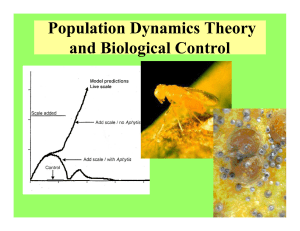
Mean extinction time of populations under toxicant stress and
... can be estimated from life table data, the responses in terms of the intrinsic rate to exposure of chemicals are evaluated if several life tables are estimated under different concentrations of chemicals. Published toxicological data based on life table evaluation or on population growth experiments ...
... can be estimated from life table data, the responses in terms of the intrinsic rate to exposure of chemicals are evaluated if several life tables are estimated under different concentrations of chemicals. Published toxicological data based on life table evaluation or on population growth experiments ...
Predator – Prey Simulation
... the prey species can benefit because predators help to reduce competition for food amongst the prey species and also sick and aged animals can be removed. Some species that interact as predator and prey undergo cyclic changes in their numbers, with sharp increases and periodic crashes. For example t ...
... the prey species can benefit because predators help to reduce competition for food amongst the prey species and also sick and aged animals can be removed. Some species that interact as predator and prey undergo cyclic changes in their numbers, with sharp increases and periodic crashes. For example t ...
Effective carrying capacity and analytical solution of a
... time-dependent intrinsic and extrinsic growth rates. The simplest way to deal with population growth is to consider one-species models. In these models, individuals do not explicitly interact with the external ones and, at time t, the number of individuals is N (t) ≥ 0, with initial condition N0 ≡ N ...
... time-dependent intrinsic and extrinsic growth rates. The simplest way to deal with population growth is to consider one-species models. In these models, individuals do not explicitly interact with the external ones and, at time t, the number of individuals is N (t) ≥ 0, with initial condition N0 ≡ N ...
Ecology Unit 2B Vocabulary and Standards
... *Explain the correlation between population density and the rate of increase during logistic growth. *Explain the difference between populations whose life history is K-selected versus populations that are r-selected. (Include when they are most likely to reproduce) *Explain what demographic data su ...
... *Explain the correlation between population density and the rate of increase during logistic growth. *Explain the difference between populations whose life history is K-selected versus populations that are r-selected. (Include when they are most likely to reproduce) *Explain what demographic data su ...
Biocontrol and Population Dynamics Theory
... not be obvious at first which natural enemies is best. If a series of species are introduced and if by chance less effective species come first, these may later be out competed and replaced by ...
... not be obvious at first which natural enemies is best. If a series of species are introduced and if by chance less effective species come first, these may later be out competed and replaced by ...
INTRODUCTION - Information technology
... Organism Size and Population Density • In general, population density declines with increasing organism size. – Damuth found the population density of herbivorous mammals decreased with increased body size. – Peters and Wassenberg found aquatic invertebrates tend to have higher population densities ...
... Organism Size and Population Density • In general, population density declines with increasing organism size. – Damuth found the population density of herbivorous mammals decreased with increased body size. – Peters and Wassenberg found aquatic invertebrates tend to have higher population densities ...
xuefei method uw
... species like trees, and higher vulnerability to environmental disturbance as well. This group takes over from above ground to understory, sometimes even sub canopy in forest vertical structure. They shade grasses but not to a deathly extent, and shelter tree seeds and seedlings from herbivore browsi ...
... species like trees, and higher vulnerability to environmental disturbance as well. This group takes over from above ground to understory, sometimes even sub canopy in forest vertical structure. They shade grasses but not to a deathly extent, and shelter tree seeds and seedlings from herbivore browsi ...
Ecology PowerPoint - Leon County Schools
... • The variety of life in an area that is determined by the number of different species in that area. • Increases the stability of an ecosystem and contributes to the health of the biosphere. ...
... • The variety of life in an area that is determined by the number of different species in that area. • Increases the stability of an ecosystem and contributes to the health of the biosphere. ...
Resilience Thresholds in resources use Carrying capacity and limits
... Population – sooner or later population expands beyond the “means of subsistence” and some people – the poorest inevitably – will suffer. However the fact is that global population is now six times bigger and the economy 68 times bigger than it was in 1800 – technological changes explain the differe ...
... Population – sooner or later population expands beyond the “means of subsistence” and some people – the poorest inevitably – will suffer. However the fact is that global population is now six times bigger and the economy 68 times bigger than it was in 1800 – technological changes explain the differe ...
Anthony R. Ives: Theoretical and Empirical Community Ecology
... perturbations.(D)Press perturbations to systems with a stable equilibrium. The arrows trace the equilibrium densities of species i and j in a six-species ecosystem as the intrinsic rates of increase decline for all species. In the left panel, the equilibrium point collides with the unstable point at ...
... perturbations.(D)Press perturbations to systems with a stable equilibrium. The arrows trace the equilibrium densities of species i and j in a six-species ecosystem as the intrinsic rates of increase decline for all species. In the left panel, the equilibrium point collides with the unstable point at ...
A Qualitative Model of Plant Growth Based on Exploitation of
... whereas in the middle pathway, growth is slower and resources actually reach high levels before the plant population is large enough to start suppressing them. However, each of these two pathways end in the same state (state 20), with resources low (i.e., equal to R*) and plant populations high. The ...
