* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download A population and its sustainability
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
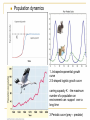
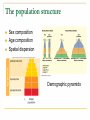
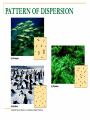
Kostanay Baitursynov State University Course “Ecology and Sustainable Development” Theme “A population and its sustainability” G.Yunussova Plan: 1 The concept of population. 2 Population size, density of a population 3. Population structure 4 Degree of population isolation. Population A group of living organisms of same species, constantly living on the same territory, freely interbreed. an interbreeding group of individuals of a single species that occupy the same general area. A flock of butterflies herd of hippos flock of pelicans a school of dolphins Population characteristics Static – Density of population Degree of isolation butterfly population Dynamic Numbers (size) Demographic structure plant population A population number or abundance or population size or magnitude population - a quantity or count of individuals of a population on occupied territory Survivorship curves N=B–D+E–I Are we a population? What size have the population? Population dynamics 1 J-shaped exponential growth curve 2 S-shaped logistic grouth curve carring capacity K - the maximum number of a population an environment can support over a long time 3 Periodic curve (prey – predator) Population Limiting Factors 3. Population growth rate – How fast a given population grows – Factors that influence this are: • • • • birth rate) Natality (____ death rate) Mortality (_____ Emigration (the number of individuals moving away from a population) _________ moving to Immigration (the number of individuals _________ a population) Population Limiting Factors • Density-independent factors – Factors that limit population size, regardless of population density. – These are usually abiotic factors – They include natural phenomena, such as weather events • Drought, flooding, extreme heat or cold, tornadoes, hurricanes, fires, etc. Population Limiting Factors • Density-dependent factors – Any factor in the environment that depends on the number of members in a population per unit area – Usually biotic factors – These include • • • • Predation Disease Parasites Competition Population Growth Rate What population do you think this is? So, what do you think is going to happen to the human population? • We will probably reach our carrying capacity. • Our growth rate will start to look like most organisms, which is the Logistic Growth Model Carrying Capacity (k) What letter does this curve kind of look like? Population Limiting Factors • Population growth models – Logistic Growth Model • Often called the S-shaped growth curve • Occurs when a population’s growth slows or stops following exponential growth. • Growth stops at the population’s carrying capacity • Populations stop increasing when: – Birth rate is less than death rate (Birth rate < Death rate) – Emigration exceeds Immigration (Emigration > Immigration) Population Limiting Factors • Population growth models – Logistic Growth Model The S-curve is not as pretty as the image looks 1. Carrying capacity can be raised or lowered. How? Example 1: Artificial fertilizers have raised k Example 2: Decreased habitat can lower k 2. Populations don’t reach k as smoothly as in the logistic graph. • • Boom-and-Bust Cycles Predator-Prey Cycles Example Problem • There are 10,400 mice living in a 1000m x 1000m field. What is the density of this population? Answer • The area of the field is 1,000,000 square meters (m2). • The density of mice is therefore 10,400 mice/1,000,000m2=.0104/m2. The population structure Sex composition Age composition Spatial dispersion Demographic pyramids PATTERN OF DISPERSION What types of spatial dispersion? An isolation of populations a apartness of one population from the adjacent similar one. Natural boundaries Artificial (man-made) borders What kind of boundaries? Control questions What population characteristics we learned are static or dynamic? What population characteristics static or dynamic we consider as more important and why? Hometask Study by self questions: 1 Types of Survivorship curves 2 K-selection and r-selection in a population surviving