Cellular Respiration - Spokane Public Schools
... •Goal: take pyruvate and put it into the Krebs's cycle, producing NADH and FADH2 ...
... •Goal: take pyruvate and put it into the Krebs's cycle, producing NADH and FADH2 ...
CBSE Class 10 Biology Life Processes Notes
... 2) Life processes are the vital processes carried out by living organisms in order to maintain and sustain life. Molecular movements are essential to carry out the various life processes. ...
... 2) Life processes are the vital processes carried out by living organisms in order to maintain and sustain life. Molecular movements are essential to carry out the various life processes. ...
PDF
... according to the above-described alternation of the two systems. The changes of the above-mentioned enzyme systems affect the energy level in the pupa. Both the amount of the fraction ATP + ADP as of AMP varies along a U-shaped curve. During metamorphosis first a decomposition and later a rebuilding ...
... according to the above-described alternation of the two systems. The changes of the above-mentioned enzyme systems affect the energy level in the pupa. Both the amount of the fraction ATP + ADP as of AMP varies along a U-shaped curve. During metamorphosis first a decomposition and later a rebuilding ...
UNIT 2
... o It remove carbon dioxide and waste product from the metabolism The circulatory system is made up of: o Circulatory fluid. Internal circulating fluid. Can be: blood ( in vertebrates) or hydrolymph and haemolymph ( in invertebrates) o Vessels: Ducts which carry circulatory fluid. Arteries carry bloo ...
... o It remove carbon dioxide and waste product from the metabolism The circulatory system is made up of: o Circulatory fluid. Internal circulating fluid. Can be: blood ( in vertebrates) or hydrolymph and haemolymph ( in invertebrates) o Vessels: Ducts which carry circulatory fluid. Arteries carry bloo ...
Name - TeacherWeb
... 2. Is the following sentence true or false? Electrons first fill the antibonding molecular orbital to produce a stable covalent bond. 3. When two s atomic orbitals combine and form a molecular orbital, the bond that forms is called a(n) bond. 4. Circle the letter of each type of covalent bond that c ...
... 2. Is the following sentence true or false? Electrons first fill the antibonding molecular orbital to produce a stable covalent bond. 3. When two s atomic orbitals combine and form a molecular orbital, the bond that forms is called a(n) bond. 4. Circle the letter of each type of covalent bond that c ...
Organic Acids The basics
... A block in the breakdown of an organic acid can lead to its accumulation in the cell and its elevation in plasma and urine. The first transamination step and second dehydrogenation step of amino acid catabolism generate organic acids. Often this leads to a metabolic acidosis but this is not always t ...
... A block in the breakdown of an organic acid can lead to its accumulation in the cell and its elevation in plasma and urine. The first transamination step and second dehydrogenation step of amino acid catabolism generate organic acids. Often this leads to a metabolic acidosis but this is not always t ...
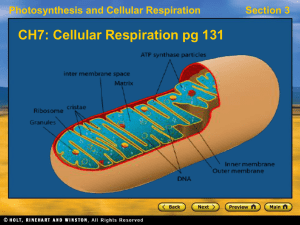
Cellular Respiration
... Equation for Cellular Respiration • C6H12O6 + O2 6 CO2 + 6H2O + ENERGY (ATP) ...
... Equation for Cellular Respiration • C6H12O6 + O2 6 CO2 + 6H2O + ENERGY (ATP) ...
Overview of ATP Production
... – ATP transfers energy to many different chemical reactions; almost all metabolic pathways directly or indirectly run on energy supplied by ATP. ATP Production - Dion ...
... – ATP transfers energy to many different chemical reactions; almost all metabolic pathways directly or indirectly run on energy supplied by ATP. ATP Production - Dion ...
Purine Oct 20 - LSU School of Medicine
... The phosphate groups are responsible for the net negative charge associated with DNA and RNA. The hydroxyl group at the 2’position accounts for the greater ease with which RNA is degraded by alkali. ...
... The phosphate groups are responsible for the net negative charge associated with DNA and RNA. The hydroxyl group at the 2’position accounts for the greater ease with which RNA is degraded by alkali. ...
Cell and Molecular Biology
... Ultimately, aerobic respiration produces ~36 ATP molecules from each individual glucose molecule. www.soran.edu.iq ...
... Ultimately, aerobic respiration produces ~36 ATP molecules from each individual glucose molecule. www.soran.edu.iq ...
Protein content and amino acids profile of
... (Glycine max) with 36.1% (USDA, 2011). The most important aspect of a protein, from a nutritional point of view, is its essential amino acids (EAA), because they have carbon skeletons that cannot be synthesised by humans, therefore they must be provided through the diet. For this reason essential am ...
... (Glycine max) with 36.1% (USDA, 2011). The most important aspect of a protein, from a nutritional point of view, is its essential amino acids (EAA), because they have carbon skeletons that cannot be synthesised by humans, therefore they must be provided through the diet. For this reason essential am ...
Answer key Ws 17-1 Viruses
... What are the products of bacterial waste water decomposition? Purified water, nitrogen gas, carbon dioxide, crop fertilizer products ...
... What are the products of bacterial waste water decomposition? Purified water, nitrogen gas, carbon dioxide, crop fertilizer products ...
Structural Biochemistry/Enzyme
... catalysis, the enzyme binds more strongly to its "transition state complex rather than its ground state reactants." In essence, the transition state is more stable. The stabilization of the transition state lowers the activation barrier between reactants and products thus increasing the rate of reac ...
