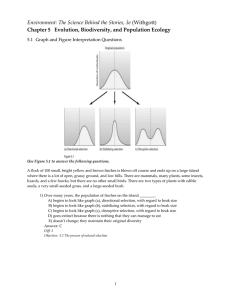
Population Ecology
... selects for life history traits that are sensitive to population density – r-selection, or density-independent selection, selects for life history traits that maximize reproduction – The concepts of K-selection and r-selection are somewhat controversial and have been criticized by ecologists as over ...
... selects for life history traits that are sensitive to population density – r-selection, or density-independent selection, selects for life history traits that maximize reproduction – The concepts of K-selection and r-selection are somewhat controversial and have been criticized by ecologists as over ...
05_3eTIF
... 3) Differentiate between exponential and logistic growth curves. Give examples of the conditions under which each would occur. Answer: Exponential growth (a J-shaped curve) is growth when there are no constraints. This occurs when a population is small and environmental conditions are ideal for the ...
... 3) Differentiate between exponential and logistic growth curves. Give examples of the conditions under which each would occur. Answer: Exponential growth (a J-shaped curve) is growth when there are no constraints. This occurs when a population is small and environmental conditions are ideal for the ...
Lotka-Volterra Predator
... X: the population of prey Y: the population of predators a: natural growth rate of prey in the absence of predation b: death rate due to predation c: natural death rate of predators in the absence of prey d: growth rate due to predation ...
... X: the population of prey Y: the population of predators a: natural growth rate of prey in the absence of predation b: death rate due to predation c: natural death rate of predators in the absence of prey d: growth rate due to predation ...
IOSR Journal of Mathematics (IOSR-JM)
... The stability of the steady state is of important since the eigen-valves have different roots, in general it is unstable. If it were stable, none zero population might be attracted towards the extinction of both species for many cases of initial levels. However as the fixed point at the origin is un ...
... The stability of the steady state is of important since the eigen-valves have different roots, in general it is unstable. If it were stable, none zero population might be attracted towards the extinction of both species for many cases of initial levels. However as the fixed point at the origin is un ...
Engage - NC Science Wiki
... humans, and other organisms. There is a high degree of interdependence among populations of organisms and the non-living components of their environments. These interactions may support a stable population, but often result in wide fluctuation of population numbers over time in natural environments. ...
... humans, and other organisms. There is a high degree of interdependence among populations of organisms and the non-living components of their environments. These interactions may support a stable population, but often result in wide fluctuation of population numbers over time in natural environments. ...
Chapter 51 Introduction to Ecology
... Introduction to Ecology: Population Ecology Copyright © 2005 Brooks/Cole — Thomson Learning ...
... Introduction to Ecology: Population Ecology Copyright © 2005 Brooks/Cole — Thomson Learning ...
The population dynamics of the mangrove Avicennia marina
... Population studies of mangrove species, and most other long-lived plants, often concentrate on components of the life cycle to explain present distribution and abundance. In mangroves, propagule predation (e.g. Robertson et al., 1990), dispersal (e.g. Rabinowitz, 1978), seedling growth (e.g. Ball, 1 ...
... Population studies of mangrove species, and most other long-lived plants, often concentrate on components of the life cycle to explain present distribution and abundance. In mangroves, propagule predation (e.g. Robertson et al., 1990), dispersal (e.g. Rabinowitz, 1978), seedling growth (e.g. Ball, 1 ...
Unit 2 - OpenWetWare
... 14. Define and give examples of niche and habitat. 15. Explain how organisms interact in a community through competition, predation, and symbiosis (mutualism, commensalism, and parasitism). 16. Explain how the introduction of exotic/invasive species (p153) into an unoccupied habitat can affect that ...
... 14. Define and give examples of niche and habitat. 15. Explain how organisms interact in a community through competition, predation, and symbiosis (mutualism, commensalism, and parasitism). 16. Explain how the introduction of exotic/invasive species (p153) into an unoccupied habitat can affect that ...
mangroves - Department of Environmental Science and Policy
... The Optimal State was identified in two scenarios – with and without storm protection. ...
... The Optimal State was identified in two scenarios – with and without storm protection. ...
Provided for non-commercial research and educational use. Not for
... Eusocial systems are an evolutionarily advanced level of colonial existence in which adult colonial members (1) belong to two or more overlapping generations, (2) care cooperatively for the offspring, and (3) are divided into either reproductive and nonreproductive (or less-reproductive) castes. The ...
... Eusocial systems are an evolutionarily advanced level of colonial existence in which adult colonial members (1) belong to two or more overlapping generations, (2) care cooperatively for the offspring, and (3) are divided into either reproductive and nonreproductive (or less-reproductive) castes. The ...
Unit 10
... predict best management practices for a particular species in conservation biology. • Double bar graph population pyramids show proportions of males and females within age groups. • Population pyramids which have wide bases indicate high birth rates and probable population growth, and decreases from ...
... predict best management practices for a particular species in conservation biology. • Double bar graph population pyramids show proportions of males and females within age groups. • Population pyramids which have wide bases indicate high birth rates and probable population growth, and decreases from ...
Using the ESS Maximum Principle to Explore Root
... can be determined without analyses of Jacobian matrices. Using the ESS maximum principle, we confirm that coexistence between two or more species is not possible with this model. We show that this result depends on the consumer growth rate being a linear function of allocation strategy and does not ...
... can be determined without analyses of Jacobian matrices. Using the ESS maximum principle, we confirm that coexistence between two or more species is not possible with this model. We show that this result depends on the consumer growth rate being a linear function of allocation strategy and does not ...
