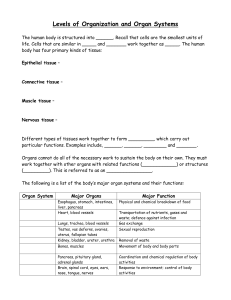
BIOANALYTICAL/CLINICAL ANALYSIS
... ASSAY: JAFFE METHOD Alkaline picrate + Creatinine Red Color at 500 nm To do Creatine add Acid Creatinine, assay as above H. PROTEIN Proteins provide a Nutritive role If protein level changes=disease of kidney Normal rate is 6 to 8mg% in serum ASSAY l. TOTAL PROTEIN BY FOLIN-CIOCALTEAU REAGENT ADD ...
... ASSAY: JAFFE METHOD Alkaline picrate + Creatinine Red Color at 500 nm To do Creatine add Acid Creatinine, assay as above H. PROTEIN Proteins provide a Nutritive role If protein level changes=disease of kidney Normal rate is 6 to 8mg% in serum ASSAY l. TOTAL PROTEIN BY FOLIN-CIOCALTEAU REAGENT ADD ...
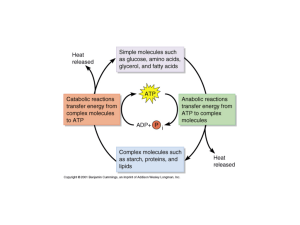
Chapter 9: How do cells harvest energy?
... B. along with carbohydrates, proteins and lipids (fats) are generally major energy sources in foods; nucleic acids are not present in high amounts in foods and thus aren’t as important in providing cells with energy C. proteins are broken into amino acids, which can be broken down further ...
... B. along with carbohydrates, proteins and lipids (fats) are generally major energy sources in foods; nucleic acids are not present in high amounts in foods and thus aren’t as important in providing cells with energy C. proteins are broken into amino acids, which can be broken down further ...
WHITTIER UNION HIGH SCHOOL DISTRICT
... b. Enzymes are proteins and catalyze biochemical reactions without altering the reaction equilibrium. The activity of enzymes depends on the temperature, ionic conditions and pH of the surroundings. c. How prokaryotic cells, eukaryotic cells (including those from plants and animals), and viruses dif ...
... b. Enzymes are proteins and catalyze biochemical reactions without altering the reaction equilibrium. The activity of enzymes depends on the temperature, ionic conditions and pH of the surroundings. c. How prokaryotic cells, eukaryotic cells (including those from plants and animals), and viruses dif ...
www.salmate.com
... The balance of dihomo gamma linolenic acid (GGLA) to arachidonic in every cell in the body determines whether or not good or bad eicosanoids are made when that cell is stimulated by its external environment. The balance of DGLA to arachidonic acid is controlled by the activity of a single enzyme - ...
... The balance of dihomo gamma linolenic acid (GGLA) to arachidonic in every cell in the body determines whether or not good or bad eicosanoids are made when that cell is stimulated by its external environment. The balance of DGLA to arachidonic acid is controlled by the activity of a single enzyme - ...
Document
... ribosomes, RNA polymerase and other needed materials. It resulted in a protein made of only phenylalanine. Further research determined the rest of the code. ...
... ribosomes, RNA polymerase and other needed materials. It resulted in a protein made of only phenylalanine. Further research determined the rest of the code. ...
Final Examination
... 27. [5 points] In a protein there is an alpha-helix composed of 11 amino acyl residues. In the folded protein, this alpha-helix lays next to a flat region of a beta-sheet that has hydrophobic amino acids on the surface nearest the alpha-helix. The other side of the alpha-helix is exposed to solvent ...
... 27. [5 points] In a protein there is an alpha-helix composed of 11 amino acyl residues. In the folded protein, this alpha-helix lays next to a flat region of a beta-sheet that has hydrophobic amino acids on the surface nearest the alpha-helix. The other side of the alpha-helix is exposed to solvent ...
