* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Populations
Source–sink dynamics wikipedia , lookup
Storage effect wikipedia , lookup
Two-child policy wikipedia , lookup
The Population Bomb wikipedia , lookup
Human overpopulation wikipedia , lookup
World population wikipedia , lookup
Molecular ecology wikipedia , lookup
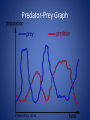
Populations Rates That Affect Population Size • Natality- the birth rate; the number of births over time • Mortality- the death rate; the number of deaths over time Rates That Affect Population Size • Immigration- the rate of individuals entering the population from a different population; the number of individuals entering over time • Emigration- the rate of individuals leaving a populations to go to a different population; the number of individuals leaving a population Population Growth • Two Types of Growth: – Exponential – Logistic Exponential Growth • Occurs when the individuals in a population reproduce at a constant rate • Under ideal conditions with unlimited resources, a population will grow exponentially Exponential Growth J-Curve Logistic Growth • Occurs when a population's growth slows or stops following a period of exponential growth Logistic Growth S-Curve • Carrying Capacity- the maximum population size that environment can sustain. – Usually determined by a limiting factor • As resources become less available the growth of a population slows or stops. • New or early populations show exponential growth • Old, stable populations show no growth, but stay near the carrying capacity of the environment • What happens if a population exceeds its carrying capacity? • If a population exceeds the carrying capacity of its environment, the carrying capacity decreases Human Population • Is the human population growing exponentially or logistically? Niches and Communities • Niche - range of physical and biological conditions in which a species lives and the way the species obtains what it needs to survive and reproduce. • Different Factors: – Tolerance – ability to survive and reproduce under a range on environmental circumstances. Tolerance Graph Niche cont. • • • • • Resources – food, water, nutrients, etc Physical – abiotic factors Biological – biotic factors Competition – exactly what you would think Competitive Exclusion Principle – no two species can occupy exactly the same niche in exactly the same habitat at exactly the same time. Predator-Prey Relationships • Predation – interaction in which one animal (predator) eats another animal (prey) – Predators affect the size of prey populations within a community and determine the places where the prey can live. • Herbivory – Same concept at predation just with plants Predator-Prey Graph Symbioses • Two creatures living in harmony and helping each other survive. • Mutualism – both benefit (Clown fish – Anemone) • Parasitism – one organisms lives inside or on another organisms and harms it (Tapeworms) • Commensalism – one organism benefits and the other is neither harmed nor helped. (Barnacles and Whales)