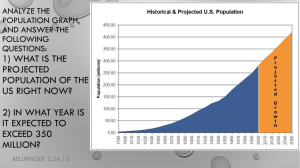
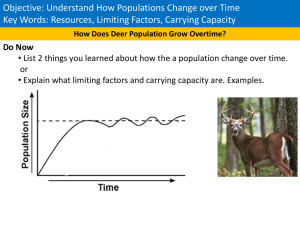
Essential Questions
... Essential Knowledge 1.C.1 - Speciation and extinction have occurred throughout the Earth’s history. Essential Knowledge 1.C.2 - Speciation may occur when two populations become reproductively isolated from each other. Essential Knowledge 4.A.5 - Communities are composed of populations of organisms t ...
... Essential Knowledge 1.C.1 - Speciation and extinction have occurred throughout the Earth’s history. Essential Knowledge 1.C.2 - Speciation may occur when two populations become reproductively isolated from each other. Essential Knowledge 4.A.5 - Communities are composed of populations of organisms t ...
Presentation Title
... II. Variation A. Variation – differences that exist naturally among members of a species 1. Because members of a population of organisms are different, some are better adapted to their environment than others. Thus they can ...
... II. Variation A. Variation – differences that exist naturally among members of a species 1. Because members of a population of organisms are different, some are better adapted to their environment than others. Thus they can ...
POPULATION VIABILITY ANALYSIS Mark S. Boyce Journal Article
... effective population size, dependin the mechanisms affecting drift. For example, Ewens (37) reviews the ation of N c ~relative to inbreeding, Ncv for the variance in gene freque ong subpopulations,NeCtargeting the rate of loss of genetic variation, for mutation effective population size. Still more ...
... effective population size, dependin the mechanisms affecting drift. For example, Ewens (37) reviews the ation of N c ~relative to inbreeding, Ncv for the variance in gene freque ong subpopulations,NeCtargeting the rate of loss of genetic variation, for mutation effective population size. Still more ...
Role of Economics
... little recognition that there might be a MWTPN curve representing the values of people in the rest of the country for the existence of wolves in Alaska. The Alaskan authorities were forced by the nonlocal group to develop new plans • Table 18-3, page 373: mean WTP of supporters; total WTP of support ...
... little recognition that there might be a MWTPN curve representing the values of people in the rest of the country for the existence of wolves in Alaska. The Alaskan authorities were forced by the nonlocal group to develop new plans • Table 18-3, page 373: mean WTP of supporters; total WTP of support ...
Biology
... operate only when the population density reaches a certain level. These factors operate most strongly when a population is large and dense. They do not affect small, scattered populations as greatly. Slide 25 of 22 Copyright Pearson Prentice Hall ...
... operate only when the population density reaches a certain level. These factors operate most strongly when a population is large and dense. They do not affect small, scattered populations as greatly. Slide 25 of 22 Copyright Pearson Prentice Hall ...
AP Biology Reading Guide Chapter 50 An Introduction To
... behavior. If males lack a functional fru gene (short for fruitless), what happens? 26. And what occurs if females are genetically manipulated to express this gene? Concept 51.4 Selection for individual survival and reproductive success can explain most behaviors 27. What is foraging behavior? 28. Wh ...
... behavior. If males lack a functional fru gene (short for fruitless), what happens? 26. And what occurs if females are genetically manipulated to express this gene? Concept 51.4 Selection for individual survival and reproductive success can explain most behaviors 27. What is foraging behavior? 28. Wh ...
population - Deer Creek Schools
... Figure 35.2A Copyright © 2003 Pearson Education, Inc. publishing as Benjamin Cummings ...
... Figure 35.2A Copyright © 2003 Pearson Education, Inc. publishing as Benjamin Cummings ...
population - Deer Creek High School
... Figure 35.2A Copyright © 2003 Pearson Education, Inc. publishing as Benjamin Cummings ...
... Figure 35.2A Copyright © 2003 Pearson Education, Inc. publishing as Benjamin Cummings ...
