14.3 Factors Affecting Population Change
... • A population is considered at risk of becoming extinct when its number falls below the minimum viable population size • Low densities in populations can mean less genetic variation and less opportunities to mate ...
... • A population is considered at risk of becoming extinct when its number falls below the minimum viable population size • Low densities in populations can mean less genetic variation and less opportunities to mate ...
Concept Review
... Carrying capacity is the maximum number of individuals an ecosystem can support. Populations may experience oscillating cycles of population growth and decline. Some species regulate population growth according to the supply of resources. A logistic growth curve, which appears as an S, or sigmoid, i ...
... Carrying capacity is the maximum number of individuals an ecosystem can support. Populations may experience oscillating cycles of population growth and decline. Some species regulate population growth according to the supply of resources. A logistic growth curve, which appears as an S, or sigmoid, i ...
Population Ecology - Madison County Schools
... Carrying capacity – Maximum number of individuals that an environment can support based off the resources available (based off of the limiting factors) ...
... Carrying capacity – Maximum number of individuals that an environment can support based off the resources available (based off of the limiting factors) ...
Unit 4 Study Guide - Effingham County Schools
... a. Random = _______________________________________________________________________________ i. Benefit is _________________________________________________________________________ b. Uniform = _______________________________________________________________________________ i. Benefit is to reduce ___ ...
... a. Random = _______________________________________________________________________________ i. Benefit is _________________________________________________________________________ b. Uniform = _______________________________________________________________________________ i. Benefit is to reduce ___ ...
Population ppt - Summit School District
... R-strategists populations are most affected by these. . . . Natural disasters ...
... R-strategists populations are most affected by these. . . . Natural disasters ...
Changing Populations A. 1.
... B. Human Population Changes 1. Human population size is affected by the same three factors that determine the sizes of all populations—birthrate, death rate, and ...
... B. Human Population Changes 1. Human population size is affected by the same three factors that determine the sizes of all populations—birthrate, death rate, and ...
No Slide Title
... Density independent affect population size regardless of its numbers. Examples are floods, hurricanes, bad weather, fire habitat destruction and pesticides (agent orange). Density dependent factors have a greater effect as population density increases. Examples are competition for resources, predati ...
... Density independent affect population size regardless of its numbers. Examples are floods, hurricanes, bad weather, fire habitat destruction and pesticides (agent orange). Density dependent factors have a greater effect as population density increases. Examples are competition for resources, predati ...
POPULATION DYNAMICS
... • LOGISTIC GROWTH -involves exponential until population encounters environmental resistance and approaches carrying capacity. – then population fluctuates – forms a sigmoid or s-shaped curve ...
... • LOGISTIC GROWTH -involves exponential until population encounters environmental resistance and approaches carrying capacity. – then population fluctuates – forms a sigmoid or s-shaped curve ...
Populations - Helena High School
... Growth – under ideal conditions with unlimited resources, a population will grow exponentially (doubles) ...
... Growth – under ideal conditions with unlimited resources, a population will grow exponentially (doubles) ...
Chapter 14 Interaction in Ecosystems Study Guide
... 12. Some birds are known as honey guides because they may be followed by humans to wild beehives. When the humans take honey from the hives, the birds are able to feast on the honey and bees, too. This type of relationship is best described as __________________________________________. 13. Starfish ...
... 12. Some birds are known as honey guides because they may be followed by humans to wild beehives. When the humans take honey from the hives, the birds are able to feast on the honey and bees, too. This type of relationship is best described as __________________________________________. 13. Starfish ...
Chapter 5 Reading Questions
... Name ________________________________ Period _____ Score _______ Page 103 1. What is a Population? 2. Why is understanding population growth important? ...
... Name ________________________________ Period _____ Score _______ Page 103 1. What is a Population? 2. Why is understanding population growth important? ...
Tropical Rain Forests
... fission to produce two bacteria in 20min. 2-after another 20 min we’d have 4. 3-after another 20 min we’d have 8 and so on. 4- after 24 we’d have 4 x 1021 bacteria In this type of growth the size of population increases exponentially; look at fig (1). ...
... fission to produce two bacteria in 20min. 2-after another 20 min we’d have 4. 3-after another 20 min we’d have 8 and so on. 4- after 24 we’d have 4 x 1021 bacteria In this type of growth the size of population increases exponentially; look at fig (1). ...
Populations - WordPress.com
... 2. Logistic Growth: Population grows rapidly until some factor limits growth a. ...
... 2. Logistic Growth: Population grows rapidly until some factor limits growth a. ...
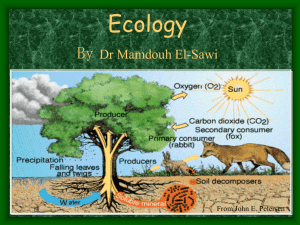
Ecology of Populations
... eight hours a day at the rate of one dollar per second. When you are finished counting, the billion dollars will be yours and only then may you begin to spend it. ...
... eight hours a day at the rate of one dollar per second. When you are finished counting, the billion dollars will be yours and only then may you begin to spend it. ...
Carrying Capacity
... Logistic growth: Population increases rapidly for a period of time, its growth begins to slow, and ultimately, growth stops. ...
... Logistic growth: Population increases rapidly for a period of time, its growth begins to slow, and ultimately, growth stops. ...
Population Growth and Stresses PPT
... Environmental resistance – combination of all factors that act to limit the growth of a population Carrying capacity (K) – maximum population of a given species that a habitat can sustain indefinitely without being degraded ...
... Environmental resistance – combination of all factors that act to limit the growth of a population Carrying capacity (K) – maximum population of a given species that a habitat can sustain indefinitely without being degraded ...
Three Key Features of a Population
... • Declining birth rate or increasing death rate are caused by several limiting factors including: • Competition: ...
... • Declining birth rate or increasing death rate are caused by several limiting factors including: • Competition: ...
Populations
... A population’s age structure refers to the number of males and females of each age a population contains. ...
... A population’s age structure refers to the number of males and females of each age a population contains. ...
PowerPoint
... resources decline. • If the growth is too rapid, resources are rapidly depleted and a population crash can occur • This pattern occurs often with many populations (including humans) Gypsy moth caterpillar ...
... resources decline. • If the growth is too rapid, resources are rapidly depleted and a population crash can occur • This pattern occurs often with many populations (including humans) Gypsy moth caterpillar ...
K = Carrying capacity
... reproduction • Exponential model of population - idealized population in an ...
... reproduction • Exponential model of population - idealized population in an ...