Chapter 8-1
... • A specialized type of peroxisome found only in plants • Contain some of same enzymes (catalase, fatty acid oxidase), but others as well • Plant seedlings rely on stored fatty acids to provide energy & material to form new plant • Glyoxylate cycle ...
... • A specialized type of peroxisome found only in plants • Contain some of same enzymes (catalase, fatty acid oxidase), but others as well • Plant seedlings rely on stored fatty acids to provide energy & material to form new plant • Glyoxylate cycle ...
CHE 145-381 – TEST #2 SPRING 2009 CHAPTERS 6, 7, 8 NAME
... You may use the Periodic Table. Please note that all quantities needed for the successful completion of this test have been given. Feel free to ask questions for clarification. 1. Indicate to which of the following types of chemical reactions each of the statements listed applies: synthesis, decompo ...
... You may use the Periodic Table. Please note that all quantities needed for the successful completion of this test have been given. Feel free to ask questions for clarification. 1. Indicate to which of the following types of chemical reactions each of the statements listed applies: synthesis, decompo ...
lecture4
... The answer: by means of transfer RNA molecules, each specific for one amino acid and for a particular triplet of nucleotides in messenger RNA (mRNA) called a codon. The family of tRNA molecules enables the codons in a mRNA molecule to be translated into the sequence of amino acids in the protein. At ...
... The answer: by means of transfer RNA molecules, each specific for one amino acid and for a particular triplet of nucleotides in messenger RNA (mRNA) called a codon. The family of tRNA molecules enables the codons in a mRNA molecule to be translated into the sequence of amino acids in the protein. At ...
What are enzymes and how do they work
... 2. For each different mutant cell described below, assume that ONE specific molecule or part of a molecule is mutated in that cell so that the molecule’s function has changed. Name as many molecules that could result in the description (but remember that for the mutant phenotype, you are considering ...
... 2. For each different mutant cell described below, assume that ONE specific molecule or part of a molecule is mutated in that cell so that the molecule’s function has changed. Name as many molecules that could result in the description (but remember that for the mutant phenotype, you are considering ...
Cellular Respiration/Fermentation Review Sheet
... 25. Why does bread dough rise? DURING FERMENTATION, THE YEAST PRODUCES CO2 26. After we exercise strenuously our muscles are sore. Why? WE EXERT/BURN ENERGY FASTER THAN WE ARE REPLACING IT AND IT CAUSES LACTIC ACID TO BUILD UP WITHIN OUR MUSCLES. OUR MUSCLE CELLS ARE FORCED TO PROVIDE ENERGY WITHOUT ...
... 25. Why does bread dough rise? DURING FERMENTATION, THE YEAST PRODUCES CO2 26. After we exercise strenuously our muscles are sore. Why? WE EXERT/BURN ENERGY FASTER THAN WE ARE REPLACING IT AND IT CAUSES LACTIC ACID TO BUILD UP WITHIN OUR MUSCLES. OUR MUSCLE CELLS ARE FORCED TO PROVIDE ENERGY WITHOUT ...
Organic Chemistry
... • Each peptide bond is planar and has the s-trans conformation. • The C=O and N-H groups of peptide bonds from adjacent chains point toward each other and are in the same plane so that hydrogen bonding is possible between them. • All R- groups on any one chain alternate, first above, then below the ...
... • Each peptide bond is planar and has the s-trans conformation. • The C=O and N-H groups of peptide bonds from adjacent chains point toward each other and are in the same plane so that hydrogen bonding is possible between them. • All R- groups on any one chain alternate, first above, then below the ...
STUDY GUIDE FOR CHAPTER 12 – DNA Two Main Processes for
... Why would DNA need to be replicated? (2 reasons – be specific) What enzyme reads one side of the DNA and makes a complementary strands? What enzyme unzips the double helix? What enzyme acts as “glue” to make sure the new DNA strands are complete? DNA is a double helix, a small portion of one side of ...
... Why would DNA need to be replicated? (2 reasons – be specific) What enzyme reads one side of the DNA and makes a complementary strands? What enzyme unzips the double helix? What enzyme acts as “glue” to make sure the new DNA strands are complete? DNA is a double helix, a small portion of one side of ...