SC.912.L.17.5
... SC.912.L.17.5#: ANALYZE HOW POPULATION SIZE IS DETERMINED BY BIRTHS, DEATHS, IMMIGRATION, EMIGRATION, AND LIMITING FACTORS (BIOTIC AND ABIOTIC) THAT DETERMINE CARRYING CAPACITY. LIMITING FACTORS? CARRYING CAPACITY? CARRYING CAPACITY IS THE NUMBER OF INDIVIDUALS OF A SPECIES THAT AN ENVIRONMENT CAN S ...
... SC.912.L.17.5#: ANALYZE HOW POPULATION SIZE IS DETERMINED BY BIRTHS, DEATHS, IMMIGRATION, EMIGRATION, AND LIMITING FACTORS (BIOTIC AND ABIOTIC) THAT DETERMINE CARRYING CAPACITY. LIMITING FACTORS? CARRYING CAPACITY? CARRYING CAPACITY IS THE NUMBER OF INDIVIDUALS OF A SPECIES THAT AN ENVIRONMENT CAN S ...
Ecology - Zanichelli online
... Logistic growth occurs when the density of a population reaches the carrying capacity of the environment; growth slows down, resulting in an S-shaped curve. It is influenced by limiting factors. ...
... Logistic growth occurs when the density of a population reaches the carrying capacity of the environment; growth slows down, resulting in an S-shaped curve. It is influenced by limiting factors. ...
投影片 1
... 5. For growing or expanding populations in general, not only is the age of maturity minimized and reproduction concentrated early in life, but also brood size should be increased and a large portion of energy flow partitioned to reproduction – a combination of traits recognizable as an re-selection ...
... 5. For growing or expanding populations in general, not only is the age of maturity minimized and reproduction concentrated early in life, but also brood size should be increased and a large portion of energy flow partitioned to reproduction – a combination of traits recognizable as an re-selection ...
Name - PGS Science
... relate factor to effect on population if population increases then competition for food increase if population increases then increased predation if population increases then increased competition, for space if population increases then increased toxic waste produced by ...
... relate factor to effect on population if population increases then competition for food increase if population increases then increased predation if population increases then increased competition, for space if population increases then increased toxic waste produced by ...
Intraspecific priority effects and disease interact to alter population
... Appendix: Table A1). Individual treatment coefficients, then, represent population abundance over time (i.e., growth rate): higher coefficients indicate higher abundance. This model also contained a smoothing term for the abundance of an unwanted species, Daphnia pulicaria. This species persisted in t ...
... Appendix: Table A1). Individual treatment coefficients, then, represent population abundance over time (i.e., growth rate): higher coefficients indicate higher abundance. This model also contained a smoothing term for the abundance of an unwanted species, Daphnia pulicaria. This species persisted in t ...
ecosystem responses
... organisms and populations they contain. When confronted with a changing environment, an individual organism responds in a way that enables it to survive. These responses affect the population the organism belongs to. Cumulative responses of a population affect the structure and biodiversity of the c ...
... organisms and populations they contain. When confronted with a changing environment, an individual organism responds in a way that enables it to survive. These responses affect the population the organism belongs to. Cumulative responses of a population affect the structure and biodiversity of the c ...
Name - take2theweb
... The influence of density-dependent factors on population change 8 effect of density factor increase as density increases 9 two density dependent factors named from list below 10 A third density dependent factor named from list bekow ...
... The influence of density-dependent factors on population change 8 effect of density factor increase as density increases 9 two density dependent factors named from list below 10 A third density dependent factor named from list bekow ...
013368718X_CH04_047
... 10. What happened to the number of wolves on Isle Royale between 1975 and 1985? 11. What happened to the moose population when the number of wolves was low? 12. What is the relationship between the moose and the wolves on Isle Royale? 13. Is the number of moose on the island a density-dependent or d ...
