* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Population Ecology - Madison County Schools
Storage effect wikipedia , lookup
Source–sink dynamics wikipedia , lookup
Two-child policy wikipedia , lookup
Human overpopulation wikipedia , lookup
World population wikipedia , lookup
The Population Bomb wikipedia , lookup
Molecular ecology wikipedia , lookup
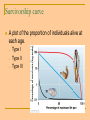
Population Ecology Chapter 36 Population Group of individuals of a single species that occupy the same general area. Population density = number of individuals unit area – The number of oak trees per square kilometer in a forest. – The number of earthworms per cubic meter in forest soil. Dispersion patterns Way individuals in a population are spaced within an area. Clumped Uniform Random Clumped dispersion individuals are grouped in patches. Most common dispersion pattern. Result of need for resources. Uniform dispersion individuals are equally spaced in the environment Result of territorial behavior. Random dispersion individuals in a population are spaced in an unpredictable way Least common dispersion pattern. Survivorship curve A plot of the proportion of individuals alive at each age. – – – Type I Type II Type III Type I Survive to old age. Humans, large mammals Produce few offspring & provides good care. Type II Likelihood of death constant throughout life. Lizards, rodents, birds. Type III Low survival rate for the very young. Oysters, invertebrates, seed plants Produce large numbers of offspring, & little care. Exponential Growth Model Gives an idealized picture of unregulated population growth. Occurs when there are NO limiting factors Population doubles every generation Ex. Population grows from 2 to 4 to 8 to 16 to 32 Bacteria, humans Logistic Growth Model Growth that occurs when there are limiting factors Limiting factors - Environmental factors that restrict population growth. Food, competition, space, predation Population will grow quickly (more births than deaths) at the beginning then will level off (equal number of deaths and births) when the population reaches the environment’s carrying capacity Carrying capacity – Maximum number of individuals that an environment can support based off the resources available (based off of the limiting factors)