... catalysis, the enzyme binds more strongly to its "transition state complex rather than its ground state reactants." In essence, the transition state is more stable. The stabilization of the transition state lowers the activation barrier between reactants and products thus increasing the rate of reac ...
Molecular cloning and computational characterization of thymidylate
... mile stone to study the basic properties of WSSV thymidylate synthase. In this study, WSSV TS was amplified by using specific primer and cloned into pTZ vector by T tail ligation and further sub-cloned into pRSET-B vector. Physico-chemical properties of amino acid, multiple sequence alignment, phylo ...
... mile stone to study the basic properties of WSSV thymidylate synthase. In this study, WSSV TS was amplified by using specific primer and cloned into pTZ vector by T tail ligation and further sub-cloned into pRSET-B vector. Physico-chemical properties of amino acid, multiple sequence alignment, phylo ...
The Kidneys
... Excess amino acids in the body are broken down by the liver, producing a waste substance called urea. This process is important because it converts toxic ammonia to urea, which is done using carbon dioxide. Once formed, urea is transported by the circulatory system to the kidneys. ...
... Excess amino acids in the body are broken down by the liver, producing a waste substance called urea. This process is important because it converts toxic ammonia to urea, which is done using carbon dioxide. Once formed, urea is transported by the circulatory system to the kidneys. ...
CHAPtER 9 Properties and reactions of organic compounds
... essentially infinite because there are so many combinations of organic compounds. However, certain general patterns involving addition, decomposition, combination, substitution or rearrangement of atoms or groups of atoms can be used to describe many common and useful reactions. It is not unusual to ...
... essentially infinite because there are so many combinations of organic compounds. However, certain general patterns involving addition, decomposition, combination, substitution or rearrangement of atoms or groups of atoms can be used to describe many common and useful reactions. It is not unusual to ...
Early Cleavage Media
... receives a complete laboratory evaluation including mouse embryo testing, endotoxin level, pH, osmolality and sterility testing. All results are provided in a lot-specific Certificate of Analysis. ...
... receives a complete laboratory evaluation including mouse embryo testing, endotoxin level, pH, osmolality and sterility testing. All results are provided in a lot-specific Certificate of Analysis. ...
Pyruvate Kinase
... ATP, AcSCoA, long chain fatty acids inhibit all isozymes L inhibited by phosphorylation by glucagon –activated cAMP-dependent protein kinase (low blood sugar cAMP) M activated by cAMP in response to epinephrine (Gprotein system) ...
... ATP, AcSCoA, long chain fatty acids inhibit all isozymes L inhibited by phosphorylation by glucagon –activated cAMP-dependent protein kinase (low blood sugar cAMP) M activated by cAMP in response to epinephrine (Gprotein system) ...
Supplementary Data
... Figure S6: The R1 domain: Top) Sequence alignment deduced from the HCA comparison of the N-terminal part of the CFTR R domain (here named the R1 domain) with the regulatory domains found in some bacterial ABC transporters immediately after their NBDs (TOBE domains). The sequences of six of these pr ...
... Figure S6: The R1 domain: Top) Sequence alignment deduced from the HCA comparison of the N-terminal part of the CFTR R domain (here named the R1 domain) with the regulatory domains found in some bacterial ABC transporters immediately after their NBDs (TOBE domains). The sequences of six of these pr ...
01_Introduction. Structure, properties and biological functions
... PLP is a coenzyme for enzymes catalyzing reactions involving amino acid metabolism (isomerizations, decarboxylations, transamination) ...
... PLP is a coenzyme for enzymes catalyzing reactions involving amino acid metabolism (isomerizations, decarboxylations, transamination) ...
Chapter 10 Structure and Function of DNA
... Mutations may result from: Errors in DNA replication Physical or chemical agents called mutagens ...
... Mutations may result from: Errors in DNA replication Physical or chemical agents called mutagens ...
Biochemistry
_and_Carl_Ferdinand_Cori.jpg?width=300)
Biochemistry, sometimes called biological chemistry, is the study of chemical processes within and relating to living organisms. By controlling information flow through biochemical signaling and the flow of chemical energy through metabolism, biochemical processes give rise to the complexity of life. Over the last decades of the 20th century, biochemistry has become so successful at explaining living processes that now almost all areas of the life sciences from botany to medicine to genetics are engaged in biochemical research. Today, the main focus of pure biochemistry is in understanding how biological molecules give rise to the processes that occur within living cells, which in turn relates greatly to the study and understanding of whole organisms.Biochemistry is closely related to molecular biology, the study of the molecular mechanisms by which genetic information encoded in DNA is able to result in the processes of life. Depending on the exact definition of the terms used, molecular biology can be thought of as a branch of biochemistry, or biochemistry as a tool with which to investigate and study molecular biology.Much of biochemistry deals with the structures, functions and interactions of biological macromolecules, such as proteins, nucleic acids, carbohydrates and lipids, which provide the structure of cells and perform many of the functions associated with life. The chemistry of the cell also depends on the reactions of smaller molecules and ions. These can be inorganic, for example water and metal ions, or organic, for example the amino acids which are used to synthesize proteins. The mechanisms by which cells harness energy from their environment via chemical reactions are known as metabolism. The findings of biochemistry are applied primarily in medicine, nutrition, and agriculture. In medicine, biochemists investigate the causes and cures of disease. In nutrition, they study how to maintain health and study the effects of nutritional deficiencies. In agriculture, biochemists investigate soil and fertilizers, and try to discover ways to improve crop cultivation, crop storage and pest control.