... 10. What happened to the number of wolves on Isle Royale between 1975 and 1985? 11. What happened to the moose population when the number of wolves was low? 12. What is the relationship between the moose and the wolves on Isle Royale? 13. Is the number of moose on the island a density-dependent or d ...
Chapter 1 - New England Complex Systems Institute
... Grass is governed by a logistic difference equation, with an added term for grazing by rabbits. Well below the saturation density, grass biomass grows by a constant multiplicative factor in each time step, while rabbits feed on the grass in proportion to their appetite. Thus when grass is plentiful, ...
... Grass is governed by a logistic difference equation, with an added term for grazing by rabbits. Well below the saturation density, grass biomass grows by a constant multiplicative factor in each time step, while rabbits feed on the grass in proportion to their appetite. Thus when grass is plentiful, ...
cold water prawns
... have collapsed in recent years due to predation by cod. As a result the inshore fishery has been closed with minor exceptions. The offshore stocks have also declined considerably since 1997 due to increased cod predation (8). ...
... have collapsed in recent years due to predation by cod. As a result the inshore fishery has been closed with minor exceptions. The offshore stocks have also declined considerably since 1997 due to increased cod predation (8). ...
organisms and populations
... They tend to lose body heat very fast when it is cold outside. They have to spend much energy to generate body heat through metabolism. Due to this reason, very small animals are rarely found in Polar Regions. ...
... They tend to lose body heat very fast when it is cold outside. They have to spend much energy to generate body heat through metabolism. Due to this reason, very small animals are rarely found in Polar Regions. ...
US in the World-4 of 4 - Population Reference Bureau
... and healthy air, water, and land, and a stable alliance is made up of climate. But as people strive to meet these fundastate and federal agenmental needs and improve their lives, they make cies, private conservademands on Earth’s resources—and leave foottion organizations, prints. No species demands ...
... and healthy air, water, and land, and a stable alliance is made up of climate. But as people strive to meet these fundastate and federal agenmental needs and improve their lives, they make cies, private conservademands on Earth’s resources—and leave foottion organizations, prints. No species demands ...
How To Be a Predator Department of Zoology, University of
... Assuming for the moment that the predator is concerned with maximal steady-state yield, it need only leave behind enough of the prey population to just replace itself. What are the limits on this process? The ultimate limit is the maximal possible rate of increase of the prey population. In a consta ...
... Assuming for the moment that the predator is concerned with maximal steady-state yield, it need only leave behind enough of the prey population to just replace itself. What are the limits on this process? The ultimate limit is the maximal possible rate of increase of the prey population. In a consta ...
Wolf & Deer Populations
... 4. Explain why an ecosystem with a variety of predator species might be more stable over a long period of time than an ecosystem with only one predator species. • The more variety of predators, the more biodiversity, the more complex the food web is, the more stable the ecosystem is. ...
... 4. Explain why an ecosystem with a variety of predator species might be more stable over a long period of time than an ecosystem with only one predator species. • The more variety of predators, the more biodiversity, the more complex the food web is, the more stable the ecosystem is. ...
Population size
... nesting sites – In any environment, one essential factor will run out first, and acts as the brake on population growth ...
... nesting sites – In any environment, one essential factor will run out first, and acts as the brake on population growth ...
... caused a lack of proper covering for nests and protection from predators. On the other hand, the recent torrential rainfall on the Rolling Plains flooded nests, forcing the hens from brooding and the chicks died from hypothermia. “Clearly, precipitation is a controlling factor for bobwhite populati ...
Unit A: Nervous and Endocrine Systems
... □ describe the process of meiosis (spermatogenesis and oogenesis) and the necessity for the reduction of chromosome number □ compare the processes of mitosis and meiosis □ describe the processes of crossing over and nondisjunction and evaluate their significance to organism inheritance and developme ...
... □ describe the process of meiosis (spermatogenesis and oogenesis) and the necessity for the reduction of chromosome number □ compare the processes of mitosis and meiosis □ describe the processes of crossing over and nondisjunction and evaluate their significance to organism inheritance and developme ...