* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Ch.4 Populations
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
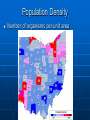
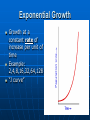
Population Dynamics Section 4.1, p.92 5/22/2017 Population Dispersion -How individuals are spaced within an area Population Density Number of organisms per unit area Population Limiting Factors Density-dependent • Deaths occur more quickly in a crowded population • Ex: resources, predation, disease Density-independent • A certain proportion dies regardless of population density • Ex: severe weather, natural disaster Predation – what happened to the moose population as the wolf population increased? Population Growth Rate How fast a given population grows Most look at birth rate and death rate Factors Affecting Growth Rate of a Population Natality – number of births Mortality – number of deaths Emigration – leaving or exiting a population I mmigration – moving population into a Carrying Capacity Max # of individuals of any species that can be supported by a particular ecosystem on a long-term basis Change in ecosystem-change in carrying capacity Exponential Growth Growth at a constant rate of increase per unit of time Example: 2,4,8,16,32,64,128 “J curve” Logistic Growth Exponential growth until carrying capacity is reached Growth then slows or stops “S” curve