... whereas in the middle pathway, growth is slower and resources actually reach high levels before the plant population is large enough to start suppressing them. However, each of these two pathways end in the same state (state 20), with resources low (i.e., equal to R*) and plant populations high. The ...
MULTIPLE CHOICE
... 42. All of the following scenarios are likely to cause the competitive exclusion of one of two competing species except: a. overlap of identical niches. b. interspecific interactions that are stronger than intraspecific interactions. c. a and b values that are close to zero. d. a and b values that a ...
... 42. All of the following scenarios are likely to cause the competitive exclusion of one of two competing species except: a. overlap of identical niches. b. interspecific interactions that are stronger than intraspecific interactions. c. a and b values that are close to zero. d. a and b values that a ...
Chapter 40 Active Reading Guide
... 23. Explain the impact of immigration and emigration on population density. (To avoid confusion between these two terms, it might help to use this memory trick: immigration is the movement into a population, while emigration is the exiting of individuals from a population.) ...
... 23. Explain the impact of immigration and emigration on population density. (To avoid confusion between these two terms, it might help to use this memory trick: immigration is the movement into a population, while emigration is the exiting of individuals from a population.) ...
CHAPTER 23
... CC or Cc. • Percentage of population with curly hair is p2 + 2pq = .64 + 2(.8*.2) = .96 or 96% of population. ...
... CC or Cc. • Percentage of population with curly hair is p2 + 2pq = .64 + 2(.8*.2) = .96 or 96% of population. ...
Biology 30 - Patricia Schwandt Courses
... discovered that several predators—such as the black Sigatoka fungus—are attacking the Cavendish. Fungi such as the black Sigatoka are extremely dangerous. However, the situation is compounded by the biological heritage of the Cavendish. It is sexless, seedless, and sterile and can only be bred by gr ...
... discovered that several predators—such as the black Sigatoka fungus—are attacking the Cavendish. Fungi such as the black Sigatoka are extremely dangerous. However, the situation is compounded by the biological heritage of the Cavendish. It is sexless, seedless, and sterile and can only be bred by gr ...
PPT - FishBase
... Conceptual drawing of the hockey stick relationship between spawning stock size and recruitment. SSBlim marks the border below which recruitment declines, SSBpa marks a precautionary distance to SSBlim, and 2 * SSBpa can be used as a proxy for SSB , the stock size that can produce the maximum sustai ...
... Conceptual drawing of the hockey stick relationship between spawning stock size and recruitment. SSBlim marks the border below which recruitment declines, SSBpa marks a precautionary distance to SSBlim, and 2 * SSBpa can be used as a proxy for SSB , the stock size that can produce the maximum sustai ...
A2 level Biology Revision Notes - A
... All populations are different organisms that live & interact together are known as a c_________. Population Growth Curves Usual pattern of growth for natural population has 3 phases: 1. Period of s___ g_____ as the initially small number of individuals reproduce to slowly build up their number 2. Pe ...
... All populations are different organisms that live & interact together are known as a c_________. Population Growth Curves Usual pattern of growth for natural population has 3 phases: 1. Period of s___ g_____ as the initially small number of individuals reproduce to slowly build up their number 2. Pe ...
Chapter 53 Population Ecology
... Evolution and Life History Diversity • Species that exhibit semelparity, or big-bang reproduction, reproduce once and die • Species that exhibit iteroparity, or repeated reproduction, produce offspring repeatedly • Highly variable or unpredictable environments likely favor big-bang reproduction, wh ...
... Evolution and Life History Diversity • Species that exhibit semelparity, or big-bang reproduction, reproduce once and die • Species that exhibit iteroparity, or repeated reproduction, produce offspring repeatedly • Highly variable or unpredictable environments likely favor big-bang reproduction, wh ...
B 262, F 2007
... human fisheries (fishing) have caused individuals in many fish populations to be genetically smaller because… a. the small pop. sizes cause genetic drift. b. fisheries are strong directional natural selection for size. c. fisheries are strong disruptive natural selection for size. d. fisheries cause ...
... human fisheries (fishing) have caused individuals in many fish populations to be genetically smaller because… a. the small pop. sizes cause genetic drift. b. fisheries are strong directional natural selection for size. c. fisheries are strong disruptive natural selection for size. d. fisheries cause ...
Chapter 36 to 38 Notes
... a. gain shelter in the cells of each coral polyp, produce sugars used by the polyps, and b. provide at least half of the energy used by the coral animals. 37.5 EVOLUTION CONNECTION: Predation leads to diverse adaptations in prey species 1. Predation benefits the predator but kills the prey. 2. Prey ...
... a. gain shelter in the cells of each coral polyp, produce sugars used by the polyps, and b. provide at least half of the energy used by the coral animals. 37.5 EVOLUTION CONNECTION: Predation leads to diverse adaptations in prey species 1. Predation benefits the predator but kills the prey. 2. Prey ...
Word Document
... A total of 107 observations of Atelopus varius have been logged since January of 2005, representing 26 unique individuals. Each individual toad is recognized based on a unique color pattern which is recorded in a population database. Although age-related color changes have been observed in individua ...
... A total of 107 observations of Atelopus varius have been logged since January of 2005, representing 26 unique individuals. Each individual toad is recognized based on a unique color pattern which is recorded in a population database. Although age-related color changes have been observed in individua ...