Full text in pdf format
... recovery in 23 yr (Anonymous 1979). The good agreement may be in part due to 2 factors; first, in the model, recruitment was assumed to be unaffected by harvesting and this turned out to be true, and second, both model and field age data (size frequency conversions) were based on the same estimate o ...
... recovery in 23 yr (Anonymous 1979). The good agreement may be in part due to 2 factors; first, in the model, recruitment was assumed to be unaffected by harvesting and this turned out to be true, and second, both model and field age data (size frequency conversions) were based on the same estimate o ...
RevShtExIB160
... Define the term carrying capacity and state the units of this value. Name two ways (biotic or abiotic causes) that the carrying capacity of fish in Lake Waughop increase or decrease. Differentiate between density dependent and density-independent mortality factors and name three examples for each ty ...
... Define the term carrying capacity and state the units of this value. Name two ways (biotic or abiotic causes) that the carrying capacity of fish in Lake Waughop increase or decrease. Differentiate between density dependent and density-independent mortality factors and name three examples for each ty ...
HW Questoins - Holy Trinity Academy
... A. First, notice that if all Hardy-Weinberg conditions are met, you cannot even have microevolution. There cannot be a change in gene or allele frequency in a population from one generation to the next if all 5 Hardy-Weinberg conditions are met. Some people feel that understanding this helps you to ...
... A. First, notice that if all Hardy-Weinberg conditions are met, you cannot even have microevolution. There cannot be a change in gene or allele frequency in a population from one generation to the next if all 5 Hardy-Weinberg conditions are met. Some people feel that understanding this helps you to ...
Glossary - Seafish
... Or by‐catch. Organisms affected incidentally in addition to the target species towards which fishing effort is directed. It may or may not be retained by the gear. Some of the bycatch may be returned to the sea as discards Quantity of fish is caught per hour’s fishing –catch‐per‐unit‐effort (CPUE ...
... Or by‐catch. Organisms affected incidentally in addition to the target species towards which fishing effort is directed. It may or may not be retained by the gear. Some of the bycatch may be returned to the sea as discards Quantity of fish is caught per hour’s fishing –catch‐per‐unit‐effort (CPUE ...
New Zealand Journal of Forestry Science
... persist, grow and expand their distribution such that extinction no longer is possible. One of the dominant causes of extinction in lowdensity populations is random chance. All populations (both sparse and abundant) are affected by stochastic abiotic effects (e.g. variation in weather conditions), b ...
... persist, grow and expand their distribution such that extinction no longer is possible. One of the dominant causes of extinction in lowdensity populations is random chance. All populations (both sparse and abundant) are affected by stochastic abiotic effects (e.g. variation in weather conditions), b ...
Chapter One Targets
... I can explain why burning fossil fuels is harmful to the environment. I can draw the general trend in carbon dioxide concentration over time. I can describe how chemicals pollute Earth’s air and water. I can describe the effect increased population growth will have on the environment. ...
... I can explain why burning fossil fuels is harmful to the environment. I can draw the general trend in carbon dioxide concentration over time. I can describe how chemicals pollute Earth’s air and water. I can describe the effect increased population growth will have on the environment. ...
printer-friendly version of benchmark
... Common misconceptions associated with this benchmark 1. Students have the misconception that all factors are limiting, except the most abundant one. The most limiting factor is the least abundant one. This misconception results from the misunderstanding about the interrelatedness of limiting factors ...
... Common misconceptions associated with this benchmark 1. Students have the misconception that all factors are limiting, except the most abundant one. The most limiting factor is the least abundant one. This misconception results from the misunderstanding about the interrelatedness of limiting factors ...
Ch 14 Jeopardy review for test Interactions in ecosystems
... species will be better suited to the niche, and the other species will be pushed into another niche or become extinct ...
... species will be better suited to the niche, and the other species will be pushed into another niche or become extinct ...
Carrying Capacity of Ecosystems
... A few examples of invasive species that have affected the carrying capacity of ecosystems include: the brown tree snake in Guam, the zebra mussel in North America, water hyacinth in Lake Victoria, and the Nile perch in Lake Victoria. ...
... A few examples of invasive species that have affected the carrying capacity of ecosystems include: the brown tree snake in Guam, the zebra mussel in North America, water hyacinth in Lake Victoria, and the Nile perch in Lake Victoria. ...
Chemostat Design and Theory
... chemostat theory and its applications see (KUBITZCHEK 1970). Equilibrium: The principle behind chemostats is very simple. As the bacteria grow N the concentration of the limiting resource declines r and thus the growth rate declines. An equilibrium is obtained when the rate of growth of the bacte ...
... chemostat theory and its applications see (KUBITZCHEK 1970). Equilibrium: The principle behind chemostats is very simple. As the bacteria grow N the concentration of the limiting resource declines r and thus the growth rate declines. An equilibrium is obtained when the rate of growth of the bacte ...
Has The Human Species Become A Cancer On The Planet
... It should also be remembered that the estimates of total population and growth rates are based on official numbers that often do not include large numbers of people, especially in the Third World countries, who are not counted because they are out of the official enumeration system. In some cases, t ...
... It should also be remembered that the estimates of total population and growth rates are based on official numbers that often do not include large numbers of people, especially in the Third World countries, who are not counted because they are out of the official enumeration system. In some cases, t ...
Predation
... Mimicry – look like something that is dangerous or tastes bad Batesian mimicry – palatable species mimics an unpalatable species model ...
... Mimicry – look like something that is dangerous or tastes bad Batesian mimicry – palatable species mimics an unpalatable species model ...
Predator-prey population dynamics are connected
... Mimicry – look like something that is dangerous or tastes bad Batesian mimicry – palatable species mimics an unpalatable species model ...
... Mimicry – look like something that is dangerous or tastes bad Batesian mimicry – palatable species mimics an unpalatable species model ...