BL / ENVS 403
... This assignment is designed to help you become familiar with the operation of PopEcoLab by studying the population growth of brown sparrows. The first screen that appears in PopEcoLab shows you an input parameter page with a table listing the default parameters for the laboratory conditions that you ...
... This assignment is designed to help you become familiar with the operation of PopEcoLab by studying the population growth of brown sparrows. The first screen that appears in PopEcoLab shows you an input parameter page with a table listing the default parameters for the laboratory conditions that you ...
Population size and the risk of local extinction: empirical evidence
... mean growth rate was based on the growth rate of populations that survived. Because populations with low growth rates will go extinct more often than those with a high growth rate, the mean growth rate of all populations was probably somewhat lower. However, even including populations that became ex ...
... mean growth rate was based on the growth rate of populations that survived. Because populations with low growth rates will go extinct more often than those with a high growth rate, the mean growth rate of all populations was probably somewhat lower. However, even including populations that became ex ...
Developing Confidence in the Creator God in the University
... The purpose of this paper is to show how faith building concepts can be integrated into most of the major topics of a college level course in general ecology. There are very few biblically neutral topics in ecology. Most ecology topics fall into one of two categories: They either show evidence for d ...
... The purpose of this paper is to show how faith building concepts can be integrated into most of the major topics of a college level course in general ecology. There are very few biblically neutral topics in ecology. Most ecology topics fall into one of two categories: They either show evidence for d ...
Viability of an endangered population of ortolan buntings: The effect
... relying on a single value. Thus, males that were observed in the same territory for 15 days or more were considered likely to be the same individual throughout the breeding season, and were included in the low estimate. On the other hand, males that were observed in the same territory for 5–15 days ...
... relying on a single value. Thus, males that were observed in the same territory for 15 days or more were considered likely to be the same individual throughout the breeding season, and were included in the low estimate. On the other hand, males that were observed in the same territory for 5–15 days ...
vs_mysterygraph_072810_lsalicaria
... support its growing population. Some other factor like weather might have caused or contributed to the crash too. It looks like the purple loosestrife population was able to maintain its 2002 cover as a result. ...
... support its growing population. Some other factor like weather might have caused or contributed to the crash too. It looks like the purple loosestrife population was able to maintain its 2002 cover as a result. ...
Estimation of population sizes and "home ranges" of polyphagous
... interpretation of pitfall trap data has generated much controversy in the entomological literature (LOvei & Samu 1987, Halsall & Wratten 1988, Topping & Sunderland 1992). Conclusions have often been drawn on the relative abundance of the species caught. However, abundance is not the only factor whic ...
... interpretation of pitfall trap data has generated much controversy in the entomological literature (LOvei & Samu 1987, Halsall & Wratten 1988, Topping & Sunderland 1992). Conclusions have often been drawn on the relative abundance of the species caught. However, abundance is not the only factor whic ...
concepts-of-biology
... Another tool used by population ecologists is a survivorship curve, which is a graph of the number of individuals surviving at each age interval versus time. These curves allow us to compare the life histories of different populations (Figure 19.4). There are three types of survivorship curves. In a ...
... Another tool used by population ecologists is a survivorship curve, which is a graph of the number of individuals surviving at each age interval versus time. These curves allow us to compare the life histories of different populations (Figure 19.4). There are three types of survivorship curves. In a ...
How community ecology links natural mortality, growth, and
... rate (see, e.g., Pitcher, 1990), despite a substantial literature on allometric patterns of this type (e.g. Peters, 1983). For example, using constant natural mortality has led to the classical relation that productivity rate P/B is equal to M (Allen, 1971). However, it is not clear that this relati ...
... rate (see, e.g., Pitcher, 1990), despite a substantial literature on allometric patterns of this type (e.g. Peters, 1983). For example, using constant natural mortality has led to the classical relation that productivity rate P/B is equal to M (Allen, 1971). However, it is not clear that this relati ...
Organization of the Biosphere:
... Define “exponential growth”. List and describe factors and conditions under which exponential growth occurs. Draw a general graph depicting an exponential growth curve in the space provided, ...
... Define “exponential growth”. List and describe factors and conditions under which exponential growth occurs. Draw a general graph depicting an exponential growth curve in the space provided, ...
19-Population ecology
... Another tool used by population ecologists is a survivorship curve, which is a graph of the number of individuals surviving at each age interval versus time. These curves allow us to compare the life histories of different populations (Figure 19.4). There are three types of survivorship curves. In a ...
... Another tool used by population ecologists is a survivorship curve, which is a graph of the number of individuals surviving at each age interval versus time. These curves allow us to compare the life histories of different populations (Figure 19.4). There are three types of survivorship curves. In a ...
Paper-6.1-Landings-Obligation-Vision
... obligation to land all catches. North Sea demersal fishing fleets will soon be operating within a CFP transformed by the discard ban and other 2013 reforms. The landings obligation will first be applied to the demersal fisheries in the North Sea in January 2016 for some species. Discard Plans will n ...
... obligation to land all catches. North Sea demersal fishing fleets will soon be operating within a CFP transformed by the discard ban and other 2013 reforms. The landings obligation will first be applied to the demersal fisheries in the North Sea in January 2016 for some species. Discard Plans will n ...
3 - Heartland Community College
... • A. average # of offspring carried to term by a species • B. greatest # of different niches possible in a given area • C. potential growth in the number of species in an area • D. maximum population size that a given environment can sustain ...
... • A. average # of offspring carried to term by a species • B. greatest # of different niches possible in a given area • C. potential growth in the number of species in an area • D. maximum population size that a given environment can sustain ...