Amino Acids and Peptides
... carbohydrate polymers, are attached to particular amino acid residues of certain proteins ...
... carbohydrate polymers, are attached to particular amino acid residues of certain proteins ...
Microsoft Word
... ability to create such a molecules through chemical synthesis. It request to construct the most complex and challenging of natures products, this endeavor-perhaps more that any other- becomes of the art of synthesis2 ...
... ability to create such a molecules through chemical synthesis. It request to construct the most complex and challenging of natures products, this endeavor-perhaps more that any other- becomes of the art of synthesis2 ...
Cellular Metabolism - Oklahoma State University–Stillwater
... • Contain specific active sites • Substrates bind to active sites, forming the enzyme-substrate complex. • Enzyme-substrate interaction results in product formation • For ex. A + B ---> C ...
... • Contain specific active sites • Substrates bind to active sites, forming the enzyme-substrate complex. • Enzyme-substrate interaction results in product formation • For ex. A + B ---> C ...
iphy 3430 8-25
... 2. Maintenance of ionic disequilibria 3. Muscle contraction 4. Transmission of information 5. Many others ...
... 2. Maintenance of ionic disequilibria 3. Muscle contraction 4. Transmission of information 5. Many others ...
heat, chemical, radiant, etc.
... 2. Maintenance of ionic disequilibria 3. Muscle contraction 4. Transmission of information 5. Many others ...
... 2. Maintenance of ionic disequilibria 3. Muscle contraction 4. Transmission of information 5. Many others ...
answers - van Maarseveen
... 3. Do the following calculations making sure that you show all the necessary steps. i) ii) iii) ...
... 3. Do the following calculations making sure that you show all the necessary steps. i) ii) iii) ...
B2 exam: Key words to understand
... Chemical that kills plants , usually used on weeds. The variety of species present within a given area. A plant that has evolved so that it is not affected by the chemicals (herbicides) usually used to kill it. Genetically engineered rice which produces betacarotene in the rice grains turning them y ...
... Chemical that kills plants , usually used on weeds. The variety of species present within a given area. A plant that has evolved so that it is not affected by the chemicals (herbicides) usually used to kill it. Genetically engineered rice which produces betacarotene in the rice grains turning them y ...
Biochemistry
_and_Carl_Ferdinand_Cori.jpg?width=300)
Biochemistry, sometimes called biological chemistry, is the study of chemical processes within and relating to living organisms. By controlling information flow through biochemical signaling and the flow of chemical energy through metabolism, biochemical processes give rise to the complexity of life. Over the last decades of the 20th century, biochemistry has become so successful at explaining living processes that now almost all areas of the life sciences from botany to medicine to genetics are engaged in biochemical research. Today, the main focus of pure biochemistry is in understanding how biological molecules give rise to the processes that occur within living cells, which in turn relates greatly to the study and understanding of whole organisms.Biochemistry is closely related to molecular biology, the study of the molecular mechanisms by which genetic information encoded in DNA is able to result in the processes of life. Depending on the exact definition of the terms used, molecular biology can be thought of as a branch of biochemistry, or biochemistry as a tool with which to investigate and study molecular biology.Much of biochemistry deals with the structures, functions and interactions of biological macromolecules, such as proteins, nucleic acids, carbohydrates and lipids, which provide the structure of cells and perform many of the functions associated with life. The chemistry of the cell also depends on the reactions of smaller molecules and ions. These can be inorganic, for example water and metal ions, or organic, for example the amino acids which are used to synthesize proteins. The mechanisms by which cells harness energy from their environment via chemical reactions are known as metabolism. The findings of biochemistry are applied primarily in medicine, nutrition, and agriculture. In medicine, biochemists investigate the causes and cures of disease. In nutrition, they study how to maintain health and study the effects of nutritional deficiencies. In agriculture, biochemists investigate soil and fertilizers, and try to discover ways to improve crop cultivation, crop storage and pest control.