FST Human Follistatin Human Recombinant Catalog No. CB
... It is recommended to reconstitute the lyophilized Follistatin in sterile 18MΩ-cm H2O not less than 100µg/ml, which can then be further diluted to other aqueous solutions. Stability: Lyophilized Follistatin although stable at room temperature for 3 weeks, should be stored desiccated below -18°C. Upon ...
... It is recommended to reconstitute the lyophilized Follistatin in sterile 18MΩ-cm H2O not less than 100µg/ml, which can then be further diluted to other aqueous solutions. Stability: Lyophilized Follistatin although stable at room temperature for 3 weeks, should be stored desiccated below -18°C. Upon ...
10-3 Getting Energy to Make ATP
... i. Occurs when no oxygen is present ii. Not very efficient---only produces 2 ATP molecules from one glucose iii. There are different types of anaerobic respiration ...
... i. Occurs when no oxygen is present ii. Not very efficient---only produces 2 ATP molecules from one glucose iii. There are different types of anaerobic respiration ...
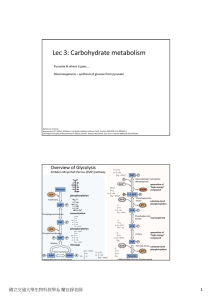
Lec 3: Carbohydrate metabolism
... use glucose as their sole or primary energy source, but they lack the enzymatic machinery to synthesize it. Liver and kidney cortex are the primary gluconeogenic tissues. ...
... use glucose as their sole or primary energy source, but they lack the enzymatic machinery to synthesize it. Liver and kidney cortex are the primary gluconeogenic tissues. ...
Name - wwphs
... Aerobic – takes place in mitochondria & requires oxygen Anaerobic – takes place in cytoplasm & does not require oxygen What are the similarities in the two? Both processes begin with Glycolysis and ultimately produce ATP to keep the organism alive 8. What is the initial molecule that begins cellular ...
... Aerobic – takes place in mitochondria & requires oxygen Anaerobic – takes place in cytoplasm & does not require oxygen What are the similarities in the two? Both processes begin with Glycolysis and ultimately produce ATP to keep the organism alive 8. What is the initial molecule that begins cellular ...
Sunday School Jeopardy - Chapman @ Norquay School
... The overall equation for photosynthesis (in words) is: ...
... The overall equation for photosynthesis (in words) is: ...
SAMPLE PAPER -2 Time Allowed: 3 Hrs
... (b) (i) Chloroacetic acid is more acidic than acetic acid. When an chlorine atom, which is an electron withdrawing group is present in the chain attached to a carboxyl group, it exerts -I effect and withdraws electrons from the carbon of the carboxyl group as well as from the oxygen of the O-H bond. ...
... (b) (i) Chloroacetic acid is more acidic than acetic acid. When an chlorine atom, which is an electron withdrawing group is present in the chain attached to a carboxyl group, it exerts -I effect and withdraws electrons from the carbon of the carboxyl group as well as from the oxygen of the O-H bond. ...
Unit 8 - Macromolecules Processes
... 5) polymer – repea.ng units of polypep.de chains fall off and the protein is made Process starts all over again in the ribosomes ...
... 5) polymer – repea.ng units of polypep.de chains fall off and the protein is made Process starts all over again in the ribosomes ...
Fall_Final_Exam_Review
... • Enzymes speed up reactions by lowering the activation energy. • Proteins ...
... • Enzymes speed up reactions by lowering the activation energy. • Proteins ...
Course Content Form - Pima Community College
... Define the rate of a reaction and the rate law, determine the components of the rate law, and describe the effects of concentration, temperature and catalysts on the rate of a reaction. Write and calculate equilibrium constants for a chemical reaction, calculate equilibrium concentrations from initi ...
... Define the rate of a reaction and the rate law, determine the components of the rate law, and describe the effects of concentration, temperature and catalysts on the rate of a reaction. Write and calculate equilibrium constants for a chemical reaction, calculate equilibrium concentrations from initi ...
Cellular Respiration - Parkway C-2
... When oxygen is present, it’s aerobic; when oxygen is absent, it’s anaerobic. There are four pathways in cellular respiration (not all function at the same place or at the same time): glycolysis, fermentation (2 types – alcoholic and lactic acid), Krebs cycle, and electron transport chain. Respiratio ...
... When oxygen is present, it’s aerobic; when oxygen is absent, it’s anaerobic. There are four pathways in cellular respiration (not all function at the same place or at the same time): glycolysis, fermentation (2 types – alcoholic and lactic acid), Krebs cycle, and electron transport chain. Respiratio ...
Regulation of Glycolysis - Valdosta State University
... -Fast response (sec or less) – usually allosteric control (faster response than synthesis or degradation of enzyme) -Covalent modification (also fast) most common: phosphorylation/dephosphorylation -Slower response (sec to hours) –exterior effects such as hormones, growth factors Overall regulatory ...
... -Fast response (sec or less) – usually allosteric control (faster response than synthesis or degradation of enzyme) -Covalent modification (also fast) most common: phosphorylation/dephosphorylation -Slower response (sec to hours) –exterior effects such as hormones, growth factors Overall regulatory ...
IB Topics DNA HL no writing
... • DNA is unwound by RNA polymerase; • DNA is split into two strands; • mRNA is made by transcription; • promoter region (by start of gene) causes RNA polymerase to bind; • anti-sense / template strand of DNA is transcribed; • direction of transcription is ; • free nucleotide triphosphates used; • co ...
... • DNA is unwound by RNA polymerase; • DNA is split into two strands; • mRNA is made by transcription; • promoter region (by start of gene) causes RNA polymerase to bind; • anti-sense / template strand of DNA is transcribed; • direction of transcription is ; • free nucleotide triphosphates used; • co ...
