Population Biology - Blue Valley Schools
... Describes distribution of species along a straight line Useful for identifying and describing CHANGE in a habitat ...
... Describes distribution of species along a straight line Useful for identifying and describing CHANGE in a habitat ...
5.3 Populations
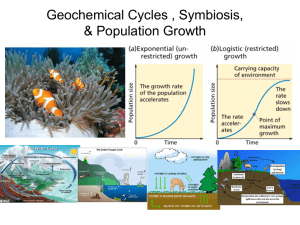
... *Any population has the potential to increase exponentially but conditions are never perfect. Food resources are limited, predation occurs, and abiotic conditions are factors. This limits population growth. ...
... *Any population has the potential to increase exponentially but conditions are never perfect. Food resources are limited, predation occurs, and abiotic conditions are factors. This limits population growth. ...
POPULATIONS
... constant rate Under ideal conditions with unlimited resources, a population will grow exponentially ...
... constant rate Under ideal conditions with unlimited resources, a population will grow exponentially ...
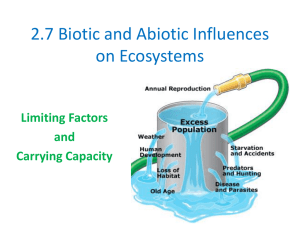
2.7 Biotic and Abiotic Influences on Ecosystems
... ex) a whale and a barnacle • the barnacle attaches to the whale and gets a habitat and a free ride to a new food source while the whale is not harmed ...
... ex) a whale and a barnacle • the barnacle attaches to the whale and gets a habitat and a free ride to a new food source while the whale is not harmed ...
Population Growth Curves
... are influenced by environmental and social factors • Uniform distribution results from intense competition or antagonism between individuals. • Random distribution occurs when there is no competition, antagonism, or tendency to aggregate. • Clumping is the most common distribution because environmen ...
... are influenced by environmental and social factors • Uniform distribution results from intense competition or antagonism between individuals. • Random distribution occurs when there is no competition, antagonism, or tendency to aggregate. • Clumping is the most common distribution because environmen ...
PopulationsPP
... 3. Growth Rate (includes immigration & emigration): the difference between birth and death rate of a population. • Immigration – movement of individuals of a population moving into an area. (I = in) • Emigration – movement of individuals of a population out of an area. (E = exit) ...
... 3. Growth Rate (includes immigration & emigration): the difference between birth and death rate of a population. • Immigration – movement of individuals of a population moving into an area. (I = in) • Emigration – movement of individuals of a population out of an area. (E = exit) ...
global population
... (a) Its performance is usually best at intermediate values. (b) Its performance can be shown with a tolerance curve. (c) Tolerance levels cannot change over the lifetime. (d) Tolerance levels can change through acclimation. ...
... (a) Its performance is usually best at intermediate values. (b) Its performance can be shown with a tolerance curve. (c) Tolerance levels cannot change over the lifetime. (d) Tolerance levels can change through acclimation. ...
Population Biology
... Earth with a layer 30 cm deep. The highest rate of reproduction under ideal conditions is called a population’s ...
... Earth with a layer 30 cm deep. The highest rate of reproduction under ideal conditions is called a population’s ...
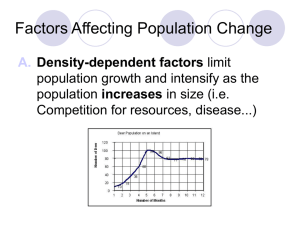
FACTORS AFFECTING POPULATION CHANGE
... 3. Allee effect: Warder Allee found that some density-dependent factors reduce population growth when the population is at a low density rather than high density. Ex. harder for individuals to find a mate and successfully reproduce thus lowering the growth rate of species. ...
... 3. Allee effect: Warder Allee found that some density-dependent factors reduce population growth when the population is at a low density rather than high density. Ex. harder for individuals to find a mate and successfully reproduce thus lowering the growth rate of species. ...
