* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Population ppt - Summit School District
Overexploitation wikipedia , lookup
Source–sink dynamics wikipedia , lookup
The Population Bomb wikipedia , lookup
World population wikipedia , lookup
Two-child policy wikipedia , lookup
Human overpopulation wikipedia , lookup
Storage effect wikipedia , lookup
Molecular ecology wikipedia , lookup
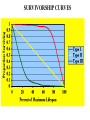
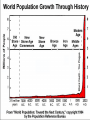
• POPULATION = a group of interbreeding organisms (same species) that live in the same place at the same time and compete for the same resources. • Resources = food, water, shelter, mates, and so on . . . • resources • resources pop. size pop. size The population size of a species in a given space at a given time is determined by the interplay between BIOTIC POTENTIAL and ENVIRONMENTAL RESISTANCE. Biotic potential = growth rate with unlimited resources. Environmental resistance = all the factors acting jointly to limit population growth. Four variables change population size: 1. NATALITY = birth rate 2. MORTALITY = death rate 3. IMMIGRATION = rate of organisms moving in 4. EMIGRATION = rate of organisms moving out DENSITY DEPENDENT FACTORS = affect a populations’ size depending on its population density. 1. Predation 2. Disease Feedback!! 3. Availability of food Negative and water 4. Space Populations change in response to environmental stress or changes in environmental conditions. 1. In size = # of individuals 2. Density = # of individual / specific space 3. Age distribution = proportions / age group 4. Dispersion = Clumped (elephants) Uniform (creosote bush) Random (dandelions) DENSITY INDEPENDENT FACTORS = affect a populations’ size regardless of its population density. 1. Weather 2. Earthquakes 3. Floods 4. Fires R-strategists populations are most affected by these. . . . Natural disasters No population can grow indefinitely! Number of sheep (millions) Every environment has a CARRYING CAPACITY = the maximum number of individuals of a given species that can be sustained indefinitely in 2.0 a given space. 1.5 1.0 .5 1800 1825 1850 1875 Year 1900 1925 Factors that affect carrying capacity: 1. Competition with/in and between species. 2. Natural and human caused catastrophes. 3. Immigration and emigration. 4. Seasonal fluctuations in food, water, shelter, and nesting sites. “J” population growth curve Population size (N) A population that has few if any resource limitations grows exponentially. EXPONENTIAL GROWTH starts out slowly and then proceeds faster and faster as the population increases. Time (t) LOGISTIC GROWTH involves initial exponential growth and then there is a steady decrease in growth as the population encounters environmental resistance and approaches carrying capacity and levels off. “S or sigmoid” population growth curve Population size (N) K Time (t) Plateau phase K Population size (N) Transitional phase Exponential phase Time (t) Opportunistic or r-Selected Species cockroach dandelion Many small offspring Little or no parental care and protection of offspring Early reproductive age Most offspring die before reaching reproductive age Small adults Adapted to unstable climate and environmental conditions High population growth rate (r) Population size fluctuates wildly above and below carrying capacity (K) Generalist niche Low ability to compete Early successional species Competitor or K-Selected Species elephant saguaro Fewer, larger offspring High parental care and protection of offspring Later reproductive age Most offspring survive to reproductive age Larger adults Adapted to stable climate and environmental conditions Lower population growth rate (r) Population size fairly stable and usually close to carrying capacity (K) Specialist niche High ability to compete Late successional species REPRODUCTIVE STRATEGIES Carrying capacity K Number of individuals K species; experience K selection r species; experience r selection Time SURVIVORSHIP CURVES Reindeer on St. Paul Island • 41 mi2 • Started with 25 Reindeer (4 males and 21females) • No predators • 200 mi from mainland so no on or off • No hunting End Result Start with 25 1938= 2046 deer 1950= 8 deer Growth Rate of 16% Did bounce back to a steady 250 deer Birth and Death Calculations Crude Birth Rate (CBR)= # of births per 1000 individuals/yr CBR=(Births/Pop. Size)x1000 The world CBR is 20.3 Crude Death Rate (CDR) = # of deaths per 1000 individuals/yr CDR= (Deaths/Pop. Size)x1000 The world CDR is 9.6 More Calculations Natural Increase Rate in % (NIR) NIR = (CBR-CDR)/10 Doubling Rate = how many years it will take to double the population DR= 70/NIR Density= # of individuals in a given area D= Pop./ Area IB Acronyms for Countries • MEDC= More Economically Developed Country • LEDC= Less Economically Developed Country • NIC= Newly Industrialized Country