Metabolism Basics
... these compounds can be released for use by the body or stored in body tissues, especially the liver, muscles, and body fat. ...
... these compounds can be released for use by the body or stored in body tissues, especially the liver, muscles, and body fat. ...
PDF Datastream - Brown Digital Repository
... absence of oxygen. Lactic acid fermentation or ethanol fermentation occurs depending on the organism. Slide 14: Lactic acid fermentation: occurs in animal cells and some bacteria cells. The buildup of lactic acid is what makes your muscles sore while you are exercising when the muscle cells do ...
... absence of oxygen. Lactic acid fermentation or ethanol fermentation occurs depending on the organism. Slide 14: Lactic acid fermentation: occurs in animal cells and some bacteria cells. The buildup of lactic acid is what makes your muscles sore while you are exercising when the muscle cells do ...
Carbohydrate Metabolism - BITS Academic Resource Center
... Gluconeogenesis (de novo glucose synthesis). Amino acids and Glycerol can be used to produce glucose (liver) More glucose is produced via gluconeogenesis than glycogenolysis. Glycolysis is the breakdown of glucose into pyruvic acid There are multiple diseases that arise from improper carbohydrate me ...
... Gluconeogenesis (de novo glucose synthesis). Amino acids and Glycerol can be used to produce glucose (liver) More glucose is produced via gluconeogenesis than glycogenolysis. Glycolysis is the breakdown of glucose into pyruvic acid There are multiple diseases that arise from improper carbohydrate me ...
II. The Steps of Translation
... Each kind of tRNA has a sequence of 3 unpaired nucleotides — the anticodon — which can bind, following the rules of base pairing, to the complementary triplet of nucleotides — the codon — in a messenger RNA (mRNA) molecule. Just as DNA replication and transcription involve base pairing of nucleotide ...
... Each kind of tRNA has a sequence of 3 unpaired nucleotides — the anticodon — which can bind, following the rules of base pairing, to the complementary triplet of nucleotides — the codon — in a messenger RNA (mRNA) molecule. Just as DNA replication and transcription involve base pairing of nucleotide ...
Cells and energy - whsbaumanbiology
... 4.1 Chemical Energy and ATP A few types of organisms do not need sunlight and photosynthesis as a source of energy ...
... 4.1 Chemical Energy and ATP A few types of organisms do not need sunlight and photosynthesis as a source of energy ...
DNAi Timeline: A Scavenger Hunt
... 4. J. Craig Venter’s Company, Celera Genomics, worked on this very important project. ________________________________________ 5. I first isolated DNA using pus collected from bandages at a local hospital. Since white blood cells are a major component of pus, they were my source of DNA. YUCK! ______ ...
... 4. J. Craig Venter’s Company, Celera Genomics, worked on this very important project. ________________________________________ 5. I first isolated DNA using pus collected from bandages at a local hospital. Since white blood cells are a major component of pus, they were my source of DNA. YUCK! ______ ...
Chemistry of Glycolysis
... 3‐P DH is positive (+6.7 kJ/mole), the reaction proceeds to the right because A) triose phosphate isomerase supplies so much starting material. B) The product of the reaction is consumed as soon as it is made. C) there are too few molecules of starting material available. D) The Gibbs free energy is ...
... 3‐P DH is positive (+6.7 kJ/mole), the reaction proceeds to the right because A) triose phosphate isomerase supplies so much starting material. B) The product of the reaction is consumed as soon as it is made. C) there are too few molecules of starting material available. D) The Gibbs free energy is ...
Review Sheet : DNA, RNA & Protein Synthesis
... following sequence of amino acids: tyrosine, proline, aspartic acid, isoleucine, and cysteine. Use the portion of the genetic code given to determine which of the following contains a DNA sequence that codes for this amino acid ...
... following sequence of amino acids: tyrosine, proline, aspartic acid, isoleucine, and cysteine. Use the portion of the genetic code given to determine which of the following contains a DNA sequence that codes for this amino acid ...
Biochemistry
_and_Carl_Ferdinand_Cori.jpg?width=300)
Biochemistry, sometimes called biological chemistry, is the study of chemical processes within and relating to living organisms. By controlling information flow through biochemical signaling and the flow of chemical energy through metabolism, biochemical processes give rise to the complexity of life. Over the last decades of the 20th century, biochemistry has become so successful at explaining living processes that now almost all areas of the life sciences from botany to medicine to genetics are engaged in biochemical research. Today, the main focus of pure biochemistry is in understanding how biological molecules give rise to the processes that occur within living cells, which in turn relates greatly to the study and understanding of whole organisms.Biochemistry is closely related to molecular biology, the study of the molecular mechanisms by which genetic information encoded in DNA is able to result in the processes of life. Depending on the exact definition of the terms used, molecular biology can be thought of as a branch of biochemistry, or biochemistry as a tool with which to investigate and study molecular biology.Much of biochemistry deals with the structures, functions and interactions of biological macromolecules, such as proteins, nucleic acids, carbohydrates and lipids, which provide the structure of cells and perform many of the functions associated with life. The chemistry of the cell also depends on the reactions of smaller molecules and ions. These can be inorganic, for example water and metal ions, or organic, for example the amino acids which are used to synthesize proteins. The mechanisms by which cells harness energy from their environment via chemical reactions are known as metabolism. The findings of biochemistry are applied primarily in medicine, nutrition, and agriculture. In medicine, biochemists investigate the causes and cures of disease. In nutrition, they study how to maintain health and study the effects of nutritional deficiencies. In agriculture, biochemists investigate soil and fertilizers, and try to discover ways to improve crop cultivation, crop storage and pest control.