Human Population Growth - Downtown Magnets High School
... K-selected Species Fewer, larger offspring High parental care Most offspring reach reproductive age Lower population growth rate Specialists ...
... K-selected Species Fewer, larger offspring High parental care Most offspring reach reproductive age Lower population growth rate Specialists ...
Biodiversity
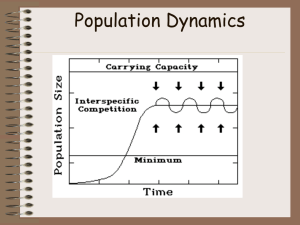
... growth of a population slows or stops. • S-shaped curve of this growth pattern is called logistic growth. • How does population growth slow or stop? ...
... growth of a population slows or stops. • S-shaped curve of this growth pattern is called logistic growth. • How does population growth slow or stop? ...
population - wsscience
... more than low density populations are DENSITY INDEPENDENT – the size of the population does not matter, a certain proportion of the population is affected no matter what the population density is, high or low ...
... more than low density populations are DENSITY INDEPENDENT – the size of the population does not matter, a certain proportion of the population is affected no matter what the population density is, high or low ...
Population Dynamics
... Factors which work best with a large dense population Interspecific competition Intraspecific competition Predation Disease Parasitism Density Independent Limiting Factors Tornado, hurricane, drought, temperature Human disturbance (Clear-cutting forests or damming rivers) ...
... Factors which work best with a large dense population Interspecific competition Intraspecific competition Predation Disease Parasitism Density Independent Limiting Factors Tornado, hurricane, drought, temperature Human disturbance (Clear-cutting forests or damming rivers) ...
Unit 6 Ecology Study Guide Behavioral ecology: study of interaction
... o R-selected population (rapid population growth, J curve style, little parental care, quick reproduction, high death rate – roaches) Survivorship curves: show survival rates for different-aged members of a population o Type I: live long life, until age is reached where death rate increases rapidly ...
... o R-selected population (rapid population growth, J curve style, little parental care, quick reproduction, high death rate – roaches) Survivorship curves: show survival rates for different-aged members of a population o Type I: live long life, until age is reached where death rate increases rapidly ...
Population ecology
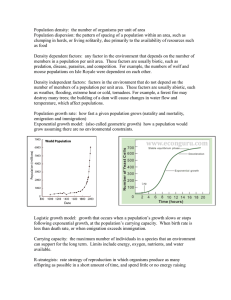
... Change in population size: N=(birth+immigration)-(death+emigration) • Growth occurs if inputs are greater than outputs. • Under ideal conditions, the intrinsic growth rate is observed. • This is the maximum potential for growth of a population. • It is essentially the maximum amount of offspring tha ...
... Change in population size: N=(birth+immigration)-(death+emigration) • Growth occurs if inputs are greater than outputs. • Under ideal conditions, the intrinsic growth rate is observed. • This is the maximum potential for growth of a population. • It is essentially the maximum amount of offspring tha ...
Population density: the number of organisms per unit of area
... Population growth rate: how fast a given population grows (natality and mortality, emigration and immigration) Exponential growth model: (also called geometric growth) how a population would grow assuming there are no environmental constraints. ...
... Population growth rate: how fast a given population grows (natality and mortality, emigration and immigration) Exponential growth model: (also called geometric growth) how a population would grow assuming there are no environmental constraints. ...
Chapter 8- Population Ecology - Pikeville Independent Schools
... Describe the various types of population distribution patterns that can occur in nature and comment on which is most common and why. ...
... Describe the various types of population distribution patterns that can occur in nature and comment on which is most common and why. ...
Chapter 5 Review: Biodiversity, Species Interaction and Population
... 4. What is the competitive exclusion principle? 5. What is a(n) omnivore, herbivore, detritivore, carnivore? 6. What methods do predators use to capture prey? 7. What methods do prey use to escape capture? 8. What are the long term effects of parasites? 9. What is camouflage? Mimicry? Give examples ...
... 4. What is the competitive exclusion principle? 5. What is a(n) omnivore, herbivore, detritivore, carnivore? 6. What methods do predators use to capture prey? 7. What methods do prey use to escape capture? 8. What are the long term effects of parasites? 9. What is camouflage? Mimicry? Give examples ...
