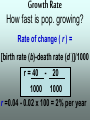* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Human Population Growth
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
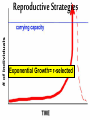
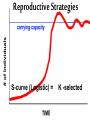
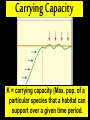
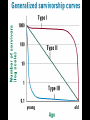
Understanding Population Growth Population Ecology •Deals with #’s of indiv. in a species •How and why their numbers are the way they are Population Density # of indiv. of a species unit of area • A better way to describe size of a pop. Manhattan, New York City 70,595 people per sq. mile Dhaka, Bangladesh: 2 7 million in 59 mi Crowded Much?!? Competition Spread of Disease Lack of Natural Resources Lack of Jobs Populations Change in Size… Dependent on: • Birth rate (b ) • Death rate (d ) • Immigration (i ) • Emigration (e ) Question: How can you get the growth rate of a population to slow down? Give reasonable solutions! Make a list with your partner Growth Rate How fast is pop. growing? Rate of change ( r ) = [birth rate (b)-death rate (d )]/1000 r = 40 - 20 1000 1000 r =0.04 - 0.02 x 100 = 2% per year Growth Rate of a Pop. r = (b - d ) + (i - e ) Total Population (1000) • Use total pop. when given. If prob. states per 1000, use 1000. Population Momentum • Pop. growth that occurs even if levels of childbearing immediately declined to replacement level Older people still have babies Doubling Time • Time for a pop. w/ a stable growth rate to double in size Doubling Time = td = 70 r (%) Practice: With a 2 % growth rate, the world population will double…. Doubling Time Population Reproductive Strategies J-curve (Exponential) = r-selected Reproductive Strategies Exponential Growth= r-selected Reproductive Strategies S-curve (Logistic) = K -selected Reproductive Strategies S-curve (Logistic) = K -selected Carrying Capacity K = carrying capacity (Max. pop. of a particular species that a habitat can support over a given time period. Carrying Capacity • May vary by: – Seasons – Changes in environment (fire, storm, etc.) R Selected vs K Selected • R-selected 1) Many small offspring 2) Little/no care of offspring 3) Most offspring die before reaching reproductive age 4) High population growth rate 5) Generalists • K-selected 1) Fewer, larger offspring 2) High parental care 3) Most offspring reach reproductive age 4) Lower population growth rate 5) Specialists What Advantages do R Selected Species have? What about K? Which would you rather be??? Density-Dependent Controls • Competition for resources due to land issues • Ex: Predation, Parasitism, Disease, Poisoning Density-Independent Controls • Controls on Population not due to space issues • Ex: Natural disasters • Ex: Severe weather Survivorship •Proportion of a pop. to survive to breeding age •Type I= Late loss: K-strategists. •Type II = Constant loss: intermediate reproductive strategists •Type III = Early loss: R-strategists