Exploring the Relationship between Abundance and
... Figure 4. N* vs. T for hypothetical unicellular and multicellular organisms in eutrophic and oligotrophic conditions (ropt, Y, and So = 1; ρ=1, σ=0.01). For the eutrophic condition case, curves are always flat; increasing the mortality rate slightly decreases N*, but greatly decreases the temperatur ...
... Figure 4. N* vs. T for hypothetical unicellular and multicellular organisms in eutrophic and oligotrophic conditions (ropt, Y, and So = 1; ρ=1, σ=0.01). For the eutrophic condition case, curves are always flat; increasing the mortality rate slightly decreases N*, but greatly decreases the temperatur ...
Spatial Variability Enhances Species Fitness in
... overall features to be remarkably generic and robust with respect to even rather drastic changes of the detailed microscopic interaction rules [20,22]. Yet to render these models more realistic and relevant for biological systems, one must obviously allow for different fitness of the individuals as ...
... overall features to be remarkably generic and robust with respect to even rather drastic changes of the detailed microscopic interaction rules [20,22]. Yet to render these models more realistic and relevant for biological systems, one must obviously allow for different fitness of the individuals as ...
Population structure and dynamics = Structure et dynamique des
... The tropical African fisheries are characterized by multiple speciespopulations of which most component species are small and mostly occur in relatively shallow waters. A second important feature is that stocks often comprise assemblagesof specieswith common evolutionaly histories and dependences SO ...
... The tropical African fisheries are characterized by multiple speciespopulations of which most component species are small and mostly occur in relatively shallow waters. A second important feature is that stocks often comprise assemblagesof specieswith common evolutionaly histories and dependences SO ...
NotesChapter7
... vulnerability to chance threats because the systematic threats reduce the population size and small populations are particularly vulnerable to chance events (Pullin 2002). Conservation Focus… Populations Extinction tends to bring specific species (e.g. the dodo - Raphus cucullatus) or other taxonomi ...
... vulnerability to chance threats because the systematic threats reduce the population size and small populations are particularly vulnerable to chance events (Pullin 2002). Conservation Focus… Populations Extinction tends to bring specific species (e.g. the dodo - Raphus cucullatus) or other taxonomi ...
NotesChapter7
... The effects of systematic threats (such as habitat fragmentation) usually include increased vulnerability to chance threats because the systematic threats reduce the population size and small populations are particularly vulnerable to chance events (Pullin 2002). Conservation Focus… Populations Ext ...
... The effects of systematic threats (such as habitat fragmentation) usually include increased vulnerability to chance threats because the systematic threats reduce the population size and small populations are particularly vulnerable to chance events (Pullin 2002). Conservation Focus… Populations Ext ...
Population Ecology
... Calculating Exponential Growth • Exponential growth in living populations can be calculated by subtracting a population’s death rate from its birth rate, which yields the population’s growth rate. • Denoted as r, this rate is also known as the population’s intrinsic rate of increase. ...
... Calculating Exponential Growth • Exponential growth in living populations can be calculated by subtracting a population’s death rate from its birth rate, which yields the population’s growth rate. • Denoted as r, this rate is also known as the population’s intrinsic rate of increase. ...
population
... Calculating Exponential Growth • Exponential growth in living populations can be calculated by subtracting a population’s death rate from its birth rate, which yields the population’s growth rate. • Denoted as r, this rate is also known as the population’s intrinsic rate of increase. ...
... Calculating Exponential Growth • Exponential growth in living populations can be calculated by subtracting a population’s death rate from its birth rate, which yields the population’s growth rate. • Denoted as r, this rate is also known as the population’s intrinsic rate of increase. ...
5-1 How Populations Grow
... population density reaches a certain level. These factors operate most strongly when a population is large and dense. They do not affect small, scattered populations as greatly. ...
... population density reaches a certain level. These factors operate most strongly when a population is large and dense. They do not affect small, scattered populations as greatly. ...
Bence_2010_tjnrev
... mortality of lake trout in Lake Huron into components due to commercial fishing, recreational fishing, sea lamprey and background (natural) morality. This allowed an evaluation of how agespecific mortality rates of lake trout would change in response to particular management actions. Predator (or pa ...
... mortality of lake trout in Lake Huron into components due to commercial fishing, recreational fishing, sea lamprey and background (natural) morality. This allowed an evaluation of how agespecific mortality rates of lake trout would change in response to particular management actions. Predator (or pa ...
chapter 52 population ecology
... In contrast to big-bang reproduction, some lizards produce only a few large eggs during their second year of life, then repeat the reproductive act annually for several years. And some species of oaks do not reproduce until the tree is 20 years old, but then produce vast numbers of large seeds each ...
... In contrast to big-bang reproduction, some lizards produce only a few large eggs during their second year of life, then repeat the reproductive act annually for several years. And some species of oaks do not reproduce until the tree is 20 years old, but then produce vast numbers of large seeds each ...
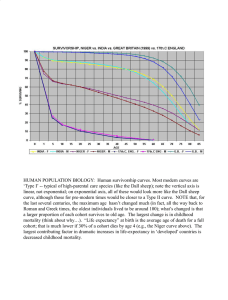
Human survivorship curves. Most modern curves are
... in survivorship affecting age structures. Even though birth rates in recent decades are well below ‘replacement level’, population is still growing because of the very large cohorts passing through child-bearing years. However, growth rate is slowing, and China’s population is predicted to peak in a ...
... in survivorship affecting age structures. Even though birth rates in recent decades are well below ‘replacement level’, population is still growing because of the very large cohorts passing through child-bearing years. However, growth rate is slowing, and China’s population is predicted to peak in a ...