Chapter 35
... growth rate decreases with population size, whereas global human population growth rate has a positive relationship. • Human population growth rate has been growing more than exponentially. • Limited resources eventually will cause human population growth to slow, but global human carrying capacity ...
... growth rate decreases with population size, whereas global human population growth rate has a positive relationship. • Human population growth rate has been growing more than exponentially. • Limited resources eventually will cause human population growth to slow, but global human carrying capacity ...
Competition Within a Population
... Mimics a “S” Population starts slow, then increases quickly, then begins to level off to support the current population at it’s maximum capacity. ...
... Mimics a “S” Population starts slow, then increases quickly, then begins to level off to support the current population at it’s maximum capacity. ...
POPULATION DYNAMICS
... births than deaths and carrying capacity can be temporarily exceeded Overshooting carrying capacity can lead to mass die-offs as resources run out Deaths exceed births and population again falls below carrying capacity ...
... births than deaths and carrying capacity can be temporarily exceeded Overshooting carrying capacity can lead to mass die-offs as resources run out Deaths exceed births and population again falls below carrying capacity ...
Limits on Population
... or more organisms fighting for the same resource in a given area Can be within species or between different species ...
... or more organisms fighting for the same resource in a given area Can be within species or between different species ...
Document
... the number of individuals that enter or leave the population. * Simply put, a population will increase or decrease in size depending on how many individuals are added to it or removed from it ...
... the number of individuals that enter or leave the population. * Simply put, a population will increase or decrease in size depending on how many individuals are added to it or removed from it ...
Population Dynamics
... - Mortality = deaths (d) + Immigration = moving in (i) - Emigration = moving out (e) ...
... - Mortality = deaths (d) + Immigration = moving in (i) - Emigration = moving out (e) ...
population growth patterns
... Population Change • Read p.660 – 670 • Practice Questions! – P.664 #1 – P.665 #2 – P.668 #3, 4 ...
... Population Change • Read p.660 – 670 • Practice Questions! – P.664 #1 – P.665 #2 – P.668 #3, 4 ...
Population
... – # of births (birth rate) – # of deaths (death rate) – # entering and # leaving • Immigration: movement of individuals into an area (growth) • Emigration: movement of individuals out of an area (decrease) ...
... – # of births (birth rate) – # of deaths (death rate) – # entering and # leaving • Immigration: movement of individuals into an area (growth) • Emigration: movement of individuals out of an area (decrease) ...
Populations
... species that can mate and produce fertile offspring. • It is important to study populations (and population sizes) for many reasons: – To monitor endangered species – To monitor environmental health – To estimate demands for natural resources – To monitor change in areas over time – To make informed ...
... species that can mate and produce fertile offspring. • It is important to study populations (and population sizes) for many reasons: – To monitor endangered species – To monitor environmental health – To estimate demands for natural resources – To monitor change in areas over time – To make informed ...
List the ecological levels of organization from the largest to smallest
... Example: Video – Yellowstone National Park ...
... Example: Video – Yellowstone National Park ...
Presentation
... Explain the relationship between the three populations of organisms and how their growth or decline rate are related to each other. Explain what density dependent factor might have influenced the two animal populations. ...
... Explain the relationship between the three populations of organisms and how their growth or decline rate are related to each other. Explain what density dependent factor might have influenced the two animal populations. ...
Describing Populations Population Distribution
... Geographic range- the area inhabited by a population Factors that determine population range: ◦ Abiotic- non-living factors in an organism's environment Ie. Climatic factors, edaphic factors, & social factors ...
... Geographic range- the area inhabited by a population Factors that determine population range: ◦ Abiotic- non-living factors in an organism's environment Ie. Climatic factors, edaphic factors, & social factors ...
Slide 1 - willisworldbio
... Populations remains the same when the birthrate equals the death rate. Populations decreases when the death rate is greater than the birthrate, or if individuals move out of an area (________). ...
... Populations remains the same when the birthrate equals the death rate. Populations decreases when the death rate is greater than the birthrate, or if individuals move out of an area (________). ...