individuals in the population population density is ...
Population growth rate
... Safer water supplies (stopped the spread of disease). U.S. infant mortality rate is high due to Inadequate health care for poor women during pregnancy and their infants Drug addiction among pregnant women High birth rate among teenagers The overall health of a region is based on life expectancy and ...
... Safer water supplies (stopped the spread of disease). U.S. infant mortality rate is high due to Inadequate health care for poor women during pregnancy and their infants Drug addiction among pregnant women High birth rate among teenagers The overall health of a region is based on life expectancy and ...
Topic 2 - Ecology
... (giant seaweed, a protist) is a major source of food and shelter for the ecosystem. Some species of crabs, snails, and geese depend on kelp for food. Many types of fish use the huge kelp forests to hide from predators. Without sea otters to control the urchin population, the entire ecosystem would c ...
... (giant seaweed, a protist) is a major source of food and shelter for the ecosystem. Some species of crabs, snails, and geese depend on kelp for food. Many types of fish use the huge kelp forests to hide from predators. Without sea otters to control the urchin population, the entire ecosystem would c ...
Carrying capacity
... capacity to regenerate. 13. Carrying capacity divides the blame for the impacts between the rich and poor. 14. The poor are blamed for having too many children. 15. This kind of discussion answers the questions related to overexploitation. In the words of one researcher: "Over the past three decades ...
... capacity to regenerate. 13. Carrying capacity divides the blame for the impacts between the rich and poor. 14. The poor are blamed for having too many children. 15. This kind of discussion answers the questions related to overexploitation. In the words of one researcher: "Over the past three decades ...
Population Ecology
... coming) Carrying Capacity of a Habitat Average age of a species and its survivorship curve Dispersion of a species and their resources ...
... coming) Carrying Capacity of a Habitat Average age of a species and its survivorship curve Dispersion of a species and their resources ...
3 major dilemmas on small-scale fisheries management:
... Logistic growth: r-K selection Carrying capacity = B∞ = K ...
... Logistic growth: r-K selection Carrying capacity = B∞ = K ...
Ch52-56MustKnows-Ecology Review
... Aquatic biomes are diverse and dynamic systems that cover most of Earth. The structure and distribution of terrestrial biomes are controlled by climate and disturbance Dynamic biological processes influence population density, dispersion, and demographics. Life history traits are products of natural ...
... Aquatic biomes are diverse and dynamic systems that cover most of Earth. The structure and distribution of terrestrial biomes are controlled by climate and disturbance Dynamic biological processes influence population density, dispersion, and demographics. Life history traits are products of natural ...
Chapter 5 Populations - Rockwood Staff Websites Staff Websites
... each new generation of a population • adds the same number of new individuals as the previous generation ...
... each new generation of a population • adds the same number of new individuals as the previous generation ...
Ecology2 - WordPress.com
... Interspecific = Between different species Intra specific= Between the same species As the population density increases, there is more competition so that growth rate slows. ...
... Interspecific = Between different species Intra specific= Between the same species As the population density increases, there is more competition so that growth rate slows. ...
Interdependence Vocabulary Key Question 1: Roles in the
... ● Describe an example of indirect observation (such as from Outdoor School). ● Describe the process of random sampling (such as the sunflower lab). ● When is mark and recapture a better method? ● Describe the counting turtles lab (it’s also on your notes from 3/31). ● What are the two main ways ...
... ● Describe an example of indirect observation (such as from Outdoor School). ● Describe the process of random sampling (such as the sunflower lab). ● When is mark and recapture a better method? ● Describe the counting turtles lab (it’s also on your notes from 3/31). ● What are the two main ways ...
CHAPTER 24: POPULATION ECOLOGY
... poorer areas are called sinks. Sink populations would often become extinct if not for the regular addition of individuals from source populations. ...
... poorer areas are called sinks. Sink populations would often become extinct if not for the regular addition of individuals from source populations. ...
Questions from reading: A Brief Introduct
... resource! Once all members of a prey species are gone the predator will have to look for alternative sources of food for energy. This brings us to the next factor that affects how an ecosystem functions-- this is how energy flows within an ecosystem. Regardless of their size, the energy flow within ...
... resource! Once all members of a prey species are gone the predator will have to look for alternative sources of food for energy. This brings us to the next factor that affects how an ecosystem functions-- this is how energy flows within an ecosystem. Regardless of their size, the energy flow within ...
Questions from reading: A Brief Introduction to Ecology
... the resource! Once all members of a prey species are gone the predator will have to look for alternative sources of food for energy. This brings us to the next factor that affects how an ecosystem functions-- this is how energy flows within an ecosystem. Regardless of their size, the energy flow wit ...
... the resource! Once all members of a prey species are gone the predator will have to look for alternative sources of food for energy. This brings us to the next factor that affects how an ecosystem functions-- this is how energy flows within an ecosystem. Regardless of their size, the energy flow wit ...