Populations
... • Population - is a set of individuals within a species living in the same place at the same time. • Populations are described in terms of: – Size, density and dispersion – Density – the number of individuals per unit of area or volume – Dispersion – describes the arrangement of its individuals in s ...
... • Population - is a set of individuals within a species living in the same place at the same time. • Populations are described in terms of: – Size, density and dispersion – Density – the number of individuals per unit of area or volume – Dispersion – describes the arrangement of its individuals in s ...
Chapter 5 and 6 study guide
... ____________________. Under ideal conditions with unlimited resources, a population will grow ____________________. A population of bacteria with a limited supply of nutrients will eventually show growth typical of the ____________________ model. Competition, predation, parasitism, and _____________ ...
... ____________________. Under ideal conditions with unlimited resources, a population will grow ____________________. A population of bacteria with a limited supply of nutrients will eventually show growth typical of the ____________________ model. Competition, predation, parasitism, and _____________ ...
Introduction to Population Dynamics
... A. What is a population? A group of organisms of the same species that interbreed and live in the same place at the same time. ...
... A. What is a population? A group of organisms of the same species that interbreed and live in the same place at the same time. ...
Document
... Geographic distribution, density, growth rate, and age structure 4. Which of those four characteristics describes the number of plants per square kilometer in a certain area? Population density 5. Define exponential growth. When individuals in a population reproduce at a constant rate 6. The various ...
... Geographic distribution, density, growth rate, and age structure 4. Which of those four characteristics describes the number of plants per square kilometer in a certain area? Population density 5. Define exponential growth. When individuals in a population reproduce at a constant rate 6. The various ...
Growth Cycles and Stresses PPT
... Carrying capacity (K) – maximum population of a given species that a habitat can sustain indefinitely without being degraded ...
... Carrying capacity (K) – maximum population of a given species that a habitat can sustain indefinitely without being degraded ...
chapter 4 vocabulary - Flushing Community Schools
... as predation, disease, and competition, that depends on the number of members in a population per unit area ...
... as predation, disease, and competition, that depends on the number of members in a population per unit area ...
Quiz 5 Key
... b. a predator keeps the population of its prey species well below its carrying capacity. c. an early frost kills a large fraction of the insects in a population d. food limitation reduces the birth rate as the population increases e. none of the above ...
... b. a predator keeps the population of its prey species well below its carrying capacity. c. an early frost kills a large fraction of the insects in a population d. food limitation reduces the birth rate as the population increases e. none of the above ...
Populations
... • Occurs when the individuals in a population reproduce at a constant rate • Under ideal conditions with unlimited resources, a population will grow exponentially ...
... • Occurs when the individuals in a population reproduce at a constant rate • Under ideal conditions with unlimited resources, a population will grow exponentially ...
6A Population Ecology 2015
... maximum number of individuals that can be supported in an environment Changes based on resource availability ...
... maximum number of individuals that can be supported in an environment Changes based on resource availability ...
UNIT 3 Chp 5.1 and 5.2
... birthrate, death rate, and the rate at which individuals enter or leave the population. ...
... birthrate, death rate, and the rate at which individuals enter or leave the population. ...
Three Key Features of Populations Size
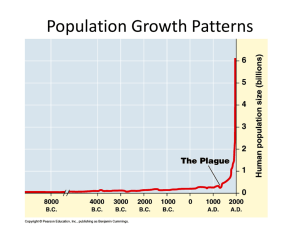
... • Doubled three times in the last three centuries • About 6.1 billion and may reach 9.3 billion by the year 2050 • Improved health and technology have lowered death rates ...
... • Doubled three times in the last three centuries • About 6.1 billion and may reach 9.3 billion by the year 2050 • Improved health and technology have lowered death rates ...
Population Size Factors
... • Three stages – 1) Slow growth – 2) Exponential growth – 3) Carrying Capacity: greatest number of individuals that a population can sustain ...
... • Three stages – 1) Slow growth – 2) Exponential growth – 3) Carrying Capacity: greatest number of individuals